Historical Background
In the centuries that followed Jesus’ death, most Christians promoted what was called “Catholic Christianity”.
The term “catholic” comes from the Greek word katholikē, which means literally “according to the whole” or “universal.” The term came to designate the most accepted form of faith passed down from the first followers of Jesus.
Must read: Buddhism vs Jainism
Roman Catholicism
At that time, Roman culture and the Latin language dominated the West, so Christianity in that region took on a decidedly Roman flavor.
Consequently, the term “Roman Catholicism” became synonymous with western Christianity.
From the early centuries CE through the Middle Ages, Roman Catholic beliefs, traditions, practices, and institutions were the normative form of Christianity.
Must read: Jaina philosophy
Birth of Protestantism
In the sixteenth century, the Protestant Reformation began. Church leaders Luther, Zwingli, Calvin, and others protested against some of the practices and abuses of the Catholic Church.
Though the protestors wanted to reform the church from within, eventually it became clear that their movement was incompatible with the mother church in Rome. So they broke away and set up their own church structures and organizations—ushering in the birth of Protestantism.
Today, many different denominations and groups make up Protestantism throughout the world. Anglican, Lutheran, Presbyterian, Methodist, Baptist, Evangelical Free, Pentecostal, and many nondenominational churches now fall under the umbrella category of Protestantism.
Must read: Lingayatism
Differences Between Catholics and Protestants
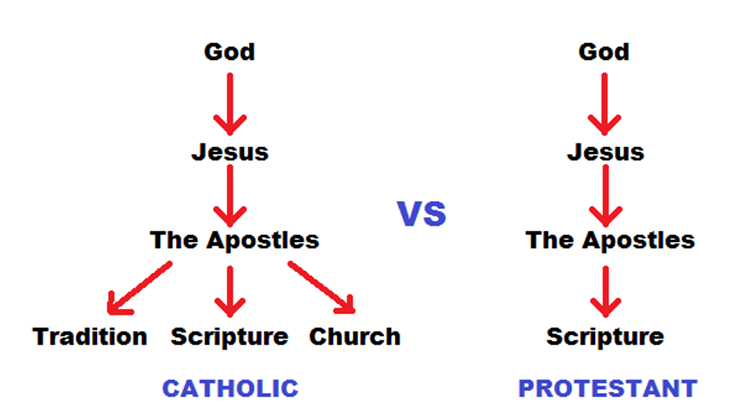
1 . The Magisterium or the pope
The term “magisterium” refers to the official teaching body of the Roman Catholic Church (the pope himself ) .Besides providing a trusted, unified voice to guide Catholics, this body also allows the church to make official pronouncements on contemporary issues which Scripture might not directly address.
There is no equivalent to the magisterium for Protestants.
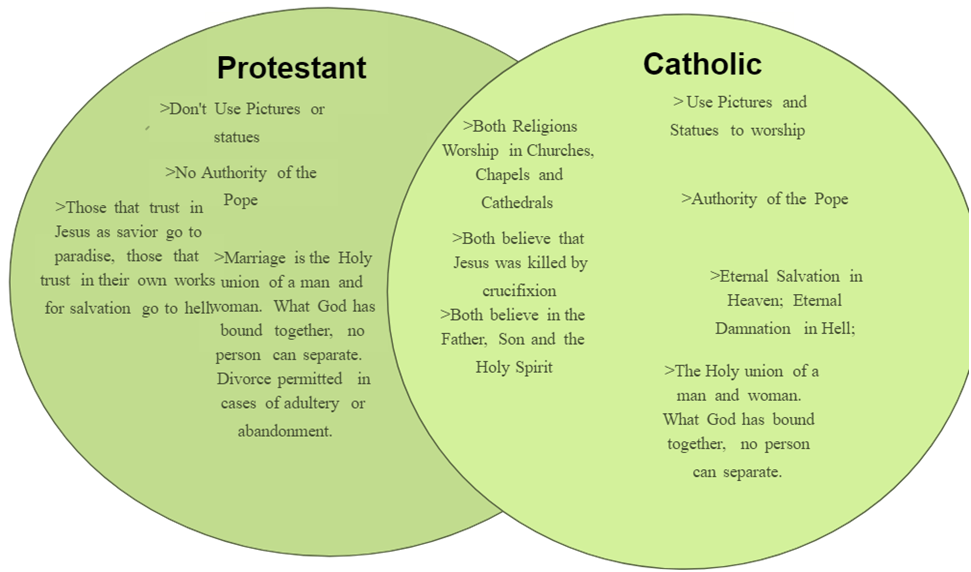
2 . Church
Catholics have them; Protestants don’t. Why? Well, Catholicism says that “humanity must discover its unity and salvation” within a church.
Protestants say all Christians can be saved, regardless of church membership.
3 . Saints
Catholics pray to saints (holy dead people) in addition to God and Jesus.
Protestants acknowledge saints, but don’t pray to them.
4 . Tradition
While Protestants don’t view tradition as equal in authority with the Scriptures, the Roman Catholic Church believes that both Scripture and tradition must be accepted and honored with equal sentiments of devotion and reverence.
5 . Holidays
Catholics have 10 Holy Days of Obligation (which mean they must go to Mass).
Protestants are more like, “Just come to church on Christmas, that’s all we ask.”
6 . Bread and wine
In Catholicism, the bread and wine “become” the body and blood of Jesus Christ, meaning that Jesus is truly present on the altar.
In Protestantism, the bread and wine are symbolic.
7 . Sacraments
Catholic are the only ones to have the concept of the seven sacraments (baptism, confirmation, the Eucharist, penance, anointing of the sick, holy orders, and matrimony).
Protestants teach that salvation is attained through faith alone.
8 . Authority to interpret Bible
In Catholicism, only the Roman Catholic Church has authority to interpret the Bible.
Protestants hold that each individual has authority to interpret the Bible.
9 . Worship
Roman Catholics embrace mystery, hierarchy, rituals, liturgy, structure, and more symbolic actions in worship.
Protestants, on the other hand, developed worship services that are plain and straightforward, focusing on Scripture.
Must read: Fire temple
Conclusion
These differences are extremely important. They continue to be the source of fruitful—and sometimes not-so-fruitful—discussions between Protestants and Roman Catholics.
However, one should not neglect the central beliefs upon which virtually all Protestants and Catholics agree.
There is one God, the Creator, who sent his only Son, Jesus, into the world to live as an example, to teach about the coming reign of God, to die on the cross, and to rise from the dead.
Through faith in Jesus, anyone can find hope, peace, and restoration with God.
External link: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Catholic%E2%80%93Protestant_relations
