QUES . Critically examine plate tectonics theory and explain its relation to the evolution of major landform features on the surface of the earth.
HINTS:
Plate tectonics is a scientific theory that explains the movement of the Earth’s lithosphere (the outermost layer of the Earth) in relation to the underlying asthenosphere. This theory states that the lithosphere is divided into a series of plates that move relative to one another, causing geological phenomena such as earthquakes, volcanic activity, and the formation of mountain ranges and ocean basins.
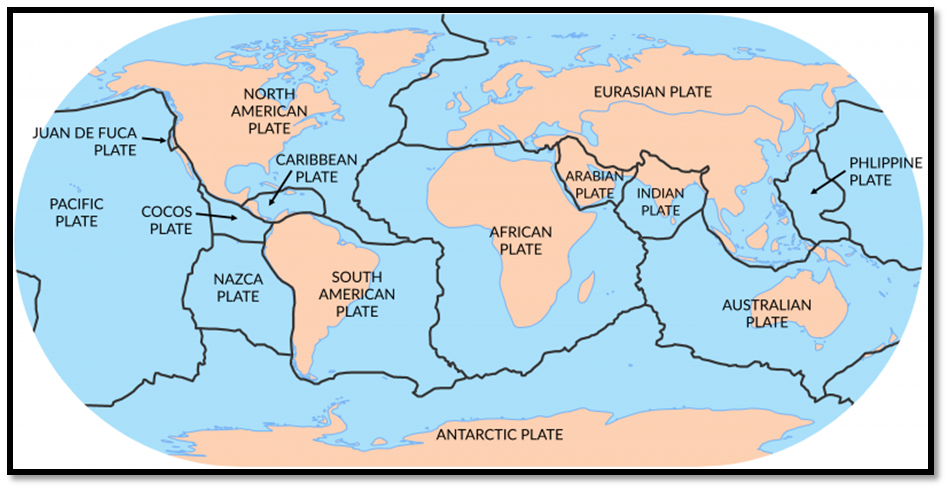
The theory of plate tectonics has been extensively researched and widely accepted by the scientific community since it was first proposed in the 1960s. It has provided a framework for understanding the formation and movement of the Earth’s crust, and it has been instrumental in explaining the evolution of major landform features on the surface of the Earth.
The movement of the tectonic plates can create a variety of geological features on the Earth’s surface. For example, when two plates move towards each other, one plate may be forced under the other in a process called subduction. This can result in the formation of mountain ranges, such as the Andes in South America and the Himalayas in Asia.
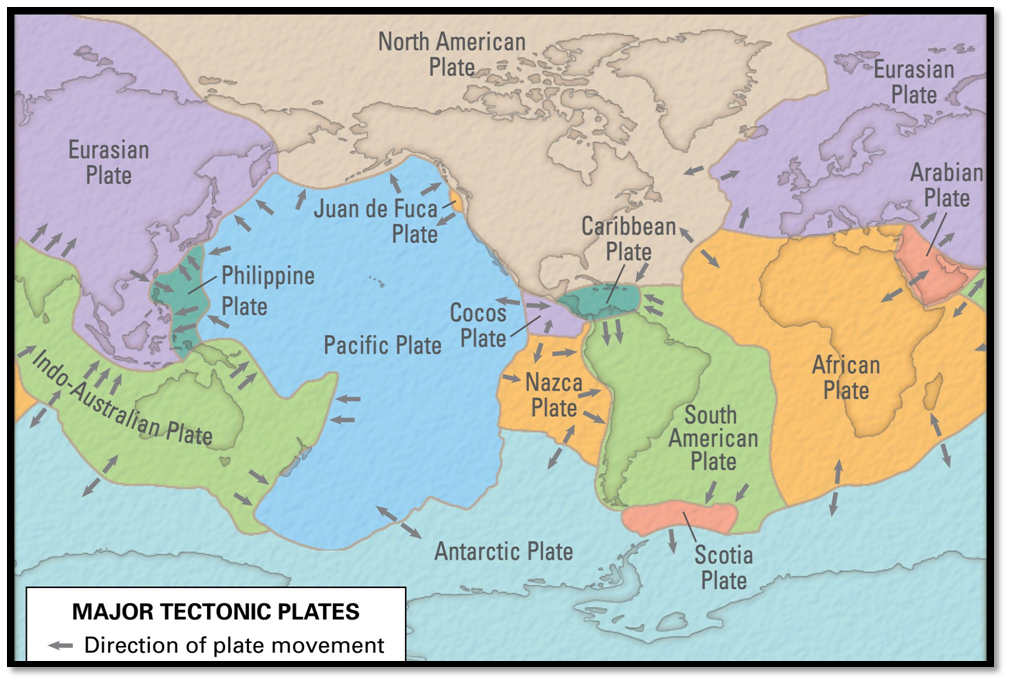
When plates move apart, new crust is formed at mid-ocean ridges, where magma rises to the surface and solidifies, creating a new oceanic crust. As this process continues, the newly formed crust moves away from the ridge and cools, creating a new ocean basin. The Mid-Atlantic Ridge is an example of a mid-ocean ridge, and the Atlantic Ocean is an example of an ocean basin that has formed in this way.
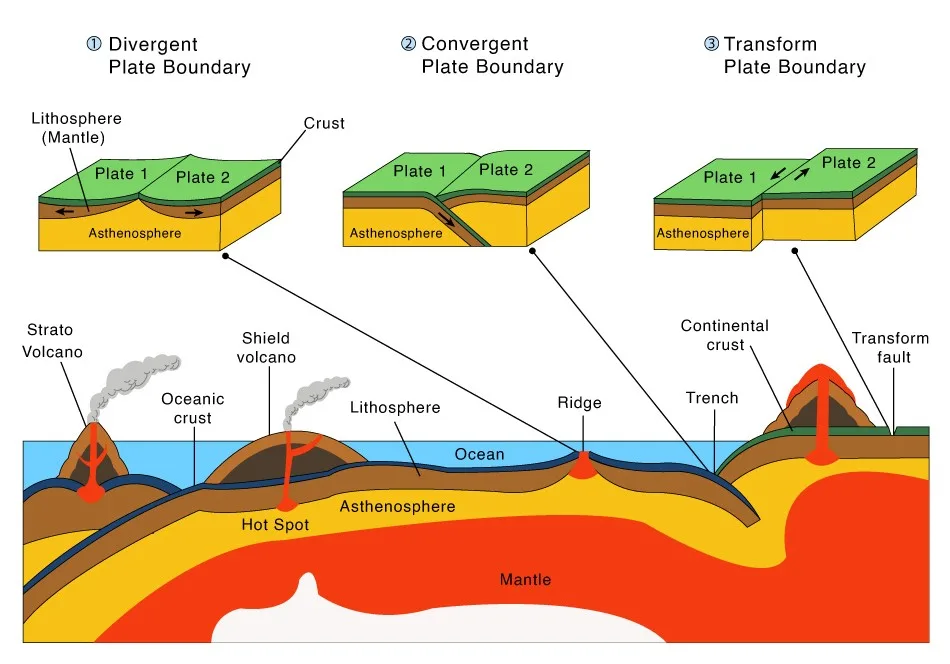
The movement of plates can also cause earthquakes and volcanic eruptions. Earthquakes occur when the plates move past each other or when one plate is forced under another. Volcanic eruptions can occur when magma rises to the surface at a subduction zone or at a mid-ocean ridge.
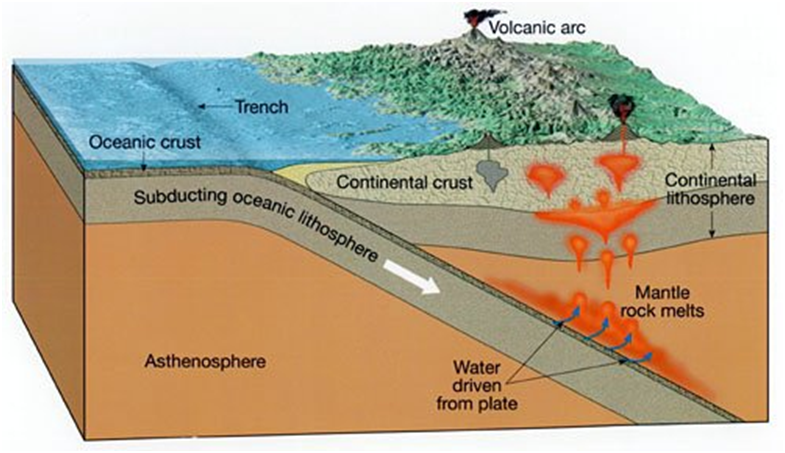
Plate tectonics has played a crucial role in the evolution of the Earth’s surface features. The movement of plates has led to the formation of continents, mountain ranges, and ocean basins. It has also influenced the distribution of flora and fauna by creating barriers and facilitating migrations.
Criticism of plate tectonics theory
While plate tectonics is widely accepted among scientists, there are also some criticisms of the theory.
• Plate tectonics does not fully explain how the plates move.
• The theory has difficulty explaining some geological phenomena, such as the formation of certain types of mountain ranges or the movement of some smaller plates. Some small plates move inside the big Pacific plate, this is not feasible.
• There are some areas, such as the African continent, where plate tectonics does not seem to apply in the same way as it does in other parts of the world.
• Some scientists argue that plate tectonics cannot fully explain the patterns of distribution of certain minerals and geological formations.
• Plate tectonics may not fully explain the formation of some geological features, such as the Hawaiian Islands, which appear to have formed from a mantle plume rather than from plate tectonics.
In conclusion, plate tectonics is a scientific theory that explains the movement of the Earth’s lithosphere and the resulting geological phenomena. It has been instrumental in explaining the evolution of major landform features on the Earth’s surface, such as mountain ranges and ocean basins, and has provided a framework for understanding the distribution of flora and fauna.
