QUES . How can a balance be struck between livelihood concerns and environmental degradation in the context of shifting cultivation?
HINTS:

Shifting cultivation, also known as slash-and-burn agriculture, involves clearing a patch of forest, burning the vegetation to release nutrients, and cultivating crops for a few years before moving on to a new patch of land. While shifting cultivation can be a sustainable way of farming in some contexts, it can also lead to environmental degradation if not managed properly.
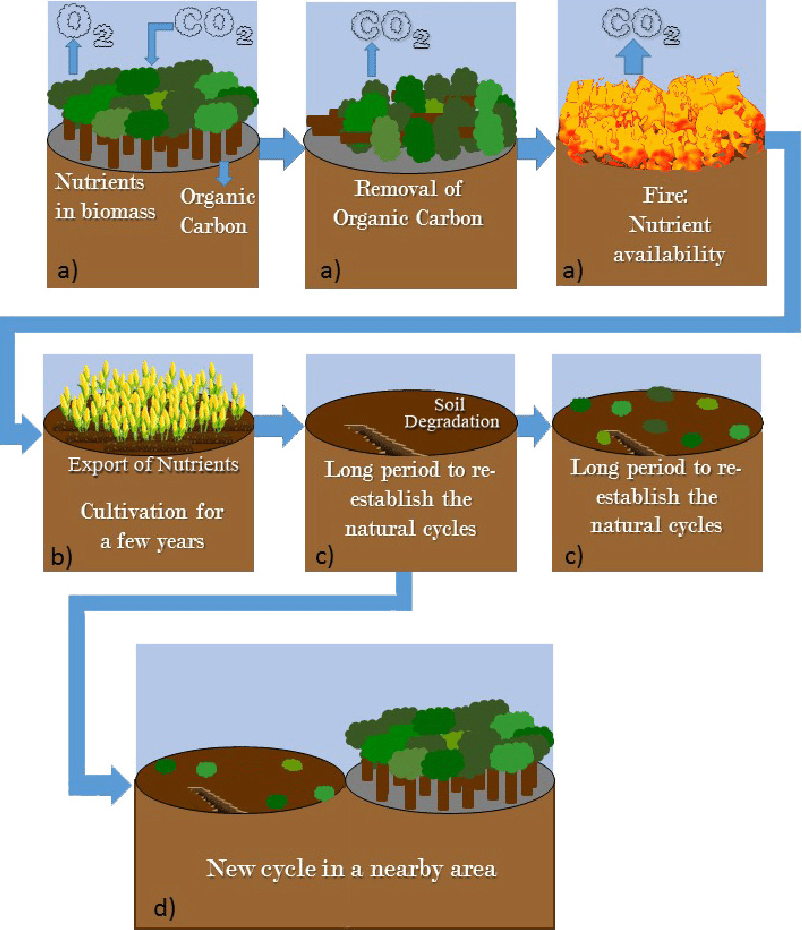
Here are some ways in which a balance can be struck between livelihood concerns and environmental degradation in the context of shifting cultivation:
Promote Agroforestry: Agroforestry is a farming system that combines trees with crops or livestock. This approach can help to restore soil fertility, prevent erosion, and provide a sustainable source of income for farmers. By integrating trees into their farming systems, farmers can reduce the need for clearing new patches of forest for cultivation.
Improve Land Management: Improved land management practices, such as contour farming and terracing, can help to prevent soil erosion and improve soil fertility. This can help to maintain the productivity of shifting cultivation while minimizing the environmental impact.
Community-Based Forest Management: Community-based forest management involves local communities in the management of forests and other natural resources. This approach can help to ensure that forest resources are used in a sustainable manner, while also providing a source of income for local communities.
Alternatives to Shifting Cultivation: In some cases, it may be necessary to explore alternatives to shifting cultivation, such as agroforestry, horticulture, or livestock production. These alternative livelihoods can provide a more sustainable source of income for farmers, while also reducing the environmental impact of shifting cultivation.
In summary, striking a balance between livelihood concerns and environmental degradation in the context of shifting cultivation requires a multi-faceted approach that involves promoting agroforestry, improving land management practices, community-based forest management, and exploring alternatives to shifting cultivation. By adopting these approaches, it may be possible to maintain the productivity of shifting cultivation while minimizing its environmental impact.
