Important facts
1 . A UNESCO World Heritage Site is a place that is listed by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization as of special cultural or physical significance.
2 . As of 2025, India has 44 heritage sites, the sixth most of any country.
3 . Of the 44 heritage sites , 7 are in the Natural World Heritage Site list , 36 are in the Cultural World Heritage Site list and one in the Mixed World Heritage Site list.
4 . One site is transnational: The Architectural Work of Le Corbusier is shared with six other countries.
5 . As of July 2025, a total of 1,248 World Heritage Sites (972 cultural, 235 natural, and 41 mixed properties) exist across 170 countries. With 61 selected areas, Italy is the country with the most sites on the list; China is the second with 60 sites, and Germany is the third with 55.
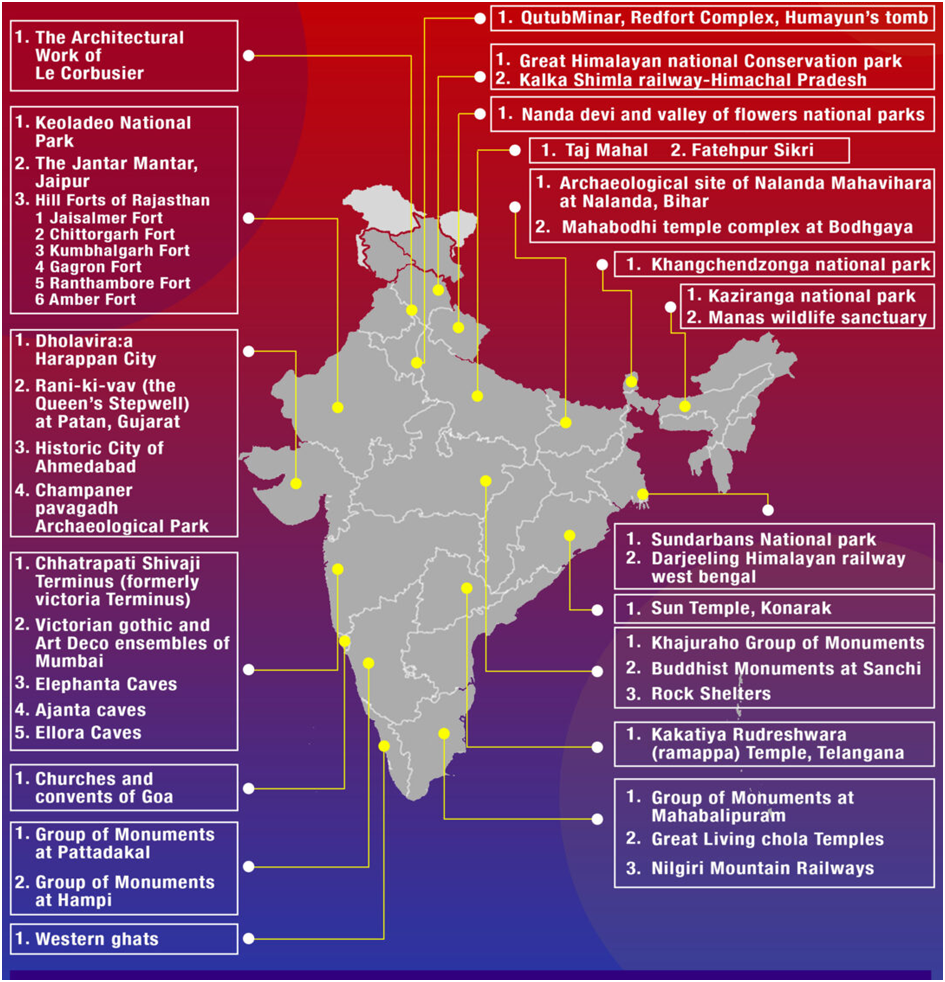
6 . Agra Fort , Ajanta Caves , Ellora Caves and Taj Mahal are the first Indian sites to be included in the World Heritage Sites List. All of them were included in 1983.
7 . The latest entrant (44th) to the list is Maratha Military Landscapes of India (Maharashtra and Tamil Nadu) in 2025.
8 . Moidams – the Mound-Burial system of the Ahom Dynasty were added to UNESCO World Heritage list in 2024 as 43rd World Heritage Site in India. Hoysala Temples of Belur, Halebid, and Somnathapura in Karnataka were added to UNESCO World Heritage list in 2023 as 42nd and Shanti Niketan in 2023 was included as 41st World Heritage Site in India.
9 . Khangchendzonga National Park(Sikkim) is the only mixed World Heritage Site in India.
Natural World Heritage Sites in India
1 . Great Himalayan National Park Conservation Area- Himachal Pradesh
2 . Western Ghats- Maharashtra ,Goa ,Karnataka, Tamil Nadu and Kerala
3 . Nanda Devi and Valley of Flowers National Parks-Uttarakhand
4 . Sundarbans National Park-West Bengal
5 . Kaziranga National Park- Assam
6 . Keoladeo National Park – Rajasthan
7 . Manas Wildlife Sanctuary – Assam
Cultural World Heritage Sites in India
1 . Historic City of Ahmadabad – Gujarat
2 . Archaeological Site of Nalanda Mahavihara (Nalanda University) at Nalanda – Bihar
3 . The Architectural Work of Le Corbusier, an Outstanding Contribution to the Modern Movement-Chandigarh
4 . Rani-ki-Vav (the Queen’s Stepwell) at Patan-Gujarat
5 . Hill Forts of Rajasthan- Rajasthan
6 . The Jantar Mantar, Jaipur- Rajasthan
7 . Red Fort Complex-Delhi
8 . Champaner-Pavagadh Archaeological Park-Gujarat
9 . Chhatrapati Shivaji Terminus (formerly Victoria Terminus)-Maharashtra
10 . Rock Shelters of Bhimbetka – Madhya Pradesh
11 . Mahabodhi Temple Complex at Bodh Gaya-Bihar
12 . Mountain Railways of India-West Bengal
13 . Humayun’s Tomb – Delhi
14 . Qutb Minar and its Monuments-Delhi
15 . Buddhist Monuments at Sanchi -Madhya Pradesh
16 . Elephanta Caves – Maharashtra
17 . Great Living Chola Temples -Tamil Nadu
18 . Group of Monuments at Pattadakal – Karnataka
19 . Churches and Convents of Goa – Goa
20 . Fatehpur Sikri – Uttar Pradesh
21 . Group of Monuments at Hampi -Karnataka
22 . Khajuraho Group of Monuments -Madhya Pradesh
23 . Group of Monuments at Mahabalipuram-Tamil Nadu
24 . Sun Temple, Konârak – Odisha
25 . Agra Fort- Uttar Pradesh
26 . Ajanta Caves – Maharashtra
27 . Ellora Caves – Maharashtra
28 . Taj Mahal – Uttar Pradesh
29 . Victorian Gothic and Art Deco Ensembles of Mumbai – Maharashtra
30. Jaipur – Rajasthan
31 . Kakatiya Rudreshwara (Ramappa) Temple, Telangana
32 . Dholavira: a Harappan City
33 . Shanti Niketan, West Bengal
34 . Sacred Ensembles of the Hoysala, Karnataka
35 . Moidams – the Mound-Burial system of the Ahom Dynasty
36 . Maratha Military Landscapes of India (Maharashtra and Tamil Nadu)
Mixed World Heritage Sites in India
1 . Khangchendzonga National Park – Sikkim
External link: https://whc.unesco.org/en/list/
UPSC Previous Year Questions
QUES . Consider the following properties included in the World Heritage List released by UNESCO : UPSC 2024
1 . Shantiniketan
2 . Rani-ki-Vav
3 . Sacred Ensembles of the Hoysalas
4 . Mahabodhi Temple Complex at Bodhgaya
How many of the above properties were included in 2023?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) Only three
(d) All four
Ans (b) Explanation: Mahabodhi Temple Complex at Bodh Gaya (2002); Rani-ki-Vav at Patan, Gujarat(2014); Sacred Ensembles of the Hoysalas (2023); Santiniketan (2023)
