After the break-up of the Maurya empire, the Satavahanas and Kushans emerged as the two large powers.
The Satavahanas acted as a stabilizing factor in the Deccan and the south to which they provided political unity and economic prosperity on the strength of their trade with the Roman empire. The Kushans performed the same role in the north. Both these empires came to an end in the mid-third century.
Must read: Astronomy, mathematics and medicine during the Gupta period
On the ruins of the Kushan empire arose a new empire that established its sway over a substantial part of the former dominions of the Kushans. This was the empire of the Guptas, who may have been of vaishya origin.
What was the extent of Gupta empire?
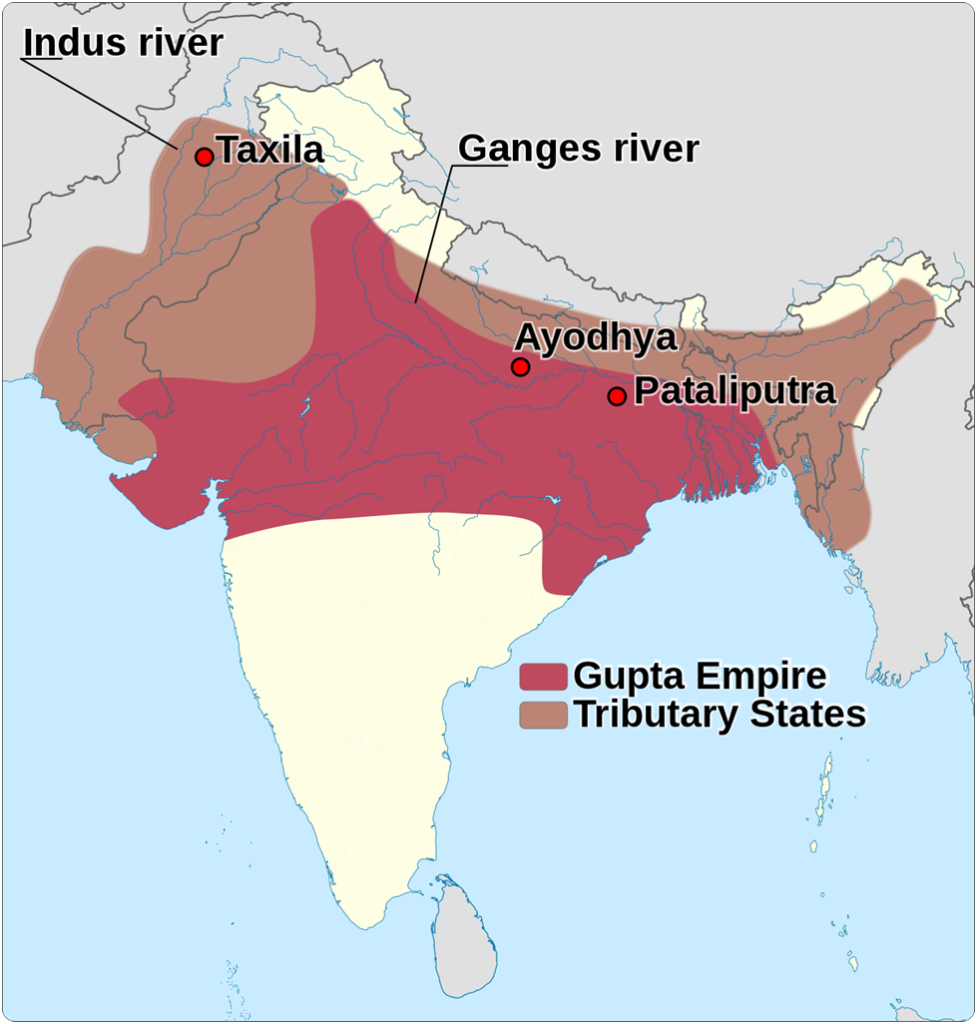
The original kingdom of the Guptas comprised UP and Bihar at the end of the third century. UP appears to have been a more important province for the Guptas than Bihar, because early Gupta coins and inscriptions are largely found in that state.
Must read: Excellence of the Gupta numismatic art
Although the Gupta empire was not as large as the Maurya empire, it kept north India politically united for over a century from AD 335 to 455.
Who were Guptas?
The Guptas were possibly feudatories of the Kushans in UP, and seem to have succeeded them without any considerable time-lag. At many places in UP and Bihar, Kushan antiquities are immediately followed by Gupta antiquities.
It is likely that the Guptas learnt the use of the saddle, reins, buttoned coats, trousers, and boots from the Kushans. All these gave them mobility and made them excellent horsemen.
Must read: Science & Technology in the Gupta Period
In the Kushan scheme of things, horse-chariots and elephants had ceased to be important, horsemen playing the central role. This also seems to have been the case with the Guptas on whose coins horsemen are represented. Although some Gupta kings are described as excellent and unrivalled chariot warriors, their basic strength lay in the use of horses.
Causes for the rise of Gupta Empire
The Guptas enjoyed certain material advantages:
The centre of their operations lay in the fertile land of Madhyadesh covering Bihar and UP.
They were able to exploit the iron ores of central India and south Bihar.
Also, they took advantage of their proximity to the areas in north India that conducted the silk trade with the eastern Roman empire, also known as the Byzantine empire.
Given these favourable factors, the Guptas established their rule over Anuganga (along the Ganges in the mid-Gangetic basin), Prayag (modern Allahabad), Saketa (modern Ayodhya), and Magadha.
In the course of time, this kingdom became an all-India empire.
The Kushan power in north India came to an end around AD 230, and then a substantial part of central India fell under the rule of the Murundas, who were possibly kinsmen of the Kushans. The Murundas continued to rule till AD 250. Twenty-five years later, in about AD 275, the Gupta dynasty came to power.
External link: https://www.cbc.gov.in/cbcdev/gupta/gupta-story.html
