Hydroelectric power plants, which convert hydraulic energy into electricity, are a major source of renewable energy. There are various types of hydropower plants: run-of-river, reservoir, storage or pumped storage.
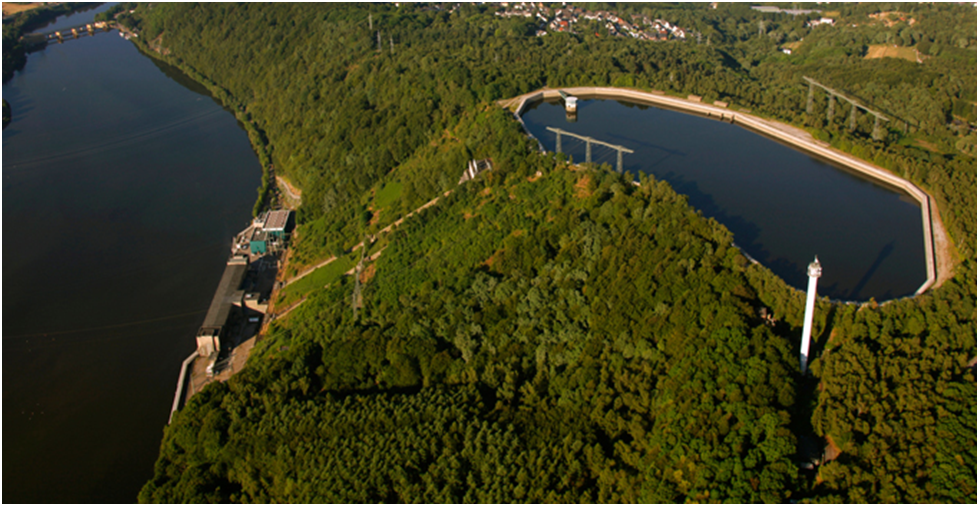

The basic operating principle is similar for all of them: water flows through a turbine to generate electricity. However, unlike run-of-river or reservoir power plants, pumped storage plants enable us to store and schedule hydroelectric power generation, while also playing a crucial role in stabilizing the power grid.
Must read: Progress made by India in access to affordable, reliable, sustainable and modern energy
What is Pumped Storage Hydropower?
Pumped Storage Hydropower is a type of hydroelectric energy storage that uses water stored in two reservoirs at different elevations to generate electricity.
When there is excess electricity available, such as during off-peak hours or from renewable sources like solar and wind, it is used to pump water from the lower reservoir to the upper reservoir.
When there is a demand for electricity, the water is released from the upper reservoir back down to the lower reservoir, passing through turbines that generate electricity.
Must read: Green energy
Working of Pumped Storage Hydropower
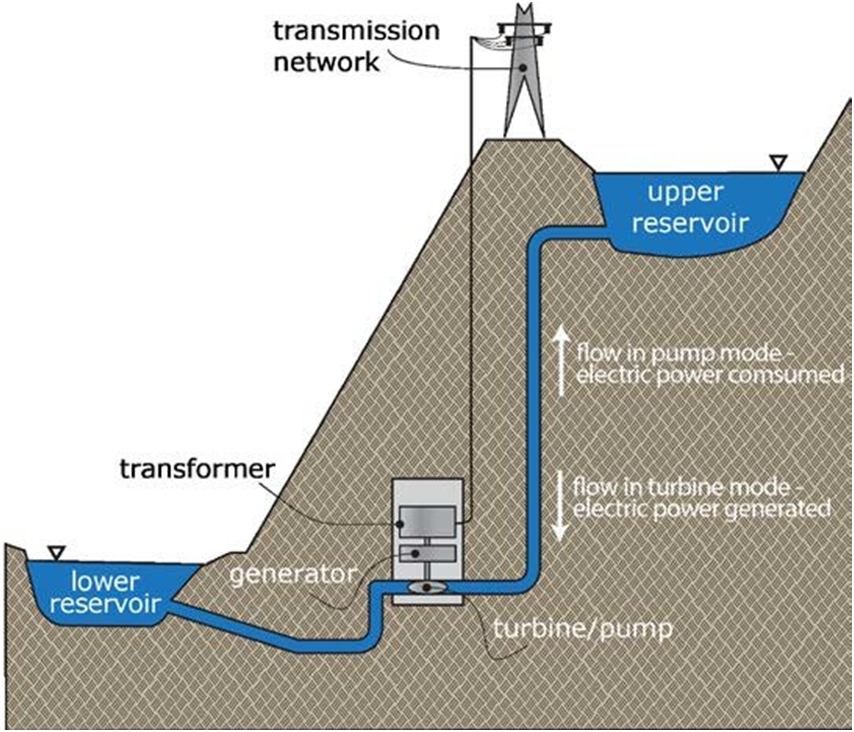
The name Pumped Storage Hydropower is derived from the pumping system that allows them to store the gravitational potential energy of water by pumping it from the lower basin to the upper basin during periods of low energy demand.
Generally, these plants use reversible turbines and generators, which can function either as pumps (moving water to the upper reservoir) or as generators (producing electricity).
Pumped Storage Hydropower acts similarly to a giant battery, because it can store power and then release it when needed.
Types of Pumped Storage Hydropower plants
Pumped storage hydropower plants fall into two categories:
Pure (or closed-loop) pumped storage: in this type of plant, naturally flowing sources of water into the upper reservoir contribute less than 5% of the volume of water that passes through the turbines annually.
Mixed (or open-loop) pumped storage: here, the upper reservoir is partially fed by naturally flowing sources of water that contribute more than 5% percent of the volume of water that passes through the turbines annually.
Advantages of Pumped Storage Hydropower
Pumped-storage projects have advantages compared with other types of storage, such as batteries. They have low operational and maintenance costs and long operating lifespans. In addition, they can provide large-scale, long-term energy storage.
Energy storage
One of the main advantages in the context of renewable energy is the ability to store water for use on demand. Reversing the flow and storing water in an upper reservoir creates an energy storage system that’s ready to be used whenever it’s needed.
High energy efficiency
Due to the fact that water is reused in a continuous cycle, the efficiency of a pumped storage plant is around 70% to 80%. This means that for every 100 kWh consumed for pumping, about 70-80 kWh is generated during the production phase.
Grid reliability
These power plants can come on line within minutes, providing backup power extremely effectively, balancing fluctuations in generation from intermittent sources and improving grid reliability.
Thus, Pumped Storage Hydropower plants help stabilize the grid by balancing supply and demand, storing water and releasing it during peak demand. Due to their ability to respond quickly, they significantly improve grid flexibility.
Reduction of CO₂ emissions
By optimizing the use of energy sources, reducing dependence on fossil fuels and maximizing power generation from renewable sources, pumped storage power plants help reduce CO₂ emissions.
Energy Resilience
In the event of a power outage, a pumped storage plant can reactivate the grid by harnessing the energy produced by sending “emergency” water – which is kept in the upper reservoir for this very purpose – through the turbines.
Disadvantages of Pumped Storage Hydropower
They can have large upfront construction costs.
The construction and operation can cause environmental and ecological issues
They are geographically constrained by land requirements.
Pumped storage is also subject to water availability.
China – the leader in Pumped Storage Hydropower
China is building pumped-storage hydropower facilities to increase the flexibility of the power grid and accommodate growing wind and solar power. As of May 2023, China had 50 gigawatts (GW) of operational pumped-storage capacity, 30% of global capacity and more than any other country.
China’s pumped-storage capacity is set to increase even more, with 89 GW of capacity currently under construction. Developers are seeking governmental approvals, land rights, or financing for an additional 276 GW of pumped-storage projects.
Internationally, the largest pumped storage hydropower plant is Fengning in China, with a capacity of 3.6 GW and a storage capacity of 40 GWh, surpassing the Bath County plant in Virginia (USA), with 3 GW of power and 24 GWh of capacity.
Pumped storage hydropower plants can play a key role in the future of energy, contributing to grid stabilization, renewable energy storage and reduced dependence on fossil fuels. The renewable energy from pumped storage power plants will be a strategic ally for a resilient, secure and sustainable energy system.
External link : https://www.energy.gov/eere/water/pumped-storage-hydropower
PRACTICE QUESTIONS
QUES . Recently, the term “pumped-storage hydropower” is actually and appropriately discussed in the context of which one of the following? UPSC PRELIMS 2024
(a) Irrigation of terraced crop fields
(b) Lift irrigation of cereal crops
(c) Long duration energy storage
(d) Rainwater harvesting system
Ans (c)
