
QUES . What is the status of digitalization in the Indian economy? Examine the problems faced in this regard and suggest improvements. UPSC 2023 GS MAINS PAPER III , 150 words, 10 Marks
HINTS:
The digital transformation has fundamentally reshaped lives in every nook and corner of India, turning it into a resounding global success story. It has opened up tremendous opportunities for economic growth across various sectors of the economy.
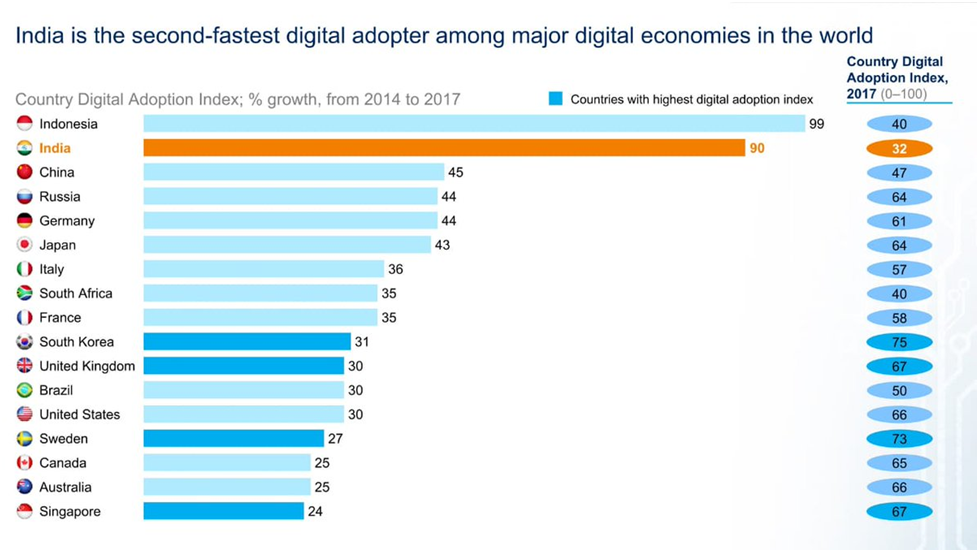
Status of digitalization in the Indian economy
Access to cheap high speed internet services (4G) through mobile telephony. A majority of Indians have become active internet users with 52% of the population or 759 million people accessing the internet at least once a month in 2022, according to a report published by IAMAI.
Aadhar forms the basis unique identity for citizens.
Digital financial services provide access to banking for the unbanked and underbanked. The Jan Dhan Yojana initiative resulted in millions of bank accounts being opened, promoting financial inclusion.
Shareable private space on a public cloud (Citizens can digitally store their documents, certificates etc.)
UPI platform for digitally and safe payments among different platforms. For example, the UPI-based BHIM (Bharat Interface for Money) app has become widely popular, enabling secure and convenient peer-to-peer transactions.
E-commerce market is rapidly growing due to convenience and affordability factors. India’s e-commerce market is projected to reach $200 billion by 2026.
Digital transformation is expected to create $1 trillion worth of economic value by 2025, resulting in 60 to 65 million jobs.
Emergence of Digital Public Infrastructure which enabled access to government services digitally. The Digital India program has made significant strides in providing e-governance services. For example:
1 . Initiatives like the e-visa and the Digital Locker system have streamlined government services.
2 . OCEN (Open Credit Enablement Network) Platform and Account Aggregators platform for easier credit disbursement to citizens and businesses.
3 . GST platform: for digital assessment and filing of tax returns.
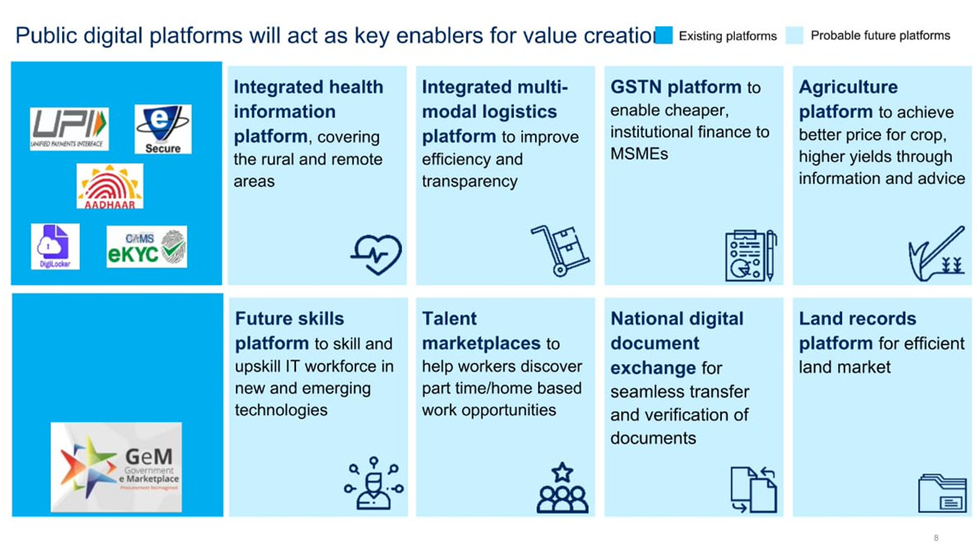
4 . UMANG (Unified Mobile Application for New-age Governance): UMANG provides a single platform for all Indian Citizens to access pan India e-Gov services ranging from Central to Local Government bodies.
5 . Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC): It will democratize e-Commerce and enable millions of small traders take advantage of opportunities thrown up by e-commerce.
6 . OpenForge platform : Government of India’s platform for open collaborative development of e-governance applications. Through this platform, the government wants to promote the use of open source software and promote sharing and reuse of e-governance related source code.
Problems faced in digitalizing the economy
Digital divide to the detriment of rural areas. Rural areas having limited access to the internet, technology and are less educated.
Lack of implementation of digital data protection law in India.With the rise in digital transactions and data sharing, concerns about privacy and data security are significant.
Complex digital regulations, taxation on e-commerce and intellectual property issues can be challenging for businesses.
Concerns with cyber security and cyber frauds. As digitization increases, the risk of cyber threats and attacks escalates. India witnessed 91 Lakh cyber security incidents in 2022.
Lack of access to broadband. Ensuring high-speed internet access and reliable digital infrastructure remains a challenge, particularly in rural areas.
Digitization disrupts traditional business models, leading to challenges in certain industries and job markets.
Lack of domestic semiconductor industry in India and dependence on imports.
The rapid pace of technological change requires a skilled workforce but only around 42% of India’s workforce possesses digital skills.
Suggestions for boosting India’s digitalisation
Invest in expanding digital infrastructure across the country. Accelerate efforts to expand broadband connectivity in rural and remote regions.
Implement nationwide digital literacy programs. This will empower individuals to access and utilize digital services effectively. For example, Pradhan Mantri Gramin Digital Saksharta Abhiyan (PMGDISHA) is a welcome initiative.
Strengthen cybersecurity measures and awareness campaigns to protect users from online threats. Enact robust data protection laws and regulations to safeguard individuals’ privacy and ensure responsible data handling by organizations. For example, more measures like National Cyber Security Policy, 2021 and Digital personal data protection act, 2023 are needed.
Encourage the growth of start-ups. Encourage MSMEs to adopt digital tools and e-commerce platforms by offering incentives and training programs.
Promote digital payment solutions tailored to diverse user groups. Continue efforts to digitize government services, making them accessible and user-friendly. Promote the use of digital identification methods like Aadhar for seamless access.
Collaborate with private sector companies to drive digitalization initiatives
Conclusion
Digitalization will increase economic efficiency and competitiveness, creating new businesses and products, and addressing challenges relating to increasing financial inclusion, improving governance and reducing disparities. For India, digitalization is especially important given the large population, with over 60% living in rural areas. Connecting the country together allows for greater access to the benefits and opportunities of a modern economy to a larger number of citizens, thereby bridging the economic divide.
