What is Web?
Web refers to the World Wide Web.
Computer scientist Tim Berners-Lee is credited with inventing the world wide web in 1989, which allowed people to hyperlink static pages of information on websites accessible through internet browsers. In 1991, he launched the world’s first website.
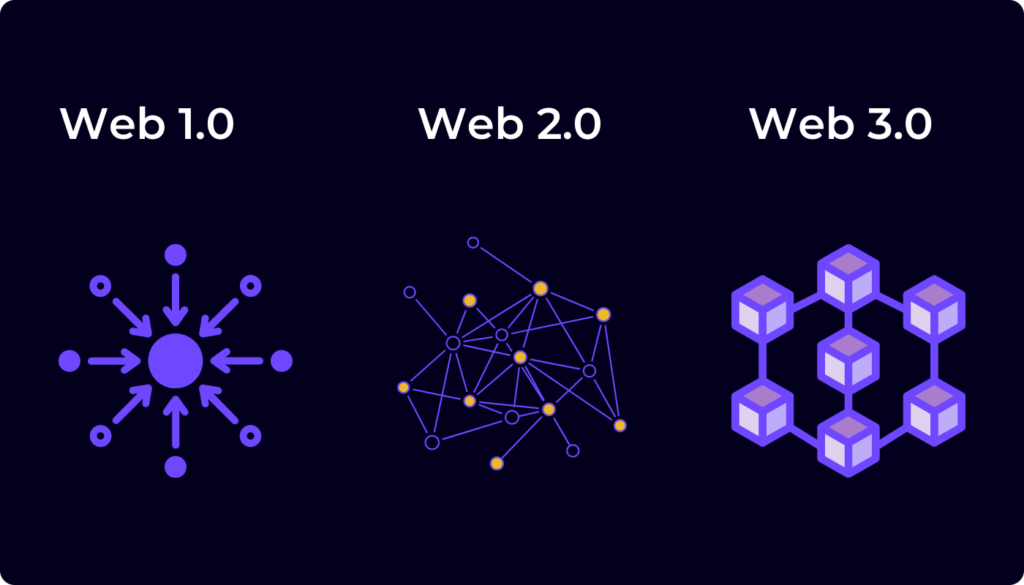
What is Web 1.0?
These basic “read-only” websites were managed by webmasters who were responsible for updating users and managing the information. In 1992, there were 10 websites. By 1994, after the web entered the public domain, there were 3,000.
What is Web 2.0?
Web 2.0 is the second and current generation, succeeding Web 1.0 of the 1990s and early 2000s.
This was a major shift for the internet as it developed from a “read-only web” to where we are currently — a “read-write web.”
Websites became more dynamic and interactive. People became mass participants in generating content through hosted services like Wikipedia, Blogger, Flickr and Tumblr.
Innovations such as smartphones, mobile internet access, and social networks have driven the exponential growth of Web 2.0.
What is Web 3.0?
Web 3.0 represents the next phase of the evolution of the web or internet and potentially could be as disruptive and represent as big a paradigm shift as Web 2.0 did.
The model, a decentralised internet to be run on blockchain technology, would be different from the versions in use, Web 1.0 and Web 2.0.
Web 3.0 is built upon the core concepts of decentralization, openness, and greater user utility.
What are the defining features of Web 3.0?
The defining features of Web 3.0 include decentralization; trustlessness and permissionlessness; artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning; and connectivity and ubiquity.
What is the core tenet of Web 3.0?
Decentralization is a core tenet of Web 3.0.
In Web 2.0, computers use HTTP in the form of unique web addresses to find information, which is stored at a fixed location, generally on a single server.
With Web 3.0, because information would be found based on its content, it could be stored in multiple locations simultaneously and hence be decentralized.
How Web 3.0 ensures that users retain ownership control?
With Web 3.0, the data generated by disparate and increasingly powerful computing resources, including mobile phones, desktops, appliances, vehicles, and sensors, will be sold by users through decentralized data networks, ensuring that users retain ownership control.
In addition to decentralization and being based upon open-source software, Web 3.0 will allow participants to interact directly without going through a trusted intermediary and anyone can participate without authorization from a governing body.
Web3 will deliver a decentralized and fair internet where users control their own data.
In web3, users will have ownership stakes in platforms and applications unlike now where tech giants like Meta and Google control the platforms.
On what types of networks Web 3.0 applications will run?
Web 3.0 applications will run on blockchains or decentralized peer-to-peer networks.
Web3 enables peer to peer (seller to buyer) transactions by eliminating the role of the intermediary.
Must read: Open Source Software – a community based software
For more information https://ethereum.org/en/web3/
PRACTICE QUESTIONS
QUES 1 . With reference to Web 3-0, consider the following statements: UPSC 2022
1 . Web 3.0 technology enables people to control their own data.
2 . In Web 3.0 world, there can be blockchain based social networks.
3 . Web 3.0 is operated by users collectively rather than a corporation.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
(d) EXPLANATION: ■ The concept of Web3, also called Web 3.0, is used to describe a potential next phase of the internet. ■ The model, a decentralised internet to be run on blockchain technology, would be different from the versions in use, Web 1.0 and Web 2.0. ■ Web3 enables peer to peer (seller to buyer) transactions by eliminating the role of the intermediary. ■ In web3, users will have ownership stakes in platforms and applications unlike now where tech giants control the platforms. ■ Web3 will deliver a decentralized and fair internet where users control their own data.
