QUES . Describe the potential marine energy resources with reference to their benefits, harvestability, and environmental impacts.
HINTS:
Ocean energy has the potential to grow fully, fuelling economic growth, reducing carbon footprint and creating jobs not only along the coasts but also inland along its supply chains.
Potential marine energy resources
Wave energy
Wave energy is generated by converting the energy within ocean waves (swells) into electricity. Wave power is produced by the up and down motion of floating devices placed on the surface of the ocean.
The total theoretical potential of wave energy is estimated to be about 40,000 MW.
The first wave energy, project with a capacity of 150 MW, has been set up at Vizhinjam near Trivandrum.
Current Energy
It is very similar to the wind above the oceans. Underwater turbines, large propellers tethered to the seabed, are moved with the marine currents to generate electricity.
Tidal Energy
Energy can be extracted from tides by creating a reservoir or basin behind a barrage and then passing tidal waters through turbines in the barrage to generate electricity.
Like conventional hydroelectric dams, power plants are built on river estuaries and hold back huge amounts of tidal water twice a day which generates electricity when released. India is expected to have 9,000 MW of tidal energy potential.

Tidal power has great potential in areas like the Gulf of Kutch in Gujarat, Gulf of Cambay and Sunderban area of West Bengal where the height of the tide is sufficient for construction and economical functioning of tidal power plants.
A major tidal wave power project costing of Rs.5000 crores, is proposed to be set up in the Gulf of Kutch in Gujarat.
Ocean Thermal Energy
The process of harnessing this energy is called OTEC (Ocean Thermal Energy Conversion). It uses the temperature differences between the surface of the ocean and the depths of about loom to operate a heat engine, which produces electric power.
OTEC has a theoretical potential of 180,000 MW in India subject to suitable technological evolution.
Osmotic Energy
This technique produces energy from the movement of water across a membrane between a saltwater reservoir and fresh water reservoir. It is also called Salinity Gradient Energy.
Benefits of marine energy
Renewable
Protecting the natural world, less carbon footprint, and no soil damage
Plenty and easily accessible
Cut back on reliance on overseas oil giants
Extensive methods for harnessing
Reliable: Wave power is dependable since it is constantly available.
Extremely high levels of energy can be generated: Power density is roughly 30 kilowatts to 40 kilowatts per linear meter of wave length along the shoreline. As we continue to dive deeper, the power density rises to around 100 kW.
Effective energy generation: At the coast, the energy density of waves is around 30–40 kW/m, but at greater depths, the energy density of waves can reach up to 100 kW/m.
Larger in stature: Wave energy devices can be made in a variety of sizes to accommodate the electricity needs of specific regions.
Cost-effective operations and reduced breakdown frequency: In most cases, once we bring up wave energy facilities, they can operate entirely on their own. Since there is no need for fuel, there are fewer negative effects from transportation, and fewer maintenance issues arise when using wave power and energy.
Environmental impacts of marine energy resources
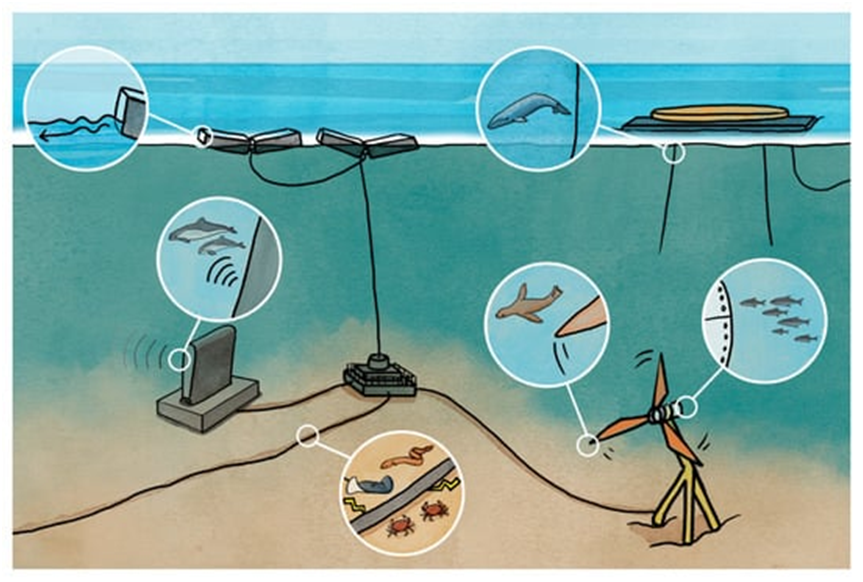
They may be due to:
Impact of underwater noise on animals
Impact of electromagnetic fields on animals
Changes in oceanographic processes, including circulation, wave height, sediment transport patterns, water quality, and marine food webs.
Changes in benthic and pelagic habitats
Encounters with moorings and cables
The risk of a marine mammal or fish colliding with a device
Limitations of marine energy resources
• Deployment is currently limited in our country and already deployed technologies are under utilised.
• Either there is not much research done on the technologies or most are currently at the initial stage of R&D, demonstration and commercialization.
• Uncertainty of the marine environment and commercial scale risks like- corrosion of materials due to the salinity of seawater, offshore maintenance difficulties, the environmental impact on landscapes and the marine ecosystem and competition from other marine activities such as fishing.
• Tremendous cost of producing marine energy is a major downside.
The oceans encompass around 70% of the Earth’s surface. There is no more pervasive or possibly more powerful renewable resource than ocean energy. It’s a resource that can be harnessed without causing harm to the ocean, and the result will be a boon to both the environment and humanity. That’s an objective well worth pursuing.
