QUES . What is “precision farming”? Write its different aspects for resource conservation.
HINTS:
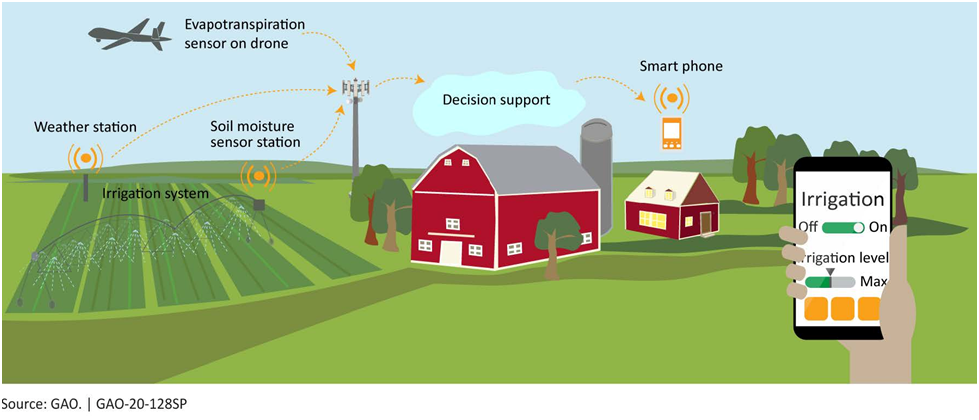
Precision farming is an agricultural management practice that uses technology such as sensors, GPS, and data analytics to optimize crop production and resource management. The goal is to increase yields, reduce waste, and conserve resources, such as water and fertilizer.
Must read: Zero Tillage – the no till approach
By applying inputs based on actual crop requirements, precision farming minimizes the use of fertilizers, pesticides, and water, thereby reducing environmental pollution and conserving precious resources.
Here are some aspects of precision farming that contribute to resource conservation:
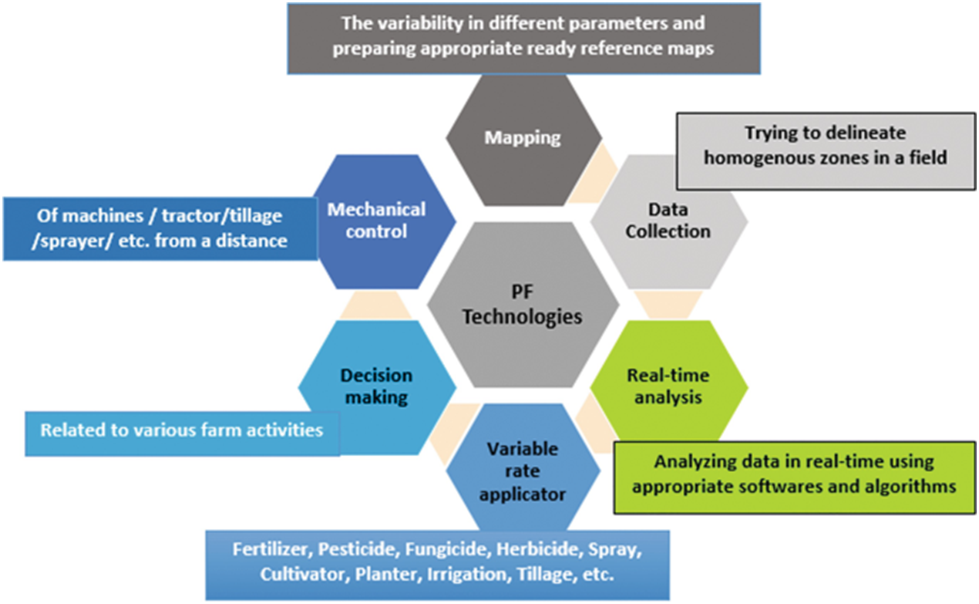
Soil mapping:
Soil mapping helps farmers understand the variability of soil nutrients and moisture content across their fields. By identifying these differences, farmers can apply fertilizers and irrigation more precisely, which reduces the number of resources wasted.
Must read: Importance of maximizing agricultural production without destroying the ecological basis
Variable rate application:
Variable rate application uses GPS and data analytics to apply fertilizers and other inputs at rates that vary according to the specific needs of each part of a field. By applying inputs more precisely, farmers can reduce waste and improve crop yields.
Must read: Global Alliance for Climate-Smart Agriculture (GACSA)
Water management:
Precision farming technologies such as soil moisture sensors, weather stations, and remote sensing help farmers monitor soil moisture levels and weather conditions in real-time. This information allows them to apply irrigation water more efficiently, reducing water waste and improving crop yields.
Must read: Zero Budget Natural Farming (ZBNF)
Crop health monitoring:
Precision farming technologies can also help farmers monitor crop health, such as detecting pests and diseases early on. This enables farmers to apply pesticides and other treatments only where they are needed, reducing the number of chemicals used and minimizing their impact on the environment.
Must read: Conservation Agriculture – principles , benefits & problems
Harvest optimization:
Precision farming technologies can also optimize the timing of harvest to ensure that crops are picked at their peak ripeness, minimizing waste and maximizing yields.
Must read: Fertigation – an efficient method of fertilizer application
Overall, precision farming is a powerful tool for conserving resources while improving crop yields, and it is likely to play an increasingly important role in the future of agriculture.
External link: https://www-ceew-in.webpkgcache.com/doc/-/s/www.ceew.in/publications/sustainable-agriculture-india/precision-farming
