What is a Heat Dome?
A heat dome is an area of high pressure that remains over a region like a lid on a pot, trapping heat.
This high pressure system forms way up in the atmosphere that helps create and encase heat, kind of like a lid on a pot that holds in steam, or a soda bottle cap that traps in gas.
How do heat domes form?
When a high pressure system moves into an area, it pushes warm air toward the ground. With the sinking air acting like a cap, the warm air can’t easily escape, and it continues to heat up the more it is compressed. It can be represented by the following four steps:
1 . Hot air masses expand vertically into the atmosphere
2 . High pressure pushes warm air down toward the ground
3 . As the air sinks, it warms by compression
4 . The dome of high pressure diverts clouds around it.
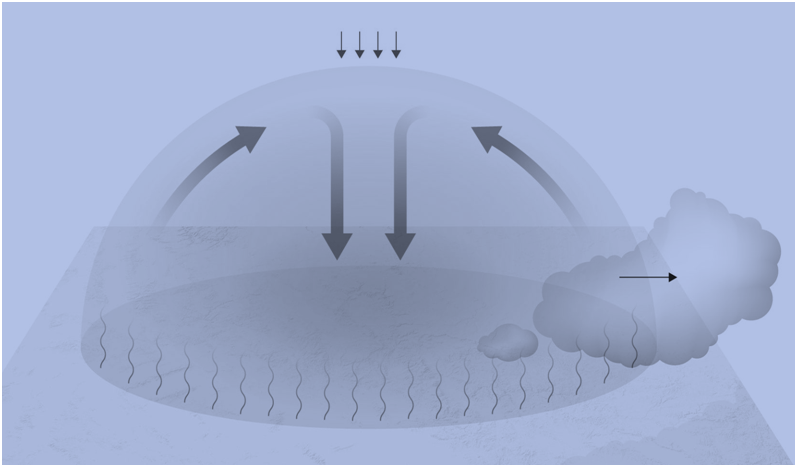
Hot air masses, born from the blazing summer sun, expand vertically into the atmosphere, creating a dome of high pressure that diverts weather systems around them.
As high-pressure systems become firmly established, subsiding air beneath them heats the atmosphere and dissipates cloud cover. The high summer sun angle combined with those cloudless skies then further heat the ground.
How heat dome is linked with jet streams?
The high atmospheric pressure is linked to the configuration of the jet streams which are bands of speedy winds that form high in the atmosphere in areas where cold air and hot air meet.
The jet streams tend to be narrow, wavy corridors of air that move west to east and migrate north to south. Sometimes jet streams can expand, becoming slower, or even stagnant, and heavier.
Can heat domes form anywhere?
Yes, they can, but areas that are farther from water, have flatter topography and are south of where jet streams migrate in the summer are more prone to oppressive heat domes.
Does heat dome intensifies under drought conditions?
Amid drought conditions, the vicious feedback loop get modified.
The combination of heat and a parched landscape can work to make a heat wave even more extreme.
With very little moisture in soils, heat energy that would normally be used on evaporation — a cooling process — instead directly heats the air and the ground.
When the land surface is drier, it can’t cool itself through evaporation, which makes the surface even hotter, which strengthens the blocking high [heat dome] further.
What is the impact of burning of fossil fuels on heat dome?
The situation is intensified by increasing background temperatures due to the burning of fossil fuels.
What is the impact of climate change on heat dome?
Evidence suggests climate change is increasing the frequency of heat domes this intense, pumping them up higher into the atmosphere, not unlike adding more air to a hot-air balloon.
What is the impact of La Niña on heat dome?
Heat dome are more likely to form during La Niña years when waters are cool in the eastern Pacific and warm in the western Pacific.
That temperature difference creates winds that blow dense, tropical, western air eastward.
Eventually that warm air gets trapped in the jet stream—a current of air spinning counterclockwise around the globe—and ends up on the U.S. West Coast.
When you get high pressure over the West, it keeps that warm air over the West.
How heat dome is related with heat wave?
A heat dome is basically that trapping dome. The heat event itself is the heat wave, lasting several consecutive days and nights that are well above normal that the heat dome helps sustain the heat wave.
