QUES . Sequential changes in land use and land cover have brought global and regional ecological changes and imbalances. Elucidate.
HINTS:
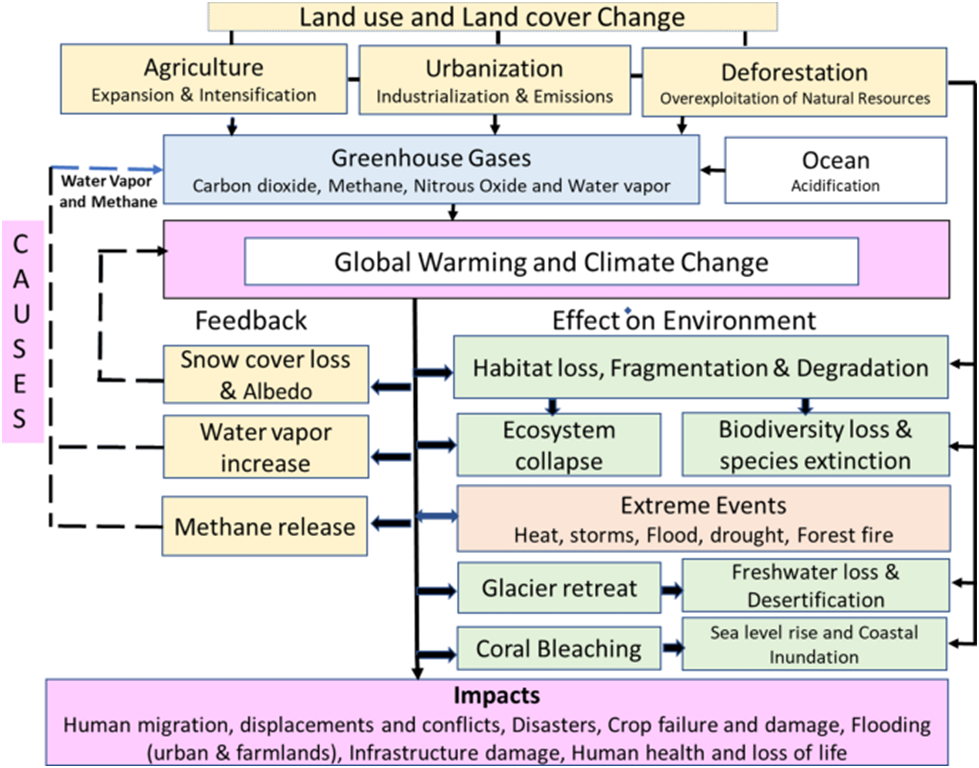
Land use and land cover changes have been occurring at an unprecedented rate in recent decades, driven primarily by human activities such as urbanization, agricultural expansion, and industrialization. These changes have led to a variety of ecological imbalances, both at the regional and global scales.
One major impact of land use change is the loss of biodiversity. As natural habitats are converted to agricultural or urban areas, many species are displaced or may even become extinct. This has a cascading effect on ecosystems, as species are interconnected and depend on each other for survival. Additionally, the introduction of non-native species into new areas can disrupt ecological balance and cause further damage.
Land use change can also contribute to climate change, as it affects the carbon cycle. Deforestation, for example, can release large amounts of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, contributing to the greenhouse effect and global warming. In addition, land use change can alter local weather patterns and lead to changes in precipitation and temperature.
The loss of natural vegetation due to land use change can also lead to soil erosion and decreased soil fertility. This can have serious impacts on agricultural productivity and food security, particularly in areas where subsistence farming is common.
Finally, land use change can have social and economic impacts as well. It can displace indigenous communities and disrupt traditional ways of life, and may also lead to conflicts over land rights and natural resources.
In summary, the sequential changes in land use and land cover have brought global and regional ecological changes and imbalances, affecting biodiversity, climate, soil, food security, and socio-economic systems. It is crucial to prioritize sustainable land use practices and conservation efforts to mitigate these impacts and ensure a more sustainable future.
