Food security is a measure of the availability of food and individuals’ accessibility to it, where accessibility includes affordability.
Based on the 1996 World Food Summit, food security is defined when all people, at all times, have physical and economic access to sufficient safe and nutritious food that meets their dietary needs and food preferences for an active and healthy life.
According to Food and agriculture organization (FAO), Food security is made up of four pillars viz. Availability, Affordability, Nutrition, and Stability.
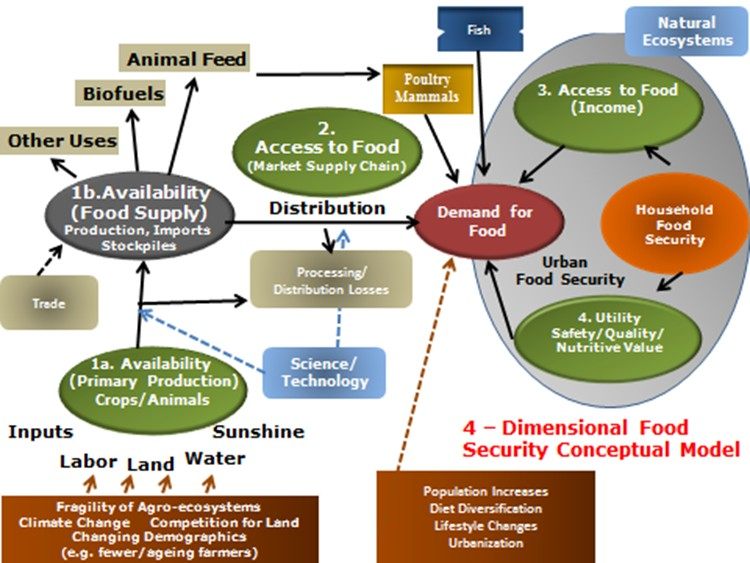
Availability
Food should be available in sufficient quantity at all times and at all places. Food availability addresses the “supply side” of food security and is determined by the level of food production, stock levels and net trade.
Affordability
Food should be affordable to poor people. An adequate supply of food at the national or international level does not in itself guarantee household level food security.
Concerns about insufficient food access have resulted in a greater policy focus on incomes, expenditure, markets and prices in achieving food security objectives.
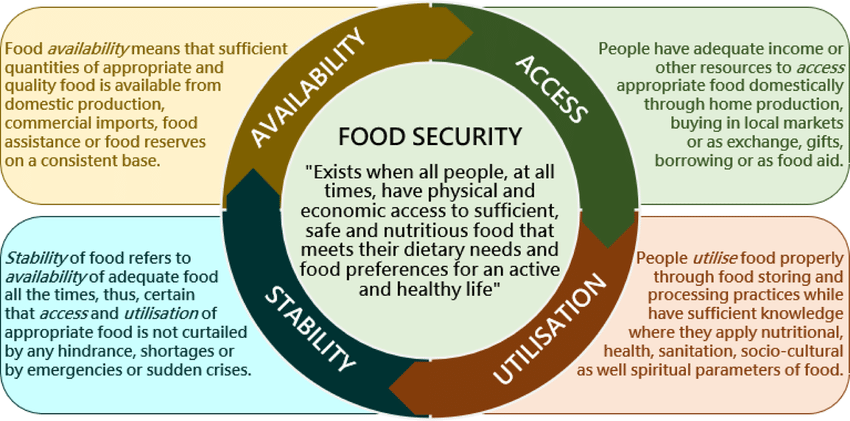
Nutrition
Food should be nutritious to ensure healthy development of body and mind.
Sufficient energy and nutrient intake by individuals are the result of good care and feeding practices, food preparation, diversity of the diet and intra-household distribution of food. Combined with good biological utilization of food consumed, this determines the nutritional status of individuals.
Stability

Food prices and supply must be stable. Otherwise political and social unrest.
Adverse weather conditions, political instability, or economic factors (unemployment, rising food prices) may have an impact on your food security status.
Measures taken by Governments to ensure food security in India
Availability
Union: MSP, fertilizer subsidy
States: cheap canal water and electricity
Together, they encourage farmers to produce more grains.
Affordability
Through Targeted-PDS and National Food Security Act (NFSA), Government provides cheap grain to poor.
Nutrition
Through Mid-day meal, Food-security Act, Integrated-Child Development scheme (ICDS),etc., Government ensures nutritious food to children.
Stability
FCI keeps ‘buffer-stock’ of grains. It can be sold to open market or distributed among people during high inflation, natural disaster etc.
