
Sulphur dioxide is a colourless and soluble gas with a pungent odor. It is a liquid when under pressure, and it dissolves in water to form sulphuric acid very easily.
Sulphur dioxide in the air comes mainly from activities such as the burning of coal and oil at power plants or from copper smelting. In nature, sulphur dioxide can be released to the air from volcanic eruptions.
Must read: Largest Emitters of Sulphur Dioxide (SO2) in the World
SO2 emissions are a significant contributor to air pollution. Its direct exposure and exposure to particulate matter PM2.5 (fine particulate matter) produced when SO2 reacts with other air pollutants to form sulphate particles, both affect human health.
Like nitrogen dioxide, sulphur dioxide can create secondary pollutants, such as sulphate aerosols, particulate matter, and acid rain, once released into the air.
Must read: Exposure to benzene pollution
Sources of Sulphur Dioxide (SO2) in the Atmosphere
The greatest source of SO2 in the atmosphere is the burning of fossil fuels in power plants and other industrial facilities. Other sources include industrial processes such as extracting metal from ore, natural sources such as volcanoes, and locomotives, ships and other vehicles and heavy equipment that burn fuel with high sulphur content.
Thermal power plants
Combustion of coal in thermal power plants emits sulphur dioxide.
Industries
Industries that carry out activities such as wood pulping, paper manufacturing, petroleum and metal refining and metal smelting, especially of ores containing sulphides, such as lead, silver and zinc, all emit sulphur dioxide into the air.
Must read: Pollution dome : formation and impacts
Natural environment
Sulphur dioxide can occur naturally in the environment through geothermal activity, which is energy from the heat of the earth, such as hot springs and volcanoes. Sulphur dioxide is also produced when vegetation on land, in wetlands and in oceans decays or breaks down.
Transport
Sulphur dioxide may be present in exhaust fumes emitted into the atmosphere by cars, buses and trucks.
Must read: Particulate pollution in Delhi NCR
In the products we buy
Common products containing sulphur dioxide include foods, such as dried fruit, preserved fruit, food preservatives, as well as wine, bleach, disinfectant and fumigants which are used to control pests.
Other sources
Textile bleaching, wineries, and fumigation, where fruit growers and farmers spray their crops to keep insects away, are also sources of sulphur dioxide.
Must read: PARTICULATE MATTER AND ITS EFFECTS
Effects of Sulphur Dioxide (SO2) Pollution
What effect does Sulphur dioxide have on the environment?
Sulfur dioxide can have serious effects on our environment.
It is absorbed by soils and plants, affecting our land and water ecosystems, and it can even be captured within and below clouds, which increases the chance of acid rain. Acid rain can damage trees and plants, inhibit plant growth, and damage sensitive ecosystems and waterways.
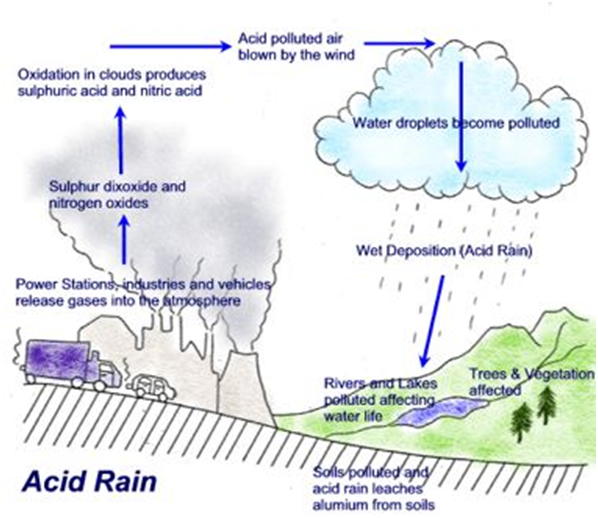
At high concentrations, gaseous SO2 can harm trees and plants by damaging foliage and decreasing growth.
What are the health effects of SO2?
Sulphur dioxide is a poisonous air pollutant that increases the risk of stroke, heart disease, lung cancer, and premature death.
Sulfur dioxide irritates the respiratory tract and increases the risk of tract infections. It causes coughing, mucus secretion and aggravates conditions such as asthma and chronic bronchitis. People with asthma, particularly children, are sensitive to these effects of SO2.
Must read: Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB)
SO2 emissions that lead to high concentrations of SO2 in the air generally also lead to the formation of other sulphur oxides (SOx). SOx can react with other compounds in the atmosphere to form small particles. These particles contribute to particulate matter (PM) pollution. Small particles may penetrate deeply into the lungs and in sufficient quantity can contribute to health problems.
Impact on Visibility
SO2 and other sulphur oxides can react with other compounds in the atmosphere to form fine particles that reduce visibility (haze).
Must read: Climate and Clean Air Coalition (CCAC)
Damage to property
Deposition of sulphate particles can also stain and damage stone and other materials, including culturally important objects such as statues and monuments. Acid rain can corrode building materials and paints.
How might people be exposed to sulphur dioxide?
People living in cities are exposed to low levels of sulphur dioxide every day. You can be exposed to sulphur dioxide in the following ways:
• Breathing polluted air.
• Living in, or near, industrial areas.
• Living in cities, near freeways and busy roads.
• Eating preserved foods and drinking wine.
• Working in workplaces where sulfur dioxide is used or produced, such as wineries, smelters and coal-burning power plants.
How to Reduce Sulphur Dioxide (SO2) Pollution?
To reduce Sulphur dioxide (SO2) pollution the objective must be to decrease the total Sulphur oxides SOx emissions. The principal approaches to controlling SO2 emissions include use of low-sulfur fuel; reduction or removal of sulfur in the feed; use of appropriate combustion technologies; and emissions control technologies such as sorbent injection and flue gas desulfurization (FGD).
A number of possible techniques for reducing emissions of sulfur oxides are:
● Improved efficiency of conversion of fuel to electricity in the power plants (this would reduce pollutant emissions per unit of electricity generated).
● Shift fossil fuel plants to lower sulfur fuels.
● Removal of sulphur from coal before combustion, or of the sulphur oxide after combustion, but before it enters the stack. The techniques to be considered are:
(i) coal preparation (conventional and advanced technology);
(ii) solvent refined coal;
(iii) low sulfur, low BTU gas from coal;
(iv) fluidized bed combustion;
● Shift fuel consumption from electricity to pipeline grade gas made from coal.
● Shift to nuclear generation as rapidly as possible since no sulphur oxide (or particulate) is emitted from nuclear plants.
It’s high time that governments reduce investments in fossil fuels and shift to safer energy sources, such as wind and solar. They must also strengthen emission standards and effectively implement flue gas pollution control technology on coal-fired power plants, smelters, and other major industrial SO2 emitters.
External link: https://www.epa.gov/so2-pollution/sulfur-dioxide-basics
PRACTICE QUESTIONS
QUES . According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), which one of the following is the largest source of sulphur dioxide emissions? UPSC 2024
(a) Locomotives using fossil fuels
(b) Ships using fossil fuels
(c) Extraction of metals from ores
(d) Power plants using fossil fuels
Ans (d) EXPLANATION: According to EPA, the largest source of SO2 in the atmosphere is the burning of fossil fuels by power plants and other industrial facilities. Smaller sources of SO2 emissions include: industrial processes such as extracting metal from ore; natural sources such as volcanoes; and locomotives, ships and other vehicles and heavy equipment that burn fuel with a high sulfur content. Hence option (d) is the correct answer.
