What are Baltic states?
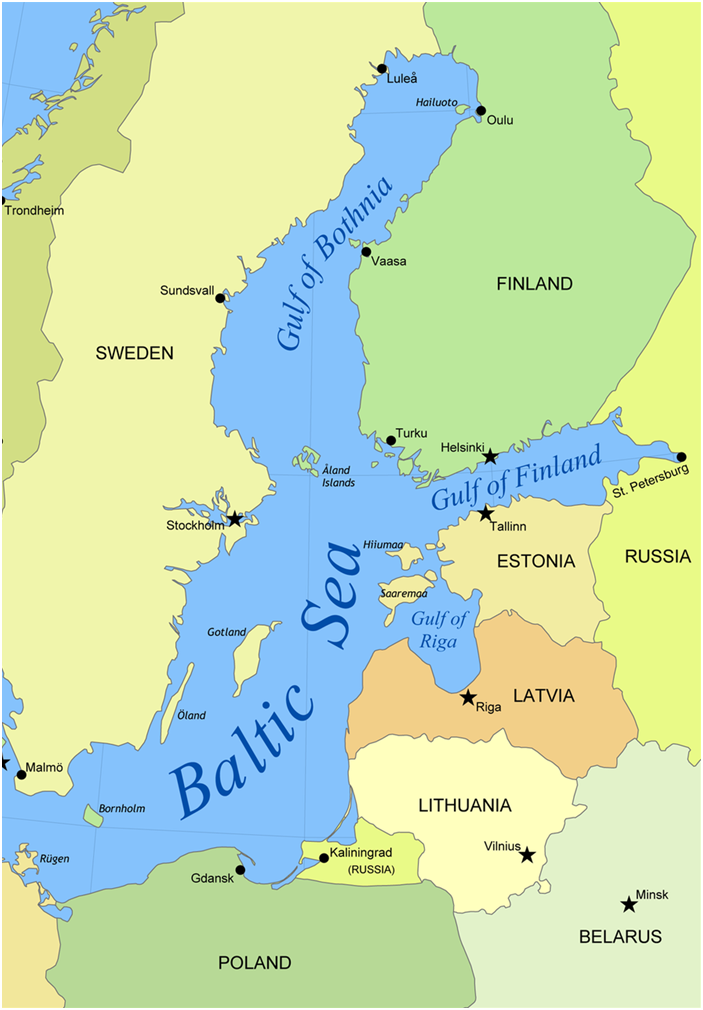
The Baltic states or the Baltic countries is a geopolitical term, which is used to group three countries: Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania.
The three sovereign states on the eastern coast of the Baltic Sea are sometimes referred to as the “Baltic nations”, also as the “Baltic republics”, the “Baltic lands”, or simply the Baltics.
When the term “Baltic states” used popularly for the first time?
After the First World War (1914–1918) the term “Baltic states” came to refer to countries by the Baltic Sea that had gained independence from the former Russian Empire.
The term included Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania, and originally also Finland, which more recently has become grouped among the Nordic countries.
What are the similarities between the three countries of the Baltic region?
● All three countries are members of NATO, the European Union, the Eurozone, and the OECD.
● All three Baltic countries are classified as high-income economies by the World Bank and maintain a very high Human Development Index.
● All three Baltic countries have shared history:
The three countries share a tumultuous history of long being occupied by others ,declaring independence in the aftermath of World War I, being occupied by the Soviet Union in World War II, and regaining independence after the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991.
Large parts of the Baltic countries were controlled by the Russian central government until the 1917 Russian Revolution and the final stages of World War I in 1918, when Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania gained their sovereignty.
The three countries were independent until the outbreak of World War II.
In 1940, all three countries were invaded, occupied and annexed by the Stalinist Soviet Union.
1941 saw the invasion and occupation of Lithuania, Latvia and Estonia by Nazi Germany, before the Red Army re-conquered the territory in 1944–1945, after which the Soviet Union maintained control over the three countries until 1991.
Soviet rule ended in the Baltic countries in 1989–1991, as the newly elected parliaments of the three nations declared the Soviet occupation illegal, culminating with the full restoration of the independence of the three countries in August 1991.
● All three are today liberal democracies, with unicameral parliaments elected by popular vote for four-year terms: Riigikogu (the unicameral parliament of Estonia) , Saeima (the unicameral parliament of Latvia) and Seimas (the unicameral parliament of Lithuania).
How the Baltic states cooperate with each other?
Currently, the governments of the Baltic states cooperate in multiple ways, including cooperation among presidents, parliament speakers, heads of government, and foreign ministers.
The three governments engage in intergovernmental and parliamentary cooperation.
There is also frequent cooperation in foreign and security policy, defence, energy, and transportation.
In 1991, the Baltic Assembly, which includes 15 to 20 MPs from each parliament, was established to facilitate inter-parliamentary cooperation.
The Baltic Council of Ministers was established in 1994 to facilitate intergovernmental cooperation.
The people of the Baltic states belong to which ethnicity?
Estonians are Finnic people, together with the nearby Finns. The Latvians and Lithuanians, linguistically and culturally related to each other, are Baltic Indo-European people.
What languages do the Baltic people speak?
The languages of the three Baltic peoples belong to two distinct language families. The Latvian and Lithuanian languages belong to the Indo-European language family and are the only extant (widely recognized) members of the Baltic language group . Latgalian and Samogitian are considered either separate languages or dialects of Latvian and Lithuanian, respectively.
The Estonian language is a Finnic language, together with neighboring Finland’s Finnish language.
General statistics about the Baltic states
Estonia
Capital : Tallinn
Area : 45,339 km2
Density : 30/km2
Population (2022/2023) : 13.57 lakh
Political system : Parliamentary republic
Latvia
Capital : Riga
Area : 64,589 km2
Density : 29/km2
Population (2022/2023) : 18.75 lakh
Political system : Parliamentary republic
Lithuania
Capital : Vilnius
Area : 65,300 km2
Density : 44/km2
Population (2022/2023) : 28.62 lakh
Political system : Semi-presidential republic
PRACTICE QUESTIONS
QUES . Latvia does not share its borders with which one of the following countries? UPSC 2004
(a) Russia
(b) Estonia
(c) Lithuania
(d) Poland
(a)
QUES . Which one of the following countries does not have border with Lithuania? UPSC 2005
(a) Poland
(b) Ukraine
(c) Belarus
(d) Latvia
(b)
QUES . Which one among the following is not a Baltic nation ? CDS 2010
(a) Latvia
(b) Slovakia
(c) Lithuania
(d) Estonia
(b)
