
QUES . Chola architecture represents a high watermark in the evolution of temple architecture. Discuss. UPSC 2013 G S MAINS PAPER 1
HINTS:
Under Cholas, the temple architecture in South India reached its pinnacle. The Pallava and Eastern Chalukyan traditions were carried on by the Chola style.
The main features of Chola temple architecture are:
• Chola temples had high boundary walls surrounding the temple.
• The vimanas rose above the sanctum sanctorum (garbhagriha) of the temple in the form of a stepped pyramid that rises up linearly rather than curved. There was only one vimana on top of the main temple.
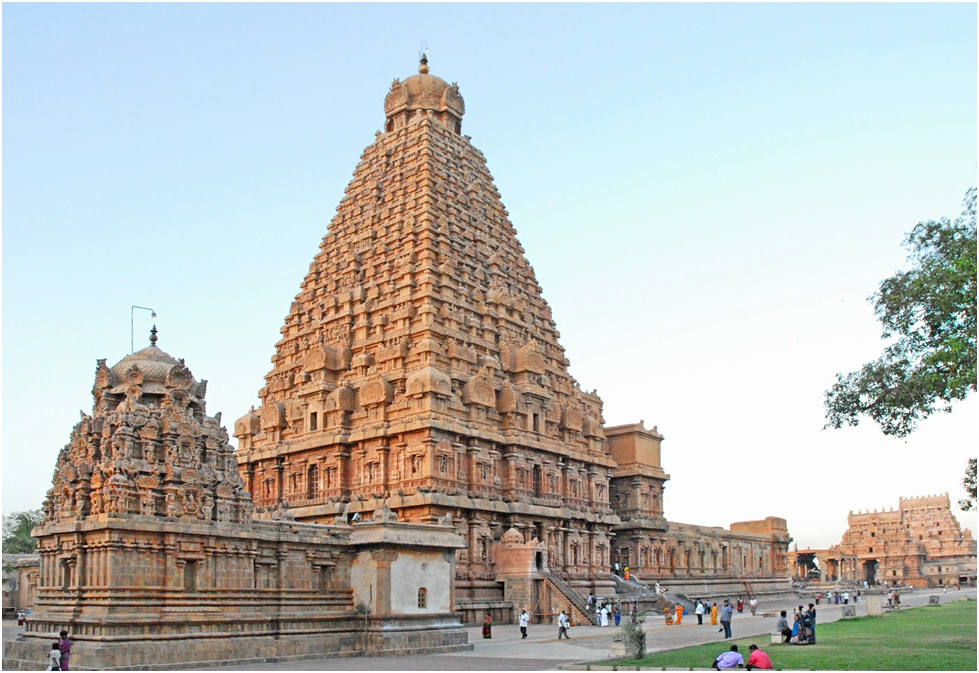

• The front wall had a high entrance gateway known as gopuram.
• The temple premise was laid out in panchayatan style with a principal temple and four subsidiary shrines.
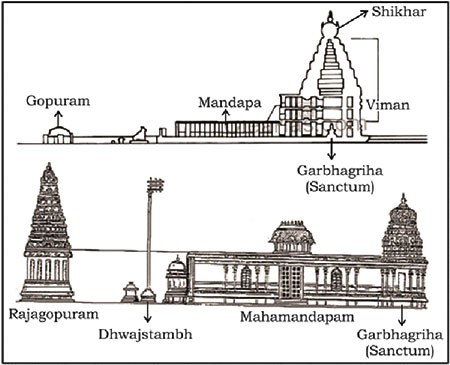
• The crowning element is shaped like an octagon and is known as shikhara.
• Antarala is the vestibular tunnel connecting the assembly hall with the garbhagriha.
• Mandap is a pillared hall with elaborately carved pillars and a flat roof.
• The entrance of the garbhagriha had statues of Dwaarpal, Mithun and Yaksha.
• The water tank inside the temple enclosure was a unique feature of the Chola style.
Following and perfecting Pallava architecture, the Cholas added the following noteworthy elements:
• Using stones rather than bricks.
• Instead of Pallava lion motifs, temple walls were adorned with statues and paintings of gods, monarchs, and queens.
• Many temples are having pillared like mahamandapa, athmandandapa, nandi mandapa etc.
During the Chola dynasty the temple architecture reached to its highest point.
Some famous temples built during Chola period:
Airavathesvara Temple Darasuram (Tamilnadu) – a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
Nataraja Temple, Chidambaram
Kampaheswarar Temple (Tamilnadu)
Gangaikondacholapuram Temple (Tamilnadu) – It is part of the UNESCO World Heritage Site known as the “Great Living Chola Temples”.
Valisvara Temple (Tamilnadu)
Rajarajeswara temple (Tanjore, Tamilnadu) – It is also known as Periya Kovil, Brihadeeshwara Temple and Rajarajesvaram.
Nageswaraswamy Temple (Tamilnadu)
Must read: Mauryan art : Chief characteristics
External link: https://igntu.ac.in/eContent/MA-AIHC-4SEM-DrManojKumar.pdf
