What is Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD) or Biological Oxygen Demand?
Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD) or Biological Oxygen Demand is the amount of dissolved oxygen needed by aerobic biological organisms to break down organic material present in a given water sample at certain temperature over a specific time period.
What is the unit of BOD?
BOD is expressed in milligrams of oxygen consumed per litre of water and is often used as a indicator of the degree of organic pollution of water.
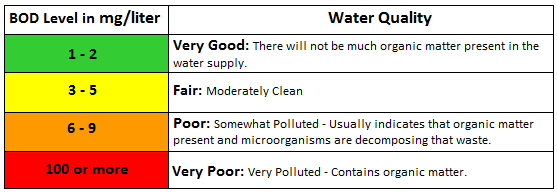
What is the relation between pollution and BOD?
Most natural waters contain small quantities of organic compounds. Aquatic microorganisms have evolved to use some of these compounds as food.
Microorganisms living in oxygenated waters use dissolved oxygen to oxidatively degrade the organic compounds, releasing energy which is used for growth and reproduction.
Populations of these microorganisms tend to increase in proportion to the amount of food available. This microbial metabolism creates an oxygen demand proportional to the amount of organic compounds useful as food.
Under some circumstances, microbial metabolism can consume dissolved oxygen faster than atmospheric oxygen can dissolve into the water or the autotrophic community (algae, cyanobacteria and macrophytes) can produce.
What happens when dissolved oxygen (DO) becomes less?
Fish and aquatic insects may die when oxygen is depleted by microbial metabolism.
Why dissolved oxygen (DO) is a crucial component of natural water bodies?
Although the amount of dissolved oxygen is small, up to about ten molecules of oxygen per million of water, it is a crucial component of natural water bodies
The presence of a sufficient concentration of dissolved oxygen is critical to maintaining the aquatic life and aesthetic quality of streams and lakes.
For what purpose BOD is used?
The waste organic matter is stabilized or made unobjectionable through its decomposition by living bacterial organisms which need oxygen to do their work.
BOD is used, often in wastewater-treatment plants, as an index of the degree of organic pollution in water.
Must read: Groundwater contamination in urban landscape of India
For more information https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Biochemical_oxygen_demand
PRACTICE QUESTIONS
QUES 1 . Biological Oxygen Demand (BOD) is a standard criterion for: UPSC 2017
(a) Measuring oxygen levels in blood
(b) Computing oxygen levels in forest ecosystems
(c) Pollution assay in aquatic ecosystems
(d) Assessing oxygen levels in high altitude regions
Answer – (c)
