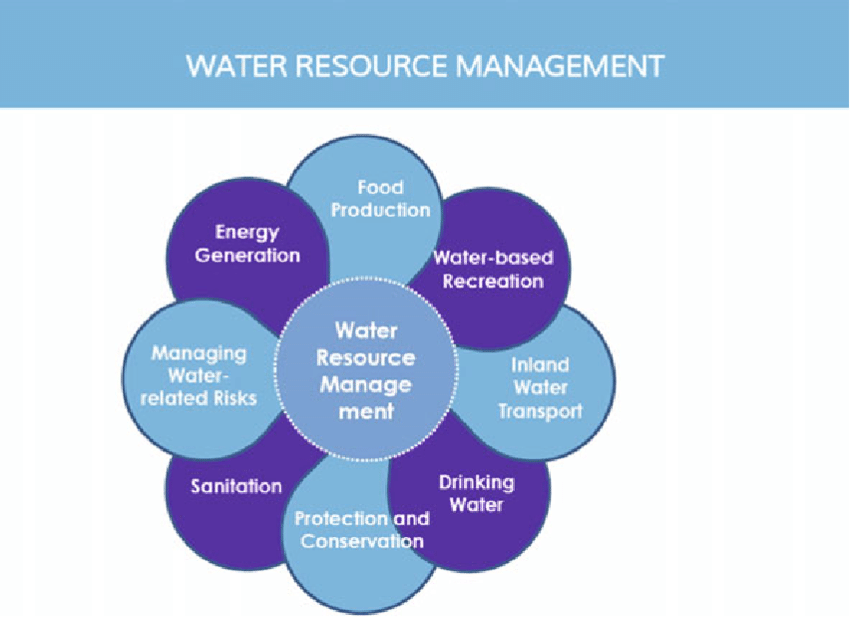
Water resource management refers to the planning, development, distribution, and sustainable use of water resources to meet the current and future needs of society while ensuring the protection and conservation of the natural environment. It encompasses a range of activities and strategies aimed at effectively managing one of the Earth’s most vital resource, that is freshwater.
Key components and aspects of water resource management
Assessment and Monitoring: Evaluating the quantity and quality of available water resources through data collection, analysis, and monitoring. This includes assessing surface water (rivers, lakes, and reservoirs) and groundwater.
Resource Planning: Developing comprehensive plans and strategies for the allocation and distribution of water resources. This involves determining the water needs of various sectors, such as agriculture, industry, municipal supply, and environmental conservation.
Infrastructure Development: Constructing and maintaining the necessary infrastructure for water storage, transportation, and distribution. This includes building dams, reservoirs, canals, pipelines, and water treatment facilities.
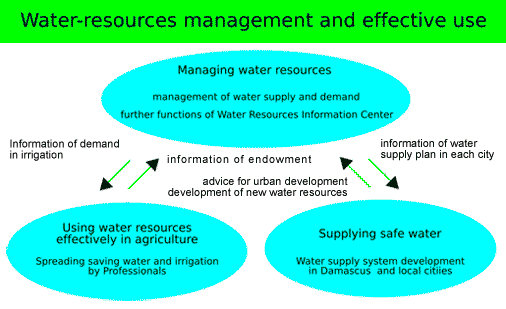
Water Allocation: Deciding how water resources will be allocated among different users and sectors. This often involves the establishment of water rights and regulations to ensure fair and sustainable use.
Water Conservation: Implementing water conservation measures and practices to reduce wastage and optimize water use efficiency. This may include promoting efficient irrigation techniques, fixing leaks in water supply systems, and encouraging water-saving behaviors.
Environmental Protection: Ensuring that water resource management takes into account the preservation and protection of aquatic ecosystems. This involves maintaining minimum environmental flows, protecting water quality, and preventing pollution.
Legal and Regulatory Frameworks: Developing and enforcing laws, regulations, and policies related to water resource management. These frameworks establish the rules and responsibilities for various stakeholders, including government agencies, industries, and communities.
Integrated Approaches: Adopting integrated water resource management (IWRM) principles, which emphasize a holistic approach that considers the interconnectedness of water resources, ecosystems, and human activities.
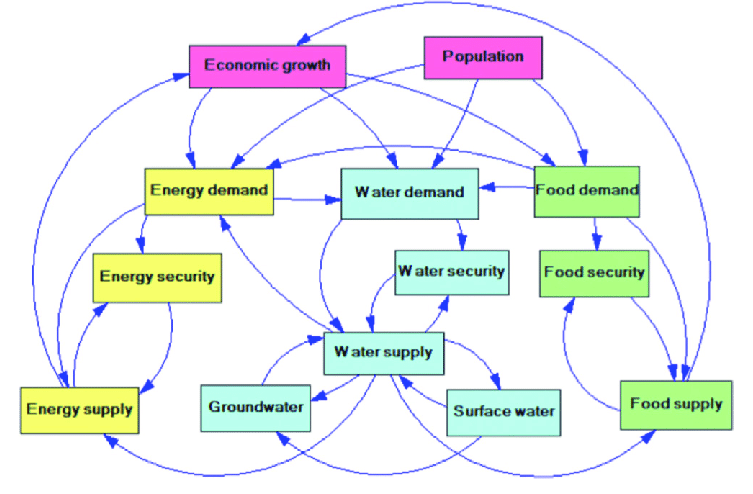
Climate Change Adaptation: Recognizing the impact of climate change on water availability and developing strategies to adapt to changing precipitation patterns, increased droughts, and altered hydrological cycles.
Public Awareness and Participation: Engaging stakeholders, including the public, local communities, and indigenous groups, in decision-making processes and fostering awareness about responsible water use.
International Cooperation: Collaborating with neighboring countries on transboundary water issues, as many water bodies and aquifers cross international borders.
Effective water resource management is essential for ensuring water security, which is crucial for sustaining human life, supporting economic activities, and maintaining ecological balance. It requires a multidisciplinary approach that considers social, economic, environmental, and political factors to achieve the sustainable and equitable utilization of this finite resource.
