What is particulate matter?
• Particulate matter or particle pollution is the general term for a mixture of solid particles and liquid droplets found in the air.
Must read: Pollution dome : formation and impacts
• There are a wide range of minute particles in the air that can be seen only using an electron microscope.
• It includes sulphates, nitrates, black carbon, particle-bound water, metals (cadmium, copper, nickel, zinc) and hydrocarbons.
Must read: Particulate pollution in Delhi NCR
• In addition, biological components such as allergens (pollen, dust mites) and microbial compounds (fungi) are also PM.
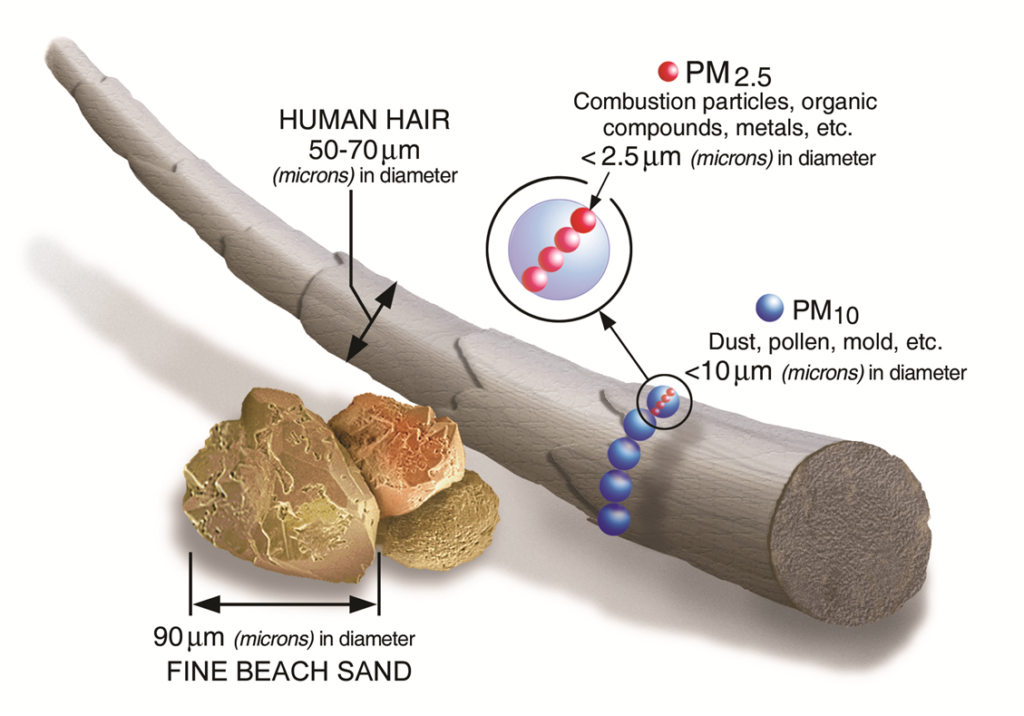
What are the different sizes of particulate matter?
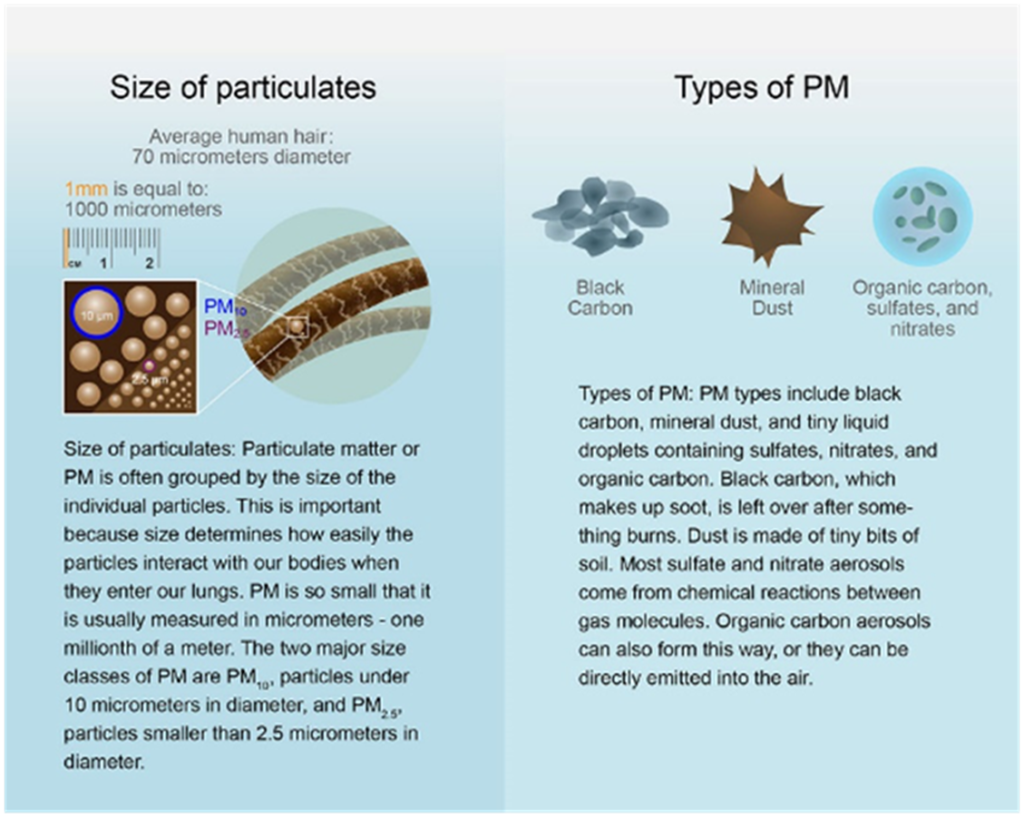
PM10: inhalable particles, with diameters that are generally 10 micrometres (average human hair is about 70 micrometres in diameter).
Must read: Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB)
PM2.5: fine inhalable particles, 2.5 micrometres and smaller.
What are the sources of particulate matter?
The major man-made sources are
• Emission from power stations, factories, industries, incinerators, diesel generators and automobiles
Must read: Exposure to benzene pollution
• Dust from construction sites and unpaved roads
• Burning of garbage
Must read: Climate and Clean Air Coalition (CCAC)
What are the harmful effects of PM?
• When inhaled, PM can cause a wide range of respiratory disorders.
• Continuous exposure to PM can cause asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and any type of bronchitis.
Must read: Largest Emitters of Sulphur Dioxide (SO2) in the World
• PM can penetrate deep inside the lungs and damage it. Any bacteria or virus can now attack the lungs and this could even lead to serious life threatening infections.
• PM can also cause chest tightening, watery eyes, sneezing, and running nose.
Must read: Exposure to benzene pollution
• According to the World Health Organisation (WHO) almost 3.7 million premature deaths annually are attributed to outdoor air pollution. About 80% of those deaths are due to heart disease and stroke, while another 20% are from respiratory illnesses and cancers related to exposure to PM2.5.
What are the standard values for PM?
According to the National Ambient Air Quality Standards of the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) of India, the 24-hour average for PM10 is 100 microgram/cubic metre and 60 microgram/ cubic metre for PM2.5.
How can we reduce exposure to particulate matter?
• According to the WHO Global Urban Ambient Air Pollution Database, more than 80% of people living in urban areas are exposed to air quality levels that exceed the WHO limits. There are no protective masks than can filter these PM.
• As individuals, we should stop burning our garbage, use public transportation and take medications for allergies as the particulate matter can worsen existing allergies.
• We need to raise our voice to sensitise the issue. All of us have seen vehicles which emit massive clouds of smoke. The Pollution Control board should understand the seriousness and start inspecting vehicles.
