QUES . The process of desertification leads to soil desiccation and soil loss. Explain.
HINTS:
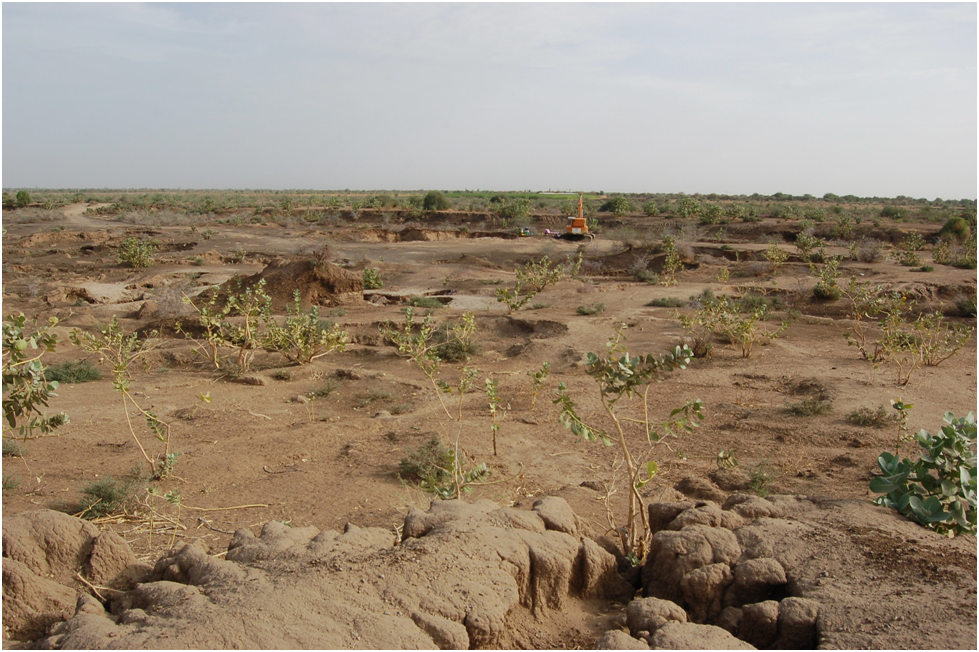

Desertification is a process that involves the degradation of land in arid, semi-arid, and dry sub-humid areas, leading to the conversion of productive land into non-productive desert-like landscapes. This process is often caused by natural factors such as drought and climate change, but it is also accelerated by human activities such as overgrazing, deforestation, and poor land management practices.
One of the major consequences of desertification is soil desiccation, which is the drying out of soil due to a lack of water. As vegetation cover decreases in a degraded landscape, the soil is exposed to the sun, and the moisture content in the soil decreases. This can lead to soil desiccation, which makes it difficult for plants to grow and can result in the loss of important soil nutrients.
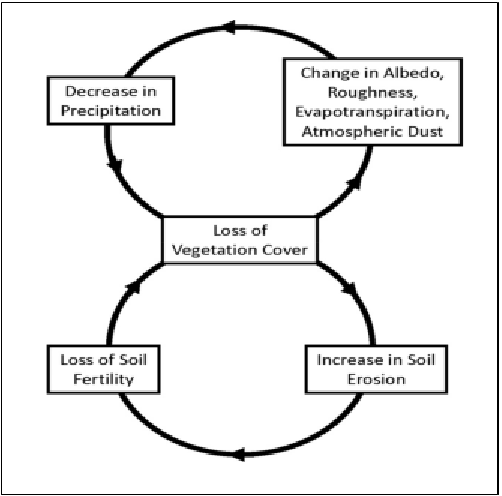
Another consequence of desertification is soil loss. As the vegetation cover decreases, the top layer of soil becomes more vulnerable to erosion by wind and water. The loss of soil can lead to decreased soil fertility and productivity, which can make it difficult for farmers to grow crops and sustain their livelihoods. Additionally, the erosion of soil can lead to sedimentation in rivers and other water bodies, causing problems such as flooding and water pollution.
Desertification can lead to soil compaction and the formation of a hard crust on the soil surface. This compaction restricts the movement of air and water into the soil, hindering plant growth and contributing to soil desiccation.
Overall, desertification is a significant environmental problem that can have serious consequences for soil health and productivity, as well as for the livelihoods of people who depend on the land for their sustenance. Addressing desertification requires a combination of measures, including sustainable land management practices, reforestation, and the restoration of degraded ecosystems.
