Deciduous Forests are the most widespread forests in India. They are also called the monsoon forests.
A deciduous forest comprises of deciduous trees which lose their leaves seasonally.
They spread over regions which receive rainfall between 70-200 cm.

Types of Tropical Deciduous Forests
On the basis of the availability of water, these forests are further divided into moist and dry deciduous.
Tropical Moist Deciduous Forests
The Moist deciduous forests are more pronounced in the regions which record rainfall between 100-200 cm.
Mean annual temperature of about 27°C
The average annual relative humidity of 60 to 75 per cent.
Characteristics
The trees drop their leaves during the spring and early summer when sufficient moisture is not available.
The general appearance is bare in extreme summers (April-May).
Tropical moist deciduous forests present irregular top storey [25 to 60 m].
Heavily buttressed trees and fairly complete undergrowth.
These forests occupy a much larger area than the evergreen forests but large tracts under these forests have been cleared for cultivation.
Distribution
These forests are found in the northeastern states along the foothills of Himalayas, eastern slopes of the Western Ghats and Odisha.
Hills of eastern Madhya Pradesh and Chhattisgarh.
Chota Nagpur Plateau.
Parts of West Bengal
Vegetation
Teak (Tectona grandis) , sal, shisham, hurra, mahua (Madhuca indica), amla, semul, kusum, and sandalwood etc. are the main species of these forests.
Tropical Dry Deciduous Forest
The Dry deciduous forest covers vast areas of the country, where rainfall ranges between 70 -100 cm. On the wetter margins, it has a transition to the moist deciduous, while on the drier margins to thorn forests.
Characteristics
In the higher rainfall regions of the Peninsular plateau and the northern Indian plain, these forests have a parkland landscape with open stretches in which teak and other trees interspersed with patches of grass are common. As the dry season begins, the trees shed their leaves completely and the forest appears like a vast grassland with naked trees all around.
In the western and southern part of Rajasthan, vegetation cover is very scanty due to low rainfall and overgrazing.
Distribution
These forests are found in rainier areas of the Peninsula and the plains of Uttar Pradesh and Bihar.
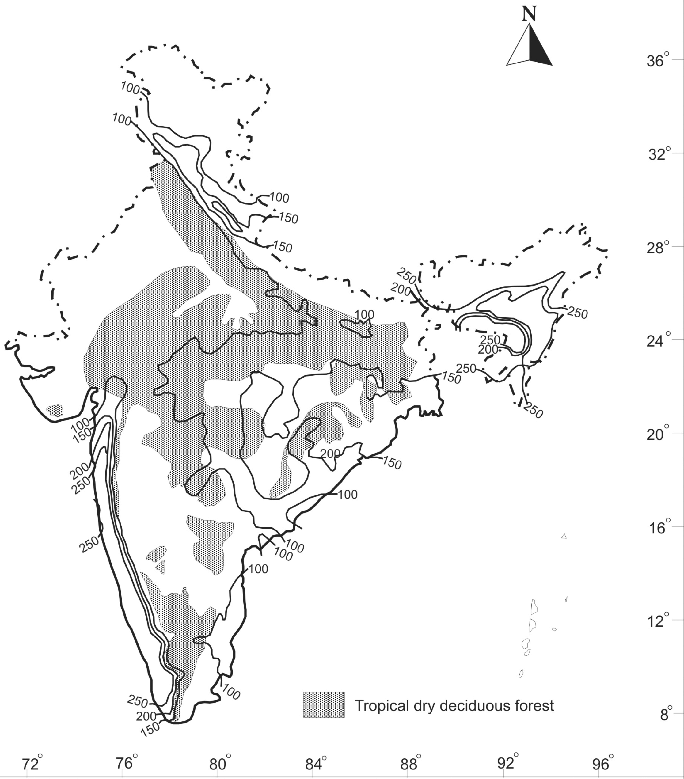
Vegetation
Tendu, palas, amaltas, bel, khair, axlewood, etc. are the common trees of these forests.
PRACTICE QUESTIONS
QUES . Consider the following trees: UPSC 2023
1 . Jackfruit (Artocarpus heterophyllus)
2 . Mahua (Madhuca indica)
3 . Teak (Tectona grandis)
How many of the above are deciduous trees?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) All three
(d) None
Ans (b)
Explanation:
● Jackfruit (Artocarpus heterophyllus) is an evergreen tree, which means they retain their leaves throughout the year and do not shed them seasonally. So, 1 is not correct.
● Mahua (Madhuca indica) is found in the dry deciduous type of forests like the forests of Chhattisgarh and Jharkhand. So, 2 is correct.
● Teak (Tectona grandis) is a moist deciduous tree. Teak wood forests are mainly found in North East India. So, 3 is correct.
Therefore, option (b) is the correct answer.
