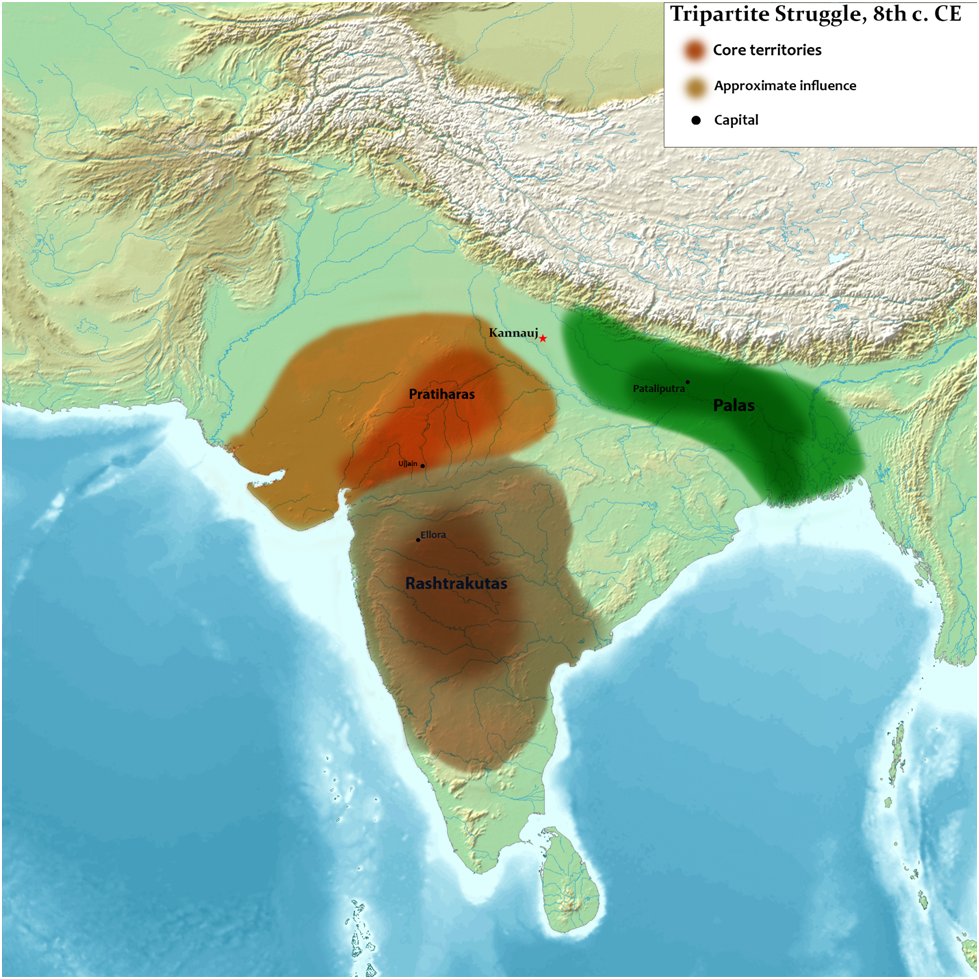
India in the eighth century was marked by the growth of three important political powers in India. These were Gurjara Pratiharas in north India, Palas in eastern India and Rashtrakutas in South India.
These powers were constantly fighting with each other with a aim to set up their control on Gangetic region in northern India. This armed conflict among these three powers is known as ‘Tripartite struggle’.
After that we notice the break up of these powers. It resulted in the rise of many smaller kingdoms all over the country in the 11th and 12 th century.
For example, in northern India, the disintegration of the Pratihara empire brought to the forefront various Rajput states in the 11th and 12 th century under the control of different Rajput dynasties such as the Chahmanas (Chauhans), Chandellas, Paramaras. etc. These were the states which fought and resisted the Turkish attacks from northwest India led by Mahmud Ghaznavi and Mohammad Ghori in the 11th and 12th centuries, but had to yield ultimately as they failed to stand unitedly against the invaders.
Gurjara Pratihara dynasty
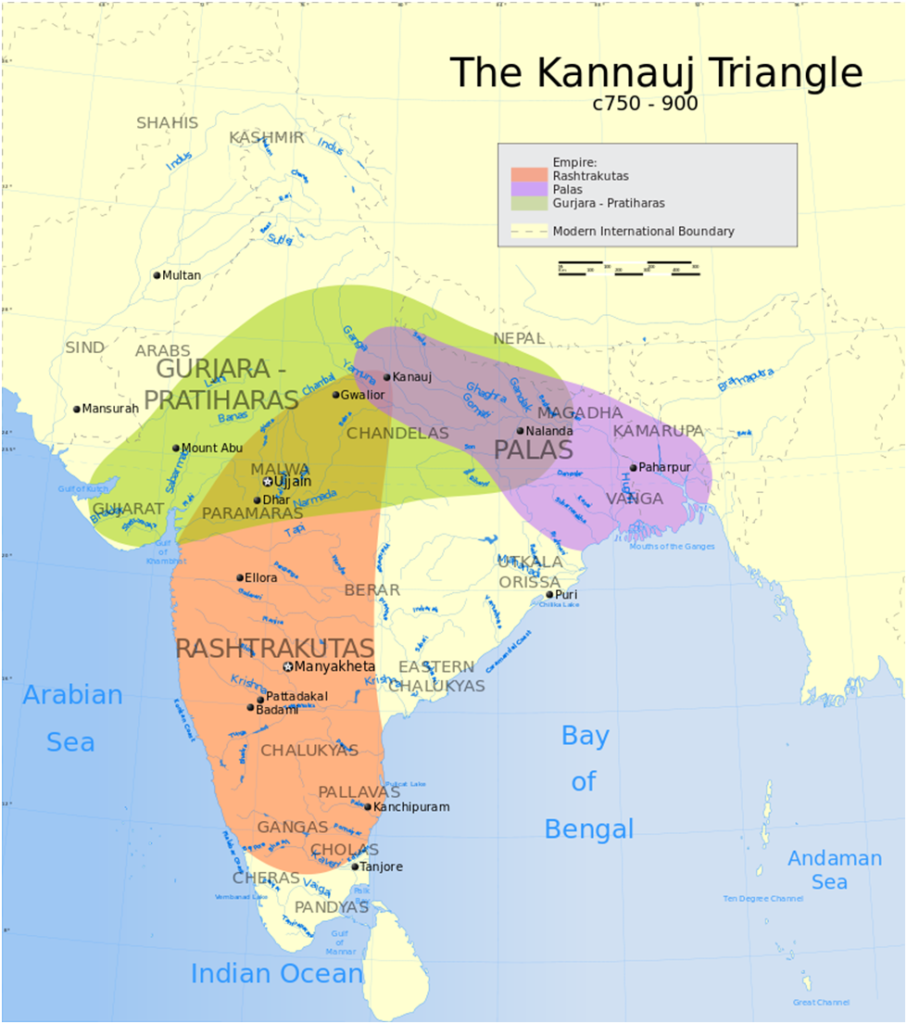
The Gurjara Pratihara dynasty was founded by Nagabhatta I in the region of Malwa in the eighth century. He belonged to a Rajput clan.
Later one of his successors, Vatsaraja extended his rule over to a large part of North India and made Kannauj in western Uttara Pradesh his capital. Vatsaraja’s policy of expansion brought him in conflict with Dharamapala, the Pala King of Bengal and Bihar.
Soon, the Rashtrakuta king Dhruva from south India jumped into the fight. And thus began what is known as ‘Tripartite Struggle’ i.e struggle among three powers. It continued for about the next hundred and fifty years under various succeeding kings with ups and downs.
The Gurjara-Pratiharas, however, could continue to maintain their hold over Kannauj till the last.
One of the important kings of this dynasty was Mihira Bhoja (ninth century). He was highly praised by an Arabian scholar Sulaiman for keeping his empire safe from robbers.
Pala dynasty
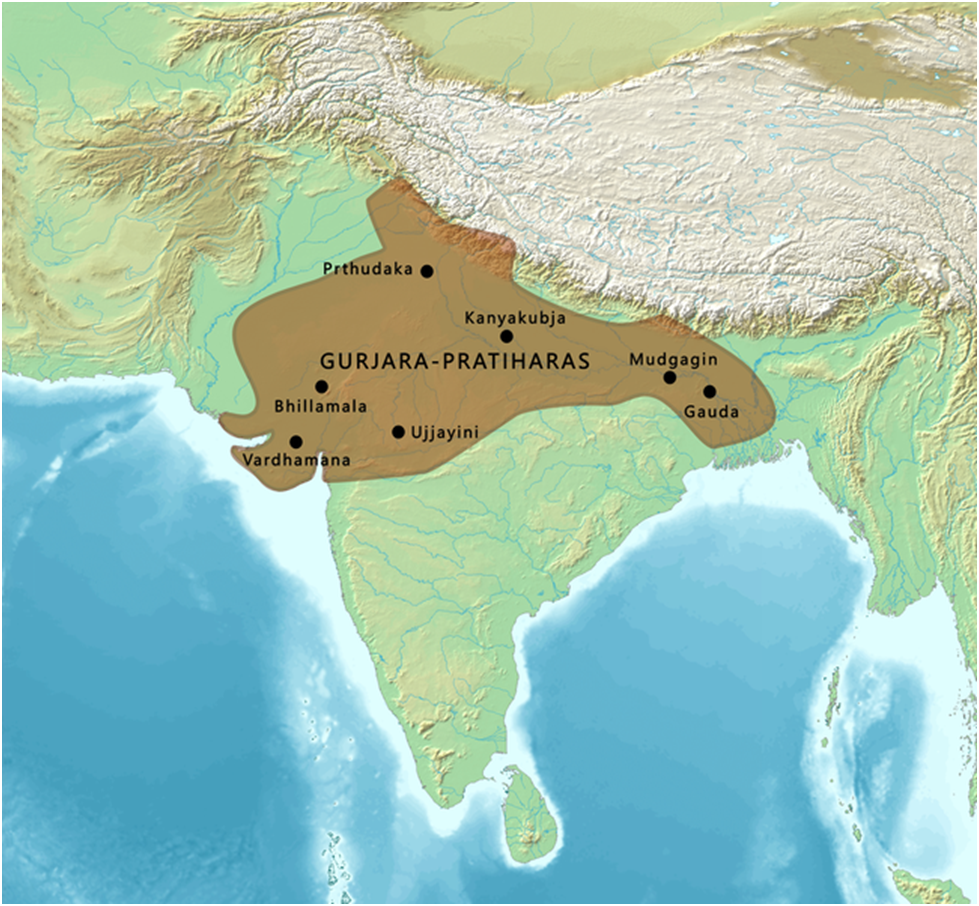
In eastern India, Pala dynasty was founded by Gopala (8th century). As the names of all the succeeding kings ended with ‘Pala’ this dynasty come to be known as the ‘Pala’ dynasty.
The son and grandson of Gopala,viz; Dharmapala and Devapala greatly extended the power and prestige of the Pala dynasty. Though their expansion towards west was checked by the Pratiharas, the Palas continued to rule over Bihar and Bengal for nearly four centuries with a small break.
The Pala kings were the followers of Buddhism. They greatly promoted this religion by making monasteries (viharas) and temples in eastern India.
Dharmapala is known to have founded the famous Vikramashila university near Bhagalpur in Bihar. Like Nalanda university, it attracted students from all parts of India and also from Tibet. Many Sanskrit texts were translated into Tibetan at this monastery.
The most celebrated name associated with Vikramashila University was that of Atisha Dipankara who was greatly respected in Tibet.
Rashtrakuta dynasty
In south, Dantidurga was the founder of the dynasty called, Rashtrakuta dynasty (8th AD).
The capital of the Rastrakutas was Manyakheta or Malkhed near Sholapur.
It was under the king Dhruva that the Rashtrakutas turned towards north India in a bid to control Kannauj, then the imperial city. And as mentioned above, it led to the beginning of ‘Tripartite struggle’.
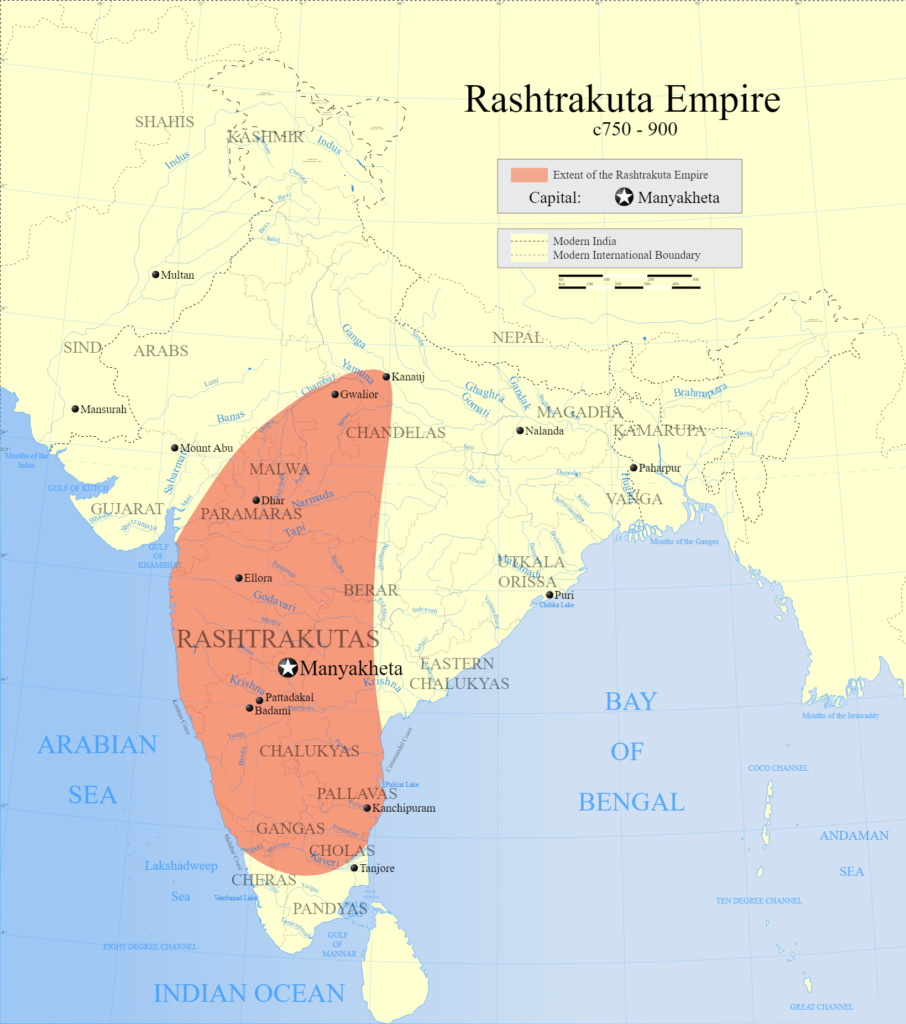
One of the important kings of the Rashtrakuta dynasty was Krishna I. He built the famous Kailasha temple at Ellora (near Aurangabad, Maharastra). It is dedicated to Lord Shiva and is monolithic i.e. made of one single piece of rock.
The Arab accounts inform us that the Rashtrakutas were quite friendly with the Arab traders who visited their empire. These traders were allowed to build mosques and follow their religion without any hindrance. It testifies to the liberal attitude of the Rashtrakuta kings and also to their desire to draw economic benefit from the growing sea trade conducted by the Arabs at that time.
Must read: Ports of ancient India
External link: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tripartite_Struggle
PRACTICE QUESTIONS
QUES . Consider the following dynasties: UPSC 2023
1. Hoysala
2. Gahadavala
3. Kakatiya
4. Yadava
How many of the above dynasties established their kingdoms in early eighth century AD?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) Only three
(d) None
(d) 1 . Hoysala era (1026 CE – 1343 CE) . 2 . Gahadavala dynasty also Gahadavalas of Kannauj was a Rajput dynasty that ruled parts of the present-day Indian states of Uttar Pradesh and Bihar, during 11th and 12th centuries. Their capital was located at Banaras in the Gangetic plains. 3 . Kakatiya dynasty ruled most of eastern Deccan region in present-day India between 12th and 14th centuries. Their territory comprised much of the present day Telangana and Andhra Pradesh, and parts of eastern Karnataka, northern Tamil Nadu, and southern Odisha. 4 . Seuna, Sevuna or Yadava dynasty (850 – 1334 A.D.) was a dynasty, which at its peak ruled a kingdom stretching from the Tungabhadra to the Narmada rivers, including present-day Maharashtra, north Karnataka and parts of Madhya Pradesh, from its capital at Devagiri (present-day Daulatabad in Maharashtra).
