
As part of its G20 presidency in 2023, India proposed a Global Biofuels Alliance (GBA) to bring countries together to expand and create new markets for sustainable biofuels.
The sharing of best practices, the technical support and the capacity building that the GBA would bring are welcome additions to international efforts to expand sustainable biofuel production and use, a key step to decarbonising transportation and heat services with secure and affordable energy supplies.
Must read: How Global Biofuels Alliance (GBA) can help get sustainable biofuels on track?
Why Global Biofuels Alliance(GBA) is formed?
While sustainable biofuels have huge potential, there are a number of hurdles as well, including feedstock supply issues, technological limitations, policy framework, and financing and investment.
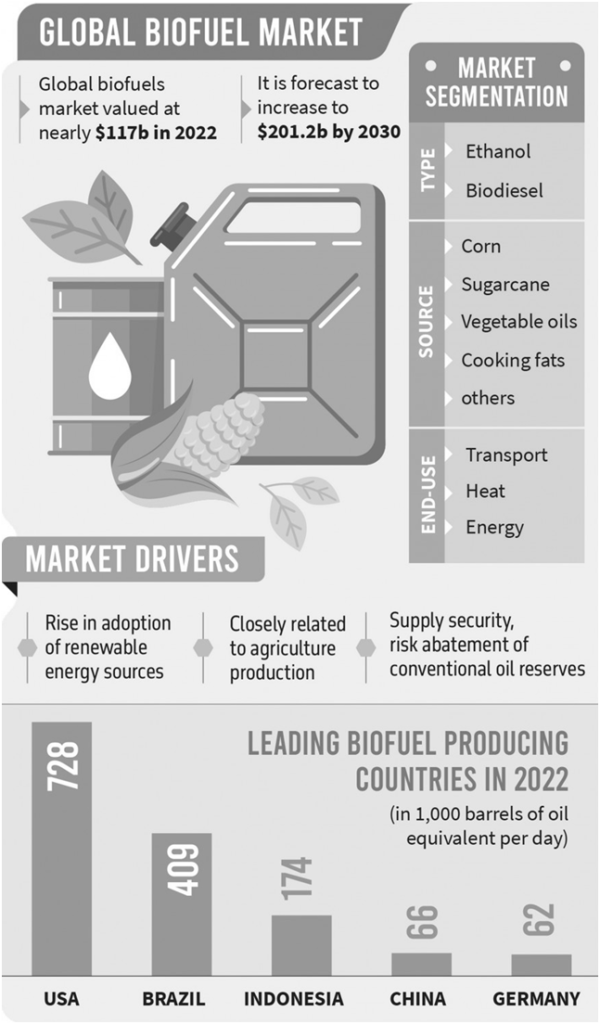
Must read: Biofuel – Types and Generations
There is an urgent need to have a global platform which can address the underlying challenges and enable wider international cooperation to realise the huge untapped potential of sustainable biofuels to cater to common global goods of climate change mitigation through reduced carbon emissions and achieving sustainable development goals.
Must read: Biofuel – Advantages, Limitations, Challenges, Initiatives
What are the objectives of Global Biofuels Alliance(GBA)?
The Alliance intends to expedite the global uptake of biofuels through facilitating technology advancements, intensifying utilization of sustainable biofuels, shaping robust standard setting and certification through the participation of a wide spectrum of stakeholders. The alliance will also act as a central repository of knowledge and an expert hub.
Must read: Types of Hydrogen Fuel Explained
What is the aim and purpose of Global Biofuels Alliance(GBA)?
GBA aims to serve as a catalytic platform, fostering global collaboration for the advancement and widespread adoption of biofuels.
The alliance is aimed at facilitating international cooperation and intensifying the use of sustainable biofuels, along with facilitating global biofuels trade and technical support for national biofuel programmes.
Must read: Fuel Cells – Uses, Benefits and Working
The Alliance is focused on securing the supply of biofuels, ensuring these biofuels remain affordable and are produced sustainably.
Which countries and organisations are associated with Global Biofuels Alliance(GBA)?
The GBA, the effort for which was spearheaded by India, the United States, and Brazil, has been launched with nine initiating members–India, the US, Brazil, Argentina, Bangladesh, Italy, Mauritius, South Africa, and the United Arab Emirates–while Canada and Singapore are observer countries.
Must read: Flexible fuel vehicles (FFVs) – Benefits and Drawbacks
In all, 22 countries and 12 international organisations have already agreed to join the GBA.
Eight of the 22 countries are from the G20, four are among the G20 invitee countries (during G 20 meet 2023) , while ten are neither G20 members nor invitees.
The World Bank, Asian Development Bank, World Economic Forum, International Energy Agency, International Energy Forum, International Renewable Energy Agency, and International Civil Aviation Organization are among the organisations that have agreed to join the alliance.
What Global Biofuels Alliance(GBA) will do?
GBA will support worldwide development and deployment of sustainable biofuels by offering capacity-building exercises across the value chain, technical support for national programs and promoting policy lessons-sharing.
Must read: Green Hydrogen and its uses
It will facilitate mobilizing a virtual marketplace to assist industries, countries, ecosystem players and key stakeholders in mapping demand and supply, as well as connecting technology providers to end users.
It will also facilitate development, adoption and implementation of internationally recognized standards, codes, sustainability principles and regulations to incentivize biofuels adoption and trade
What is the significance of Global Biofuels Alliance(GBA) for India?
This will help India become the voice of the global south by getting countries which are still to start their biofuels programme.
For India, it will provide additional opportunities to its industries by exporting technology and equipment.
It will help accelerate India’s existing biofuel programmes such as PM-JIVAN Yojna, SATAT, and GOBARdhan scheme thereby contributing to increased farmers’ income, creating jobs and overall development of the Indian eco-system.
For India, which is the world’s third-largest consumer of crude oil and depends on imports to meet over 85 per cent of its requirement of the commodity, increasing the use of biofuels is a key tool towards two ends–reducing dependency on energy imports and limiting the carbon footprint of the country’s rapidly growing energy use.
External link: https://mopng.gov.in/en/page/68
