The earth as a whole does not accumulate or loose heat. It maintains its temperature.
This can happen only if the amount of heat received in the form of insolation equals the amount lost by the earth through terrestrial radiation.
Must read: HEATING AND COOLING OF ATMOSPHERE
Heat Budget
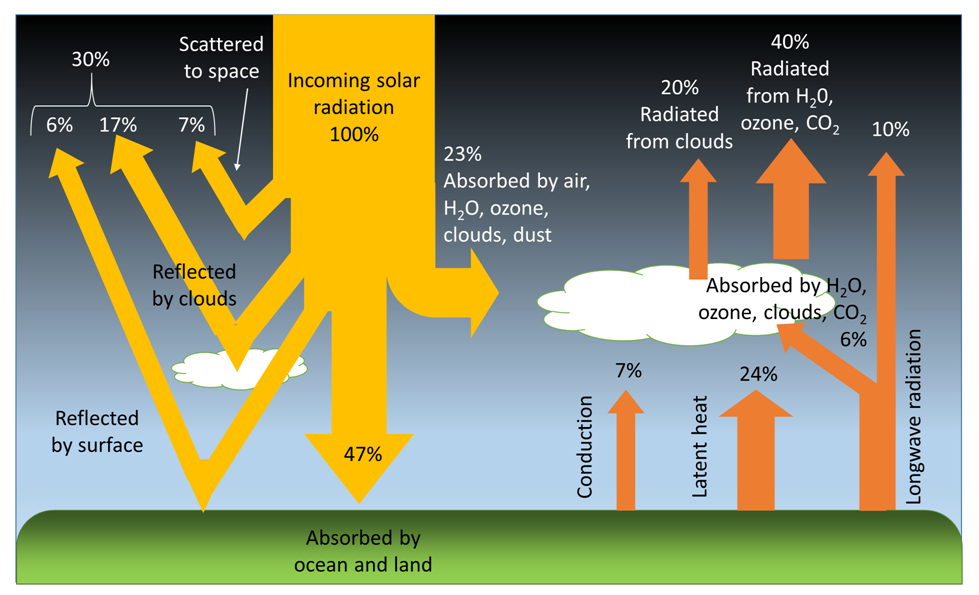
Consider that the insolation received at the top of the atmosphere is 100 per cent.
While passing through the atmosphere some amount of energy is reflected, scattered and absorbed.
Only the remaining part reaches the earth surface.
Roughly 35 units are reflected back to space even before reaching the earth’s surface. Of these, 27 units are reflected back from the top of the clouds and 2 units from the snow and ice-covered areas of the earth. The reflected amount of radiation is called the albedo of the earth.
Must read: Factors Controlling Temperature Distribution
The remaining 65 units are absorbed, 14 units within the atmosphere and 51 units by the earth’s surface.
The earth radiates back 51 units in the form of terrestrial radiation. Of these, 17 units are radiated to space directly and the remaining 34 units are absorbed by the atmosphere (6 units absorbed directly by the atmosphere, 9 units through convection and turbulence and 19 units through latent heat of condensation).
48 units absorbed by the atmosphere (14 units from insolation +34 units from terrestrial radiation) are also radiated back into space.
Thus, the total radiation returning from the earth and the atmosphere respectively is 17+48=65 units which balance the total of 65 units received from the sun. This is termed the heat budget or heat balance of the earth.
This explains, why the earth neither warms up nor cools down despite the huge transfer of heat that takes place.
Variation in the Net Heat Budget at the Earth’s Surface
There are variations in the amount of radiation received at the earth’s surface.
Must read: Variability of Insolation at the Surface of the Earth
Some part of the earth has surplus radiation balance while the other part has deficit.
Latitudinal variation in the net radiation balance of the earth — the atmosphere system
There is a surplus of net radiation balance between 40 degrees north and south and the regions near the poles have a deficit.
The surplus heat energy from the tropics is redistributed pole wards and as a result the tropics do not get progressively heated up due to the accumulation of excess heat or the high latitudes get permanently frozen due to excess deficit.
External link: https://ncert.nic.in/ncerts/l/kegy209.pdf
