What is Nominal Exchange Rate (NER)?
The nominal exchange rate is the amount of domestic currency needed to purchase foreign currency.
What is Nominal Effective Exchange Rate (NEER)?
The nominal effective exchange rate (NEER) is an unadjusted weighted average rate at which one country’s currency exchanges for a basket of multiple foreign currencies.
How a basket of foreign currencies is chosen?
Every NEER compares one individual currency against a basket of foreign currencies. This basket is chosen based on the domestic country’s most important trading partners as well as other major currencies.
The world’s major currencies are the U.S. dollar, the Euro, the British pound, the Japanese yen, the Australian dollar, the Swiss franc, and the Canadian dollar.
There is no international standard for selecting a basket of currencies.
How the value of foreign currencies in a basket are weighted?
The value of foreign currencies in a basket are weighted according to the value of trade with the domestic country. This could be export or import value, the total value of exports and imports combined or some other measure. https://www.investopedia.com/terms/n/neer.asp
When NEER is said to appreciate ?
If the price of a domestic currency increases against a basket of other currencies inside a floating exchange rate regime, NEER is said to appreciate.
A higher NEER coefficient (above 1) means that the home country’s currency is usually worth more than an imported currency.
When NEER is said to depreciate ?
If the price of a domestic currency decreases against a basket of other currencies inside a floating exchange rate regime , NEER is said to depreciate.
A lower coefficient (below 1) means that the home currency is usually worth less than the imported currency.
What is Real Effective Exchange Rate (REER)?
The Real Effective Exchange Rate (REER) is the weighted average of a country’s currency in relation to an index or basket of other major currencies. The weights are determined by comparing the relative trade balance of a country’s currency against that of each country in the index.
It is used to judge whether the nation’s currency is undervalued or overvalued or, ideally, fairly valued.
The NEER can be adjusted to compensate for the inflation rate in the home country. That adjusted number is the REER.
How an increase in a nation’s REER is an indication of losing its trade competitiveness ?
An increase in a nation’s REER is an indication that its exports are becoming more expensive and its imports are becoming cheaper. This results in losing its trade competitiveness.
What does REER indicates?
REER can be used to measure the equilibrium value of a country’s currency, identify the underlying factors of a country’s trade flow, and analyze the impact that other factors, such as competition and technological changes, have on a country and ultimately on the trade-weighted index.
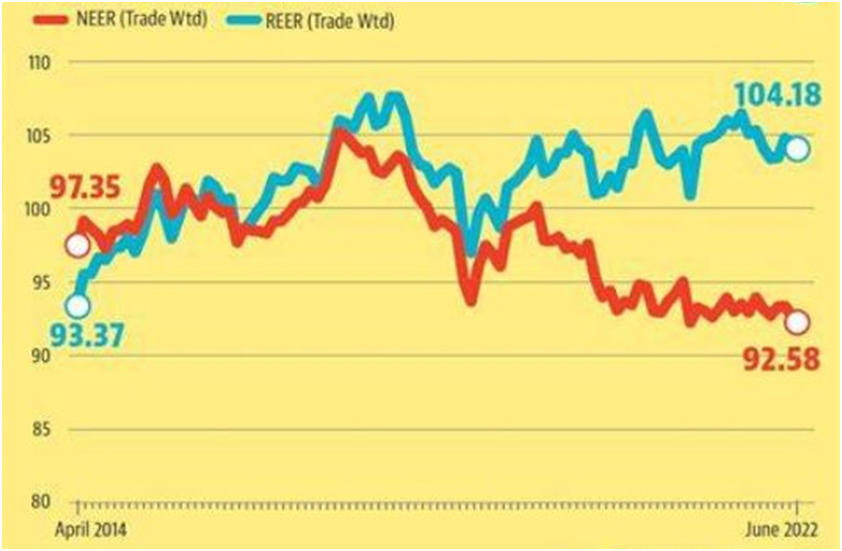
What causes an increasing divergence between NEER and REER?
An increase in domestic inflation relative to inflation in other countries is likely to cause an increasing divergence between NEER and REER.
PRACTICE QUESTIONS
QUES 1 . With reference to the Indian economy, consider the following statements: UPSC 2022
1 . An increase in Nominal Effective Exchange Rate (NEER) indicates the appreciation of rupee.
2 . An increase in the Real Effective Exchange Rate (REER) indicates an improvement in trade
competitiveness.
3 . An increasing trend in domestic inflation relative to inflation in other countries is likely to cause an
increasing divergence between NEER and REER.
Which of the above statements are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Answer: c

Very informative and helpful article 👍👍👍
Good work