QUES . “The states in India seem reluctant to empower urban local bodies both functionally as well as financially.” Comment. UPSC 2023 GS MAINS PAPER II, 150 words, 10 Marks
HINTS:
Reluctance of states to empower urban local bodies
֍ According to Niti Aayog, only total 11 states and UTs have devolved the functions to urban local bodies.
֍ State Governments have created parallel structures for the implementation of projects around agriculture, health, and education, which undermines the status of local bodies.
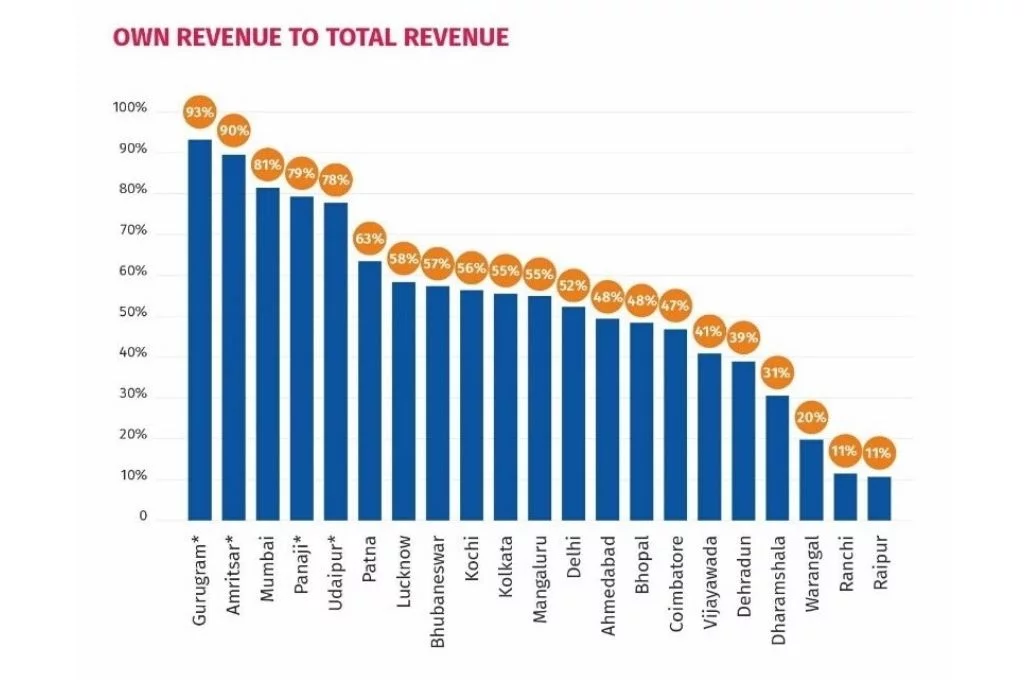
֍ There is little investment in enabling and strengthening urban local governments to raise their own taxes and user charges.
֍ District Planning Committees are non-functional in 9 states and failed to prepare integrated plans in 15
states.
֍ Mayors often have limited powers, rendering them nominal heads without adequate devolution of authority. Thus, Municipal Commissioner often overshadows the Mayor in decision-making processes within urban local bodies.
Must read: How Panchayat Raj Institutions can play their role in grassroots-level planning?
֍ Urban local bodies are heavily reliant on grants from state governments and lack diversified sources of income. Also much of the money given by state governments is inflexible; even in the case of untied grants mandated by the Union and State Finance Commissions, their use is constrained through the imposition of several conditions.
֍ Local government expenditure as a percentage of GDP is only 2%, low compared to 7% in Brazil and 11 % in China.
֍ State Finance Commissions are not established as per Constitutional requirements. Many times the recommendations of State Finance Commissions (SFCs) are not taken seriously.
֍ No dedicated cadre of people or service is working for local self-government.
Must read: Financial suitability of Urban local bodies
֍ The concept of ward committees is just followed in Kerala and in West Bengal Only. In some states, ward committees are not constituted transparently, leading to delays and potential compromises in the democratic process.
֍ In violation of the constitutional mandate of five-yearly elections to local governments, States have often postponed them.
Implications of the reluctance to empower urban local bodies
a) Most of the cities do not have 24X7 water supplies.
b) Nearly, 74 percent households, which are connected to regular piped water supply and about 80 percent of the distribution network requires upgradation, repairs or changes.
c) The sanitation system is also poor in many cities, which are required to be upgraded. The sewage treatment capacity is only 30 percent (as per the Central Pollution Control Board Report).
d) Similarly, the Solid Waste Management system is weak in most of the cities.
e) The scientific disposal of municipal solid waste is around 10 percent only, while the condition of streets, roads, bridges, footpaths, etc. is also not good in most of the cities.
f) Urban local bodies remain dependent on central and state Government.

Measures for making urban local bodies effective

֍ Provide financial autonomy to urban local bodies to enable proper functioning. Alternative options for funding to be explored.
֍ Capacity Building for Self-Governance
֍ Creating a Responsive Institutional Framework
֍ Devolution of Powers and Functions
֍ ICT should be utilised by the Local Governments in process simplification, enhancing transparency and accountability and providing delivery of services through single window.
֍ Audit committees may be constituted by the State government at the district level to exercise oversight regarding the integrity of the financial information.
֍ An Ombudsman like structure should be constituted.
֍ A suitable mechanism to evolve a system of benchmarking on the basis of identified performance indicators may be adopted by each State.
Conclusion
The 74th Constitutional Amendment Act was directed towards the strengthening of grassroot democracy, to empower the people; and to decentralise the governance process. Undoubtedly, there is an array of challenges but they teach us active participation with a clear message for the creation of better communities with diverse cultures.
External link: https://theprint.in/india/governance/30-years-of-law-to-empower-municipalities-why-agencies-remain-toothless-mayors-weak/1669635/
