The consequences of uncontrolled atmospheric warming are complex. Different regional and international responses are expected as temperature, precipitation, soil moisture, and air-masses characteristics change.
Must read: Greenhouse effect
Although, it is difficult to forecast how the change of climate will affect the environment, ecology and society, but if the average global temperature changes, ramification from this change will have far reaching consequences.
Must read: Rise of surface temperature brings severe consequences
In brief, wind and rain patterns prevalent for the last million of years could change; sea-level would rise and threaten island, sea-beaches and low-lying coastal regions. This might result into droughts, desertification, floods, landslides, avalanches, hurricanes, natural hazards, and disasters which lead to large-scale migration of human population, animals and shift in the vegetation belts.
Must read: Impact of climate change
Some of the effects of climatic change are already being felt. For instance, the Arctic Ice Cap has lost 42 per cent. According to one study, 27 per cent of the coral formations on the tropical oceans may disappear.
Must read: Causes of climate change – human & natural
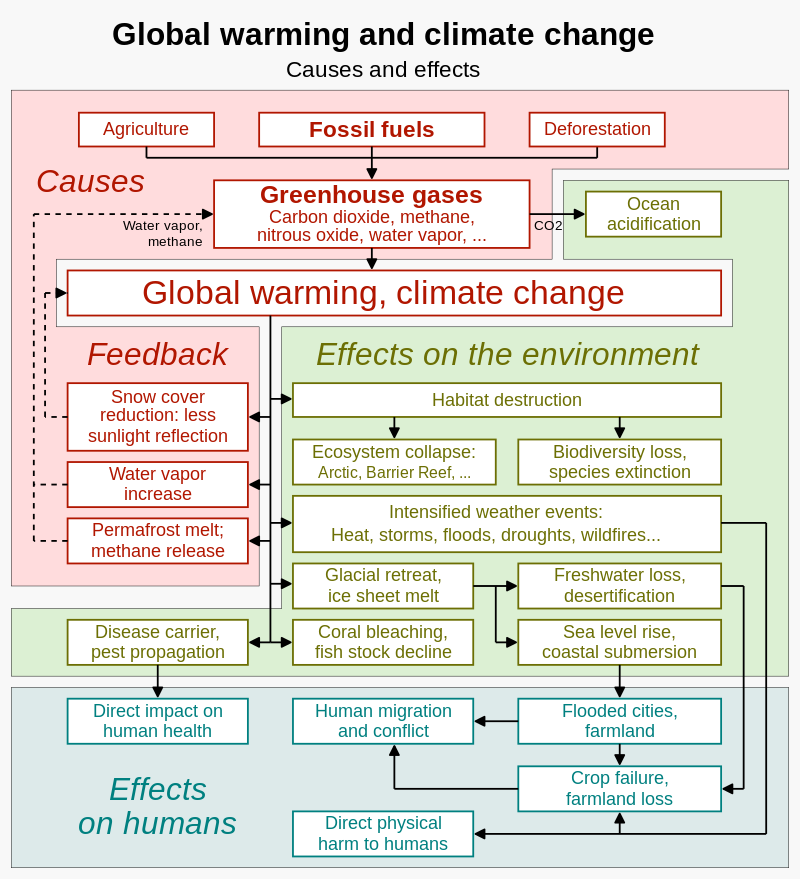
Consequences and impact of climate change
Following are some of the consequences of climate change:
1. Rise in sea level.
Must read: MELTING ICE CAPS AND SHEETS
2. Change in pressure belts and atmospheric circulation.
3. Change in the direction of permanent and periodic winds.
4. Change in the directions of warm and cold water currents.
5. The Inter-Tropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ) may mover northward in the Northern Hemisphere.
6. Increase in the frequency of tropical and temperate cyclones, cloud cover, tornadoes and storms.
Must read: Impact of climate change on tropical cyclones
7. Change in the intensity and patterns of precipitation.
8. Change in the soil-moisture, and humus contents of soils.
Must read: Adverse affect of climate change on countries dependent on agriculture
9. Alteration in natural vegetation and soil belts.
10. Change in cropping patterns, crop combination, and agricultural productivity.
Must read: AGRICULTURAL PRODUCTIVITY – DECLINE – CAUSES AND EFFECTS
11. Change in hydrological cycle and water supply.
Must read: Crisis of availability of and access to freshwater resources
12. The marine life will be favourably/adversely affected.
13. Warming of temperature of the oceans may endanger the corals worldwide.
Must read: Impact of global warming on coral life system
14. Fields of the farmers of delta regions may submerge.
15. Expansion of deserts and more desertification within the deserts.
Must read: DESERTIFICATION – AN UNDERESTIMATED THREAT
16. The land-based animals will have to adapt to changing patterns of climatic belts.
17. Effect on food supply and international trade of grains.
Must read: Climate change and global food security
18. National parks, sanctuaries and biosphere reserves may be altered.
19. Change in the international trade pacts and geo-politics of the world.
Must read: Impact of climate change on humans
20. Countries like Maldives, and greater parts of the Netherlands, etc. may submerge under water.
Must read: Hazards associated with the rising sea-surface temperature
21. Climatic change is making food crops less nutritious. Rising carbon dioxide emissions lead to iron and zinc deficiencies in food crops.
Must read: Global Climate Change Alliance
External link: https://www.un.org/en/climatechange/science/causes-effects-climate-change

Fabulous 👍
Fantastic news about climate changes 😍
Nice
👍👍
Points enumerated . Very easy to grasp.