QUES . Elaborate the scope and significance of supply chain management of agricultural commodities in India. Answer in 150 words.10 marks. UPSC MAINS 2025. GS PAPER 3
HINTS:
The supply chain management of agricultural commodities includes their production, storage, transportation, processing, packaging, distribution, and marketing . Each step has stakeholders that include farmers, processors, transporters and retailers facilitating the movement of various agriculture products from production points to consumers.
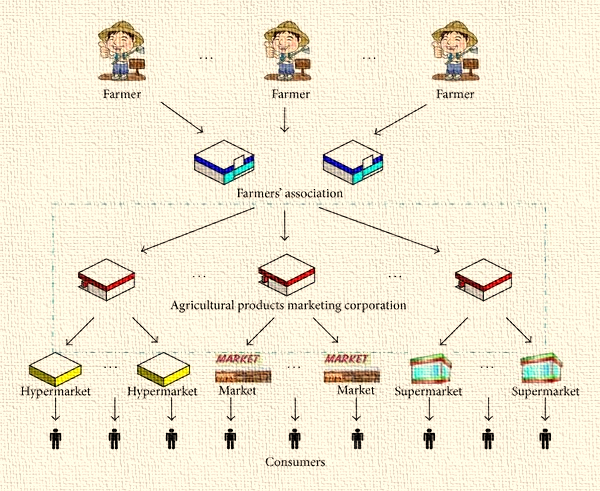
Supply chain management in agriculture provides an efficient means of doing business by reducing waste, standardizing product quality and meeting consumers’ needs from farm to fork.
Scope of Supply Chain Management of Agricultural Commodities in India
Farm Input and Supply Management: Well-timed and streamlined provision of quality seeds, fertilisers, pesticides, machinery and credit delivery through digital platforms and cooperatives.
Post-Harvest Management and storage: Grading and packaging at farm gate and a network of warehouses and cold storages, reduce wastage and preserve quality.
Processing and Value Addition: Agro-processing industries convert raw produce into higher-value commodities, expanding markets and boosting profitability.
Logistics and Transportation: Cold-chain logistics and transportation with refrigerated vehicles ensures timely delivery of perishable goods.
Marketing, Distribution and Retail Linkages: Digital and organised retail chains like APMCs, e-NAM, etc. ensure farmers’ direct access to consumers and link farmers to wider markets.
Precision Farming: Optimizing farming through IoT, AI, and precision farming boosts yield and quality.
Export orientation: Specialised agri-export zones, traceability, and quality certification link Indian farmers to global value chains.
Significance of Supply Chain Management of Agricultural Commodities in India
Reduction of post-harvest losses: By implementing strategies like proper cooling, optimized storage, and temperature-controlled transport, supply chains can significantly extend the shelf life of fruits and vegetables and can prevent spoilage and reduce annual fruit and vegetable waste.
Enhancement of farmer income: Supply chain management (SCM) enhances farmer income by improving market access, reducing intermediaries, empowering farmers with market information, and increasing the value of produce at the farm gate, leading to higher profitability and income.
Empowerment of Small Farmers: SCM empowers small farmers by improving income through direct market access and fairer pricing, reducing post-harvest losses by ensuring efficient handling and storage, and providing access to essential resources like finance and information via technology and farmer collectives.
Stabilisation of consumer prices: Supply chain management stabilizes consumer prices by mitigating disruptions, balancing supply and demand through strategies like optimized inventory management and accurate demand forecasting which prevents price surges and ensures a steady flow of goods at more predictable prices.
Boosting Food Processing: The streamlined flow of commodities from farm to factory through SCM provides processors with a reliable, high-quality input stream, enabling increased production, value addition and the development of competitive processed food products and brands for both domestic and international markets.
Employment and rural development: Supply chain management (SCM) boosts employment by creating jobs in processing, logistics, and retail, while simultaneously supporting rural development by reducing post-harvest losses, increasing farmer incomes and fostering value addition in food processing.
Ensuring Food Security: SCM ensures food security by reducing waste, stabilizing prices, increasing farmer income and improving the availability and accessibility of food.
Promotion of diversification: SCM encourages farmers to shift from traditional crops to more diverse and profitable options by improving market access, creating stable and predictable markets for a wider range of high-value products and reducing risks for farmers.
Global competitiveness: Effective SCM enhances global competitiveness by reducing costs, improving product quality, fostering technological adoption, enabling traceability to meet international standards and creating stronger export markets for agricultural commodities.
Promoting Technological Adoption: SCM promotes technological adoption in agricultural commodities by creating a demand for and facilitating the integration of new technologies, like IoT sensors and blockchain, that enhance transparency, traceability, and efficiency.
Conclusion
Overall, SCM in agriculture is pivotal for enhancing productivity, minimizing costs, and meeting consumer expectations. Strengthening logistics, increasing the use of information technology and governmental support can make agricultural supply chains in India efficient and export competitive
