
QUES . Examine the scope of the food processing industries in India. Elaborate the measures taken by the government in the food processing industries for generating employment opportunities. Answer in 250 words.15 marks. UPSC MAINS 2025. GS PAPER 3
HINTS:
India’s food processing sector, a brawny pillar of the Indian economy, has been booming in recent years. Holding a place among the largest food processing industries in the world, it is responsible for a significant portion – about 32 per cent – of India’s overall food market.
Must read: Prospects of food processing industry in India
Driven by the high-value processing of various agricultural products, increased urbanization, rising disposable incomes, the rise of nuclear families, and the demand for convenient food, India’s food processing industry is expected to reach a staggering $ 535 billion by 2026.
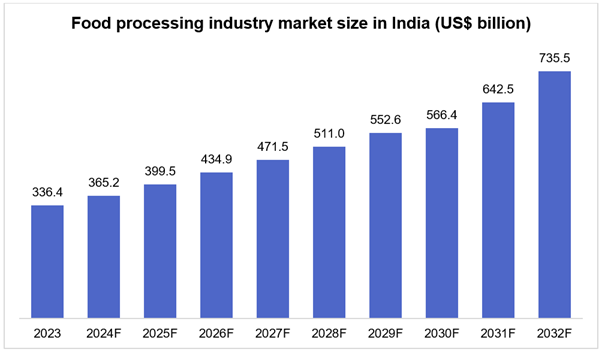
Scope of Food Processing Industries in India
Contribution to GVA and industry: As of 2024, food processing contributes around 8.80% and 8.39% of Gross Value Added (GVA) in Manufacturing and Agriculture respectively and 6% of total industrial investment. The sector contributes 12% to manufacturing GDP and nearly 32% of the national food market, underlining its industrial significance.
Employment Generator: Food processing is a labour-intensive industry with multiplier effects in logistics and retail. It employs 1.93 million in registered and 5.1 million in unregistered units, generating rural and semi-urban livelihoods.
Contribution to Exports: Processed food accounted for 13% of India’s exports and 20.4% of India’s agri-exports worth $49.4 billion in FY 2024–25.
Entrepreneurship Support & Rural Development: Supports FPOs, SHGs, and cooperatives in rural areas enabling rural entrepreneurship and women-led enterprises.
Agricultural value addition: India’s dominance in fruits, vegetables, milk, and cereals offers a vast raw material base to minimise post-harvest losses and expand value chains.
Measures Taken by the Government in the Food Processing Industries for Generating Employment Opportunities
Pradhan Mantri Kisan Sampada Yojana (PMKSY): It supports in setting up modern food processing infrastructure including cold storage, creation of backward and forward linkages, etc. As of June 30, 2025, 1,601 projects were approved under various PMKSY components. Over 7.25 lakh direct and indirect jobs are expected to be generated upon the full completion of projects sanctioned as of June 2025. These projects are projected to benefit over 50.27 lakh farmers.
Pradhan Mantri Formalisation of Micro Food Processing Enterprises (PMFME): To promote the formalization and growth of unorganized micro food processing enterprises in India. The scheme focuses on providing financial aid, technology upgradation, access to common services, and support for branding and marketing to individual micro-enterprises, as well as Farmer Producer Organizations (FPOs), Self Help Groups (SHGs), and Cooperatives.
Production Linked Incentive Scheme for Food Processing Industry (PLISFPI): It aims to create employment opportunities by boosting investments and expanding the food processing industry, supporting Indian brands in the international market. With ₹10,900 crore outlay, expected to generate 2.5 lakh jobs by 2026-27.
Financial Support: Priority Sector Lending status and 100% FDI through automatic route facilitate investment and job creation.
Skill development: Governments are encouraging local youth training tied to the food processing sector which helps them secure formal sources of employment in the agri-business sector.
Challenges in Food Processing Industries
The food processing industry in India faces challenges from a fragmented supply chain, inadequate infrastructure like cold chains and roads, complex regulations, a deficit in the skilled workforce, limited access to finance, low product development and innovation, seasonal availability of raw materials, high concentration of unorganized segments, and inconsistent quality and safety standards, which leads to high post-harvest losses and impacts export competitiveness.
Conclusion
Food processing industry’s multiplier effect on employment, farmer incomes, and export earnings makes it crucial for India’s economic transformation. But to unlock its full potential, structural bottlenecks need to be resolved.
