What is a Fuel cell?
A fuel cell uses the chemical energy of hydrogen or another fuel to cleanly and efficiently produce electricity. If hydrogen is the fuel then electricity, water, and heat are the only products.
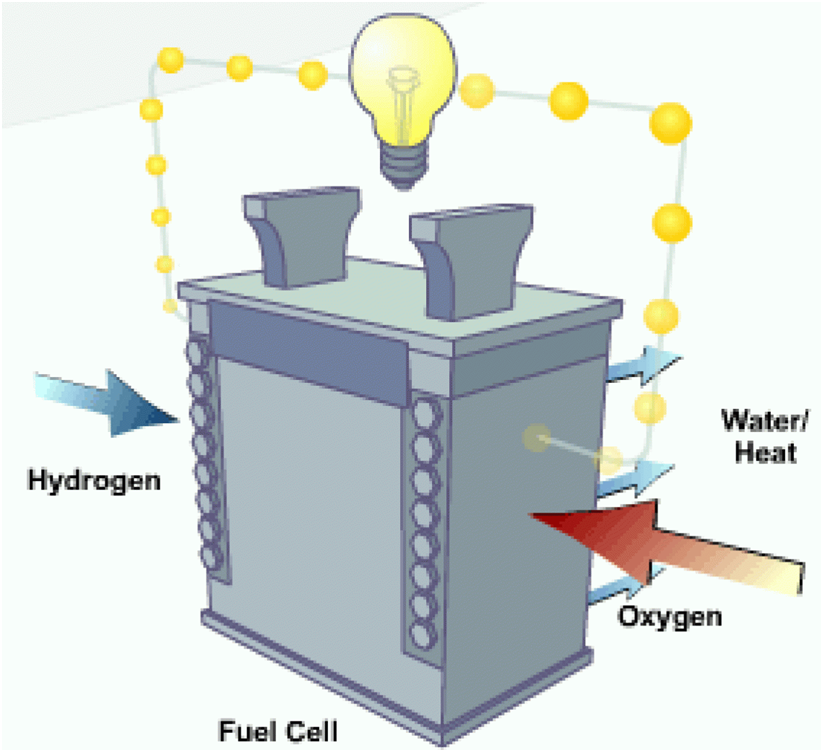
Fuel cells work like batteries, but they do not run down or need recharging. They produce electricity and heat as long as fuel is supplied.
Fuel cells are unique in terms of the variety of their potential applications; they can provide power for systems as large as a utility power station and as small as a laptop computer.
What are the uses of fuel cells?
Fuel cells can be used in a wide range of applications, including transportation, material handling, stationary, portable, and emergency backup power applications.
Must read: Flexible fuel vehicles (FFVs) – Benefits and Drawbacks
What are the benefits of fuel cells?
Fuel cells have several benefits over conventional combustion-based technologies currently used in many power plants and passenger vehicles.
Fuel cells can operate at higher efficiencies than combustion engines, and can convert the chemical energy in the fuel to electrical energy with efficiencies of up to 60%.
Fuel cells have lower emissions than combustion engines.
Must read: Types of Hydrogen Fuel Explained
Hydrogen fuel cells emit only water, so there are no carbon dioxide emissions and no air pollutants that create smog and cause health problems at the point of operation.
Also, fuel cells are quiet during operation as they have fewer moving parts.
How Fuel Cells Work?
Fuel cells work like batteries, but they do not run down or need recharging. They produce electricity and heat as long as fuel is supplied.

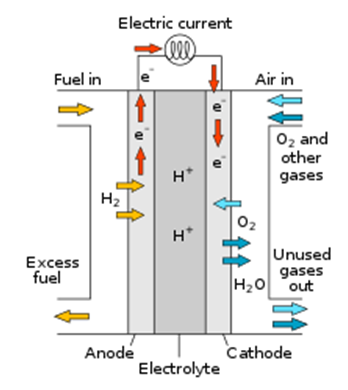
A fuel cell consists of two electrodes—a negative electrode (or anode) and a positive electrode (or cathode)—sandwiched around an electrolyte.
A fuel, such as hydrogen, is fed to the anode, and air is fed to the cathode.
In a hydrogen fuel cell, a catalyst at the anode separates hydrogen molecules into protons and electrons, which take different paths to the cathode. The electrons go through an external circuit, creating a flow of electricity. The protons migrate through the electrolyte to the cathode, where they unite with oxygen and the electrons to produce water and heat.
For furthur information: External link: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fuel_cell
PRACTICE QUESTIONS
QUES . Which one of the following is the exhaust pipe emission from Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles, powered by hydrogen? UPSC 2024
(a) Hydrogen peroxide
(b) Hydronium
(c) Oxygen
(d) Water vapour
Ans (d) EXPLANATION: If hydrogen is the fuel then electricity, water, and heat are the only products.
QUES . With reference to ‘fuel cells’ in which hydrogen-rich fuel and oxygen are used to generate electricity. consider the following statements : UPSC 2015
1 . If pure hydrogen is used as a fuel, the fuel cell emits heat and water as by-products.
2 . Fuel cells can be used for powering buildings and not for small devices like laptop computers.
3 . Fuel cells produce electricity in the form of Alternating Current (AC).
Which of the statements given above is / are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans (a) 1 only
