QUES . What is a “Geographic Information System” (GIS)? Discuss its elements and prospects in agriculture.
HINTS:
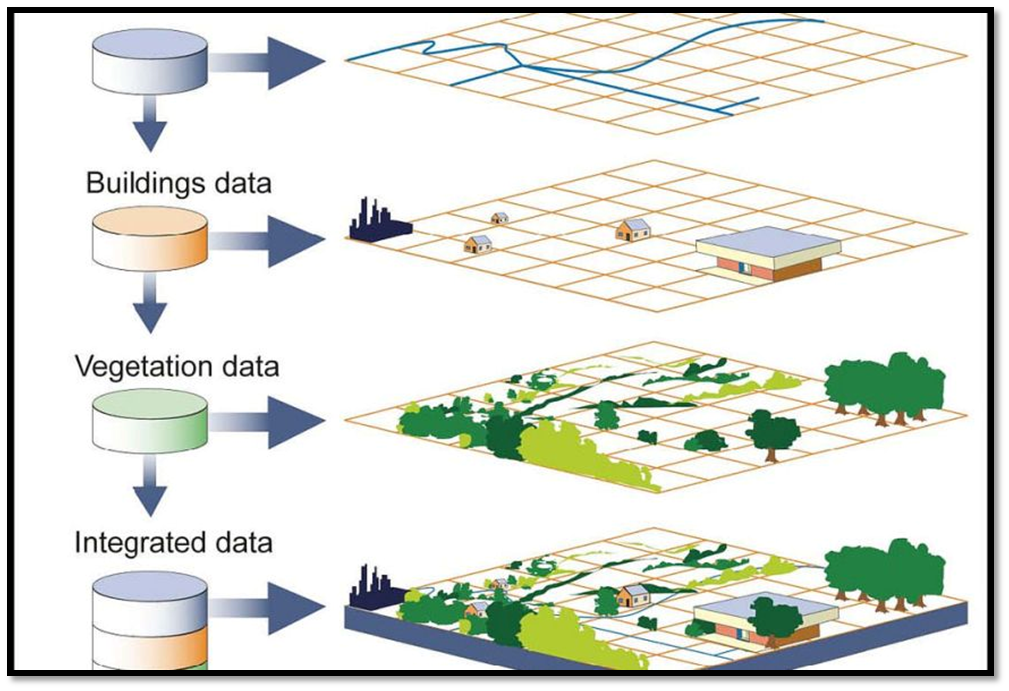
A Geographic Information System (GIS) is a computer-based tool used to capture, store, analyze, and manage spatial and geographic data. It allows users to visualize, interpret, and understand the relationships between different types of data, such as demographic, environmental, and economic information, by displaying them on maps and other types of visualizations.
The key elements of a GIS include:
Hardware: This includes the computers, servers, and other devices that store and process geographic data.
Software: This includes the GIS software that is used to create, manage, and analyze geographic data.
Data: This includes the geographic data that is used in the GIS, which can be collected from a variety of sources such as satellite imagery, GPS data, and surveys.
People: This includes the individuals who use the GIS to analyze and interpret geographic data, and make decisions based on the insights gained from the data.
GIS technology has significant prospects in agriculture.
By using GIS, farmers can create detailed maps of their fields that show soil type, slope, and other factors that affect crop growth. This information can help farmers optimize planting, irrigation, and fertilization, resulting in increased crop yields and improved resource management.
GIS can also be used to analyze and understand weather patterns and climate change impacts on agriculture, as well as to identify areas where crops are at risk of disease or pests.
By overlaying information on crop yield, soil characteristics, and weather patterns, farmers can identify areas of their fields that require special attention and target their resources accordingly.

Moreover, GIS can also help policymakers and researchers to make informed decisions related to agriculture. For example, GIS can be used to identify areas that are most suitable for specific types of crops and to analyze the impact of land use changes on food security, water resources, and biodiversity.
In summary, GIS is a powerful tool that has the potential to transform the way we understand and manage agriculture. By providing detailed and accurate information about the landscape, climate, and soil characteristics, GIS can help farmers make more informed decisions and improve the efficiency and sustainability of their operations.
