What are Stem cells?
Stem cells are special human cells that are able to develop into many different cell types.
Stem cells are the body’s raw materials — cells from which all other cells with specialized functions are generated.
In mammals, roughly 50–150 cells make up the inner cell mass during the blastocyst stage of embryonic development, around days 5–14. These have stem-cell capability. In vivo, they eventually differentiate into all of the body’s cell types (making them pluripotent).
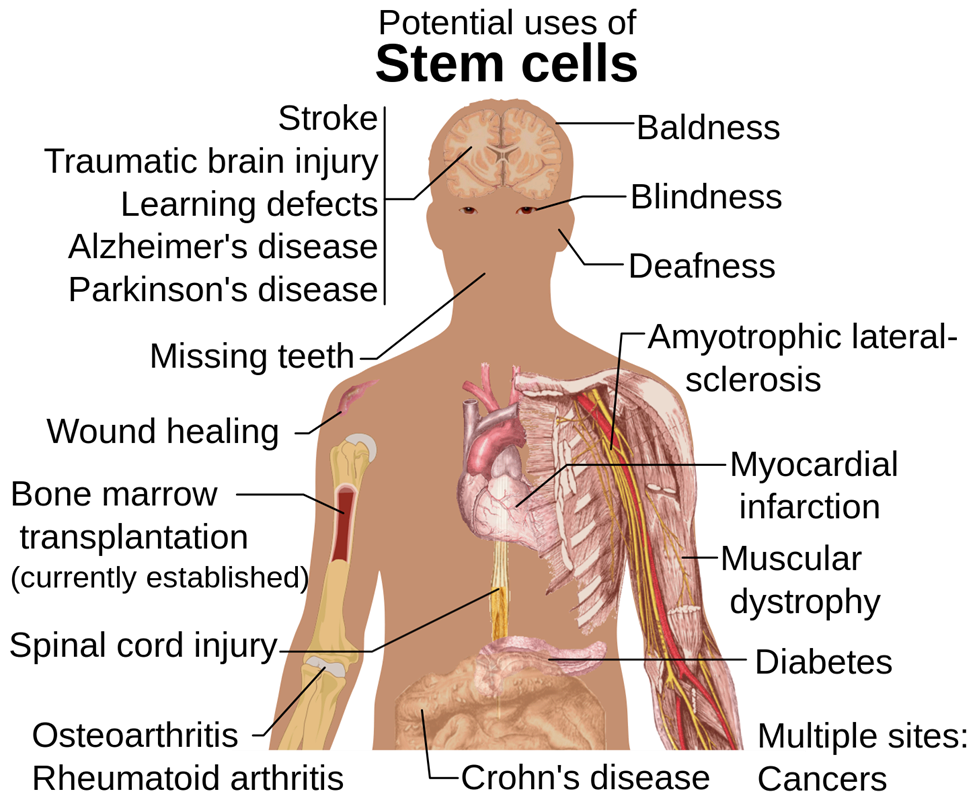
Researchers believe that stem cell-based therapies may one day be used to treat serious illnesses such as paralysis and Alzheimer disease.
What are the properties of stem cells?
Under the right conditions in the body or a laboratory, stem cells divide to form more cells called daughter cells. These daughter cells become either new stem cells or specialized cells (differentiation) with a more specific function, such as blood cells, brain cells, heart muscle cells or bone cells.
No other cell in the body has the natural ability to generate new cell types.
Stem cells possesses two properties:
Self-renewal
It is the ability to go through numerous cycles of cell growth and cell division, known as cell proliferation, while maintaining the undifferentiated state.
Potency
It is the capacity to differentiate into specialized cell types.
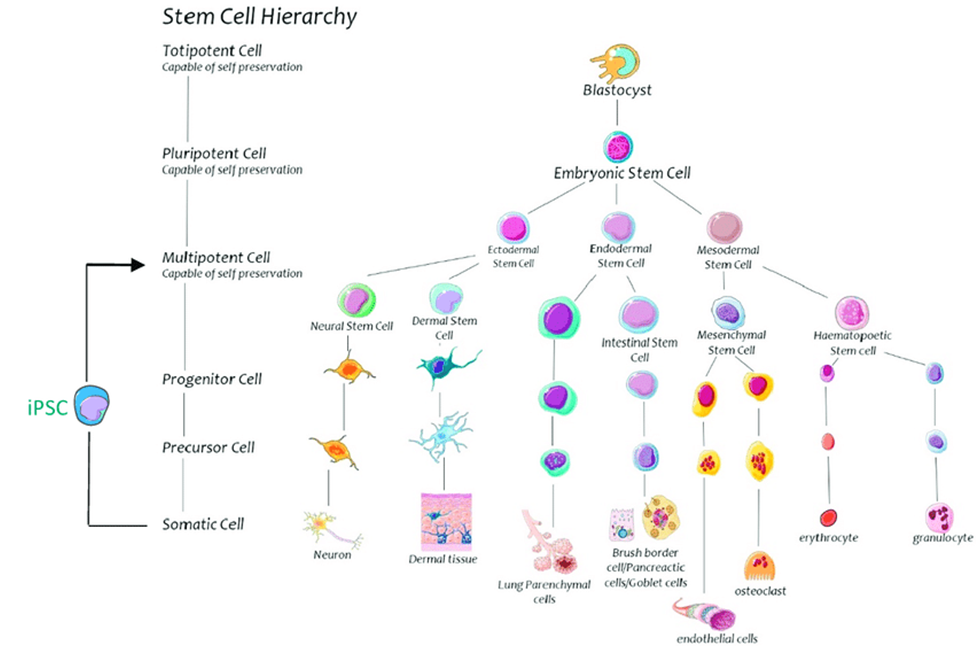
Totipotent (also known as omnipotent) stem cells can differentiate into embryonic and extraembryonic cell types. Such cells can construct a complete, viable organism. These cells are produced from the fusion of an egg and sperm cell. Cells produced by the first few divisions of the fertilized egg are also totipotent.
Pluripotent stem cells are the descendants of totipotent cells and can differentiate into nearly all cells, i.e. cells derived from any of the three germ layers.
Multipotent stem cells can differentiate into a number of cell types, but only those of a closely related family of cells.
Oligopotent stem cells can differentiate into only a few cell types, such as lymphoid or myeloid stem cells.
Unipotent cells can produce only one cell type, their own, but have the property of self-renewal, which distinguishes them from non-stem cells
What are the sources of stem cells?
There are several sources of stem cells:
Embryonic stem cells
These stem cells come from embryos that are 3 to 5 days old. At this stage, an embryo is called a blastocyst and has about 150 cells.
These are pluripotent stem cells, meaning they can divide into more stem cells or can become any type of cell in the body. This versatility allows embryonic stem cells to be used to regenerate or repair diseased tissue and organs.
Adult stem cells
These stem cells are found in small numbers in most adult tissues, such as bone marrow or fat. Compared with embryonic stem cells, adult stem cells have a more limited ability to give rise to various cells of the body.
They exist to replenish rapidly lost cell types and are multipotent or unipotent, meaning they only differentiate into a few cell types or one type of cell.
Adult cells altered to have properties of embryonic stem cells
Scientists have successfully transformed regular adult cells into stem cells using genetic reprogramming. By altering the genes in the adult cells, researchers can reprogram the cells to act similarly to embryonic stem cells.
Perinatal stem cells
Researchers have discovered stem cells in amniotic fluid as well as umbilical cord blood. These stem cells have the ability to change into specialized cells.
What are the ethical concerns with respect to the use of embryonic stem cells?
Embryonic stem cells are obtained from early-stage embryos — a group of cells that forms when eggs are fertilized with sperm at an in vitro fertilization clinic.
Because human embryonic stem cells are extracted from human embryos, several questions and issues have been raised about the ethics of embryonic stem cell research.
Where do these embryos come from?
The embryos being used in embryonic stem cell research come from eggs that were fertilized at in vitro fertilization clinics but never implanted in women’s uteruses. The stem cells are donated with informed consent from donors. The stem cells can live and grow in special solutions in test tubes or petri dishes in laboratories.
What is stem cell therapy and how does it work?
Stem cell therapy, also known as regenerative medicine, promotes the repair response of diseased, dysfunctional or injured tissue using stem cells or their derivatives.
It is the next chapter in organ transplantation and uses cells instead of donor organs, which are limited in supply.
Researchers grow stem cells in a lab. These stem cells are manipulated to specialize into specific types of cells, such as heart muscle cells, blood cells or nerve cells.
The specialized cells can then be implanted into a person. For example, if the person has heart disease, the cells could be injected into the heart muscle. The healthy transplanted heart muscle cells could then contribute to repairing the injured heart muscle.
What is therapeutic cloning and how it is done?
Therapeutic cloning, also called somatic cell nuclear transfer, is a technique to create versatile stem cells independent of fertilized eggs.
In this technique, the nucleus is removed from an unfertilized egg. This nucleus contains the genetic material. The nucleus is also removed from the cell of a donor.
This donor nucleus is then injected into the egg, replacing the nucleus that was removed, in a process called nuclear transfer.
The egg is allowed to divide and soon forms a blastocyst.
This process creates a line of stem cells that is genetically identical to the donor’s cells — in essence, a clone.
What are the benefits of therapeutic cloning?
Some researchers believe that stem cells derived from therapeutic cloning may offer benefits over those from fertilized eggs because cloned cells are less likely to be rejected once transplanted back into the donor and may allow researchers to see exactly how a disease develops.
What are the advantages of stem cell research?
Stem cell treatments may lower symptoms of the disease or condition that is being treated. The lowering of symptoms may allow patients to reduce the drug intake of the disease or condition.
Stem cell treatment may also provide knowledge for society to further stem cell understanding and future treatments.
Surgical processes by their character are harmful. Tissue has to be dropped as a way to reach a successful outcome. One may prevent the dangers of surgical interventions using stem cells.
Risks associated with anesthesia can also be eliminated with stem cells.
On top of that, stem cells have been harvested from the patient’s body and redeployed in which they’re wanted. Since they come from the patient’s own body, this is referred to as an autologous treatment. Autologous remedies are thought to be the safest because there’s likely zero probability of donor substance rejection.
What are the challenges in stem cell research?
Stem cells need much more study before their use can be expanded. Scientists must first learn more about how embryonic stem cells develop. This will help them understand how to control the type of cells created from them.
Another challenge is that the embryonic stem cells available today are likely to be rejected by the body.
And some people find it morally troubling to use stem cells that come from embryos.
Scientists also face challenges when using adult pluripotent stem cells. These cells are hard to grow in a lab, so researchers are looking into ways to improve the process. These cells are also found in small amounts in the body. There is a greater chance that they could contain DNA problems.
PRACTICE QUESTIONS
QUES . Stem cell therapy is gaining popularity in India to treat a wide variety of medical conditions including leukaemia, Thalassemia, damaged cornea and several burns. Describe briefly what stem cell therapy is and what advantages it has over other treatments? UPSC GS MAINS 2017
QUES . With reference to the latest developments in stem cell research, consider the following statements: UPSC 2002
(i) The only source of human stem cells are the embryos at blastocyst stage.
(ii) The stem cells can be derived without causing destruction to blastocysts.
(iii) The stem cells can regenerate themselves in vitro virtually forever.
(iv) Indian research centres also created a few cell lines, which can be developed into any types of tissues.
Which of these statements are correct?
(a) All of these
(b) (i), (ii) and (iii)
(c) (i), (i) and (iv)
(d) (iii) and (iv)
(d)
QUES . With reference to ‘stem cells’, frequently in the news, which of the following statements is/are correct? UPSC 2012
(i) Stem cells can be derived from mammals only.
(ii) Stem cells can be used for screening new drugs.
(iii) Stem cells can be used for medical therapies.
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) Only (iii)
(d) All of these
(b)
QUES . What is the application of Somatic Cell CJ Nuclear Transfer Technology? UPSC 2017
(a) Production of bio-larvicides
(b) Manufacture of biodegradable plastics
(c) Reproductive cloning of animals
(d) Production of organisms free of diseases
(c)
