Fisheries and Aquaculture have been considered as an important means of poverty elevation and food security besides promoting health and well being.
Fish continue to be one of the most traded food commodities worldwide.
It contributes to around 17% of the global population’s animal protein intake.
Around 125-210 million tonnes of fish is projected to be required by 2050 to meet the annual per capita requirement of 15-20 kg.
Fish is often referred to as “Rich Food for Poor People” as it provides essential nourishment with both macronutrients and micronutrients.
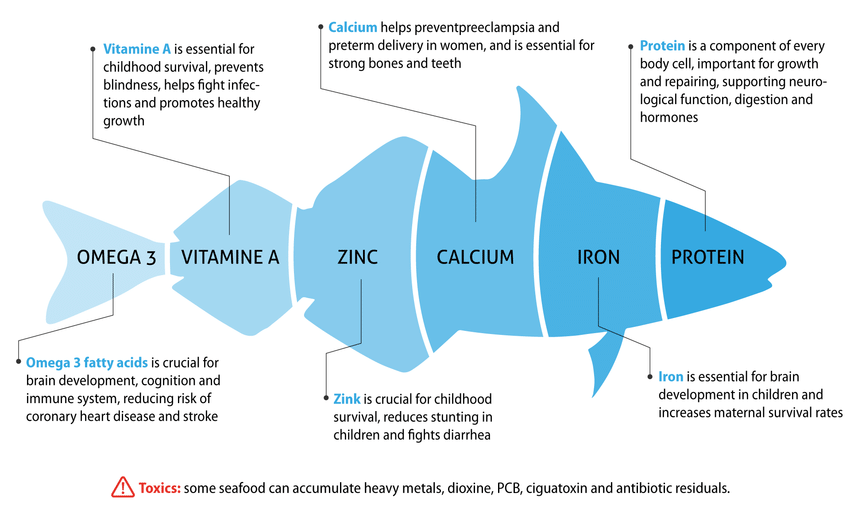
Fish contain low-fat high quality protein with omega-3 fatty acids and vitamins.
Fish is rich in calcium and phosphorus and a great source of minerals, such as iron, zinc, iodine, magnesium, and potassium.
On a fresh-weight basis, fish contains a good quantity of protein, about 18-20%, and all the eight essential amino acids including the sulphur-containing lysine, methionine, and cysteine.
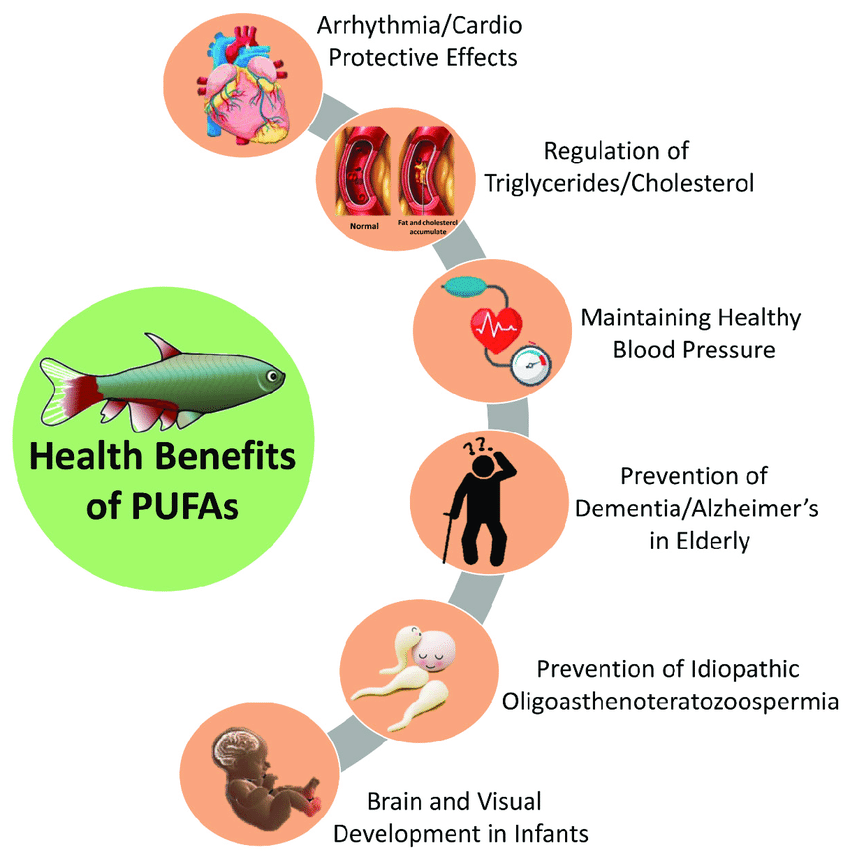
In general, fish have less fat than red meats and the fat content ranges from 0.2% to 25%. However, fats from fatty fish species contain the polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) namely EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid) which are essential for proper growth of children, proper brain development in unborn babies, reduced risk of preterm delivery and low birth weight.
The fat also contributes to energy supplies and assists in the proper absorption of fat soluble vitamins namely A, D, E, and K.
Fish is a rich source of vitamins, particularly vitamins A and D from fatty species, as well as thiamine, riboflavin and niacin (vitamins B1 , B2 and B3 ).
Vitamin D present in fish liver and oils is crucial for bone growth since it is essential for the absorption and metabolism of calcium.
Fish is also called “Brain Food” as it helps in development and function of brain, and “Heart Food” as it contributes to lower risks of heart attacks and strokes.
Consumption of fish reduces risk of autoimmune diseases, including Type-1 Diabetes, prevents and treats depression, protect from age-related brain deterioration, help prevent asthma in children, protect vision in old age by lowering risk of muscular degeneration, improves sleep quality, lowers risk of cancer, blood pressure, Alzheimer’s disease etc.
Fish is soft, easy to cook and more easily digested than meat so even young children can be fed fish, contributing to improved nutrient intake.
