What are Jet streams?
Jet streams are narrow bands of strong meandering wind that generally blow from west to east all across the globe. Jet streams are typically continuous over long distances.
A jet stream is a type of wind that forms high in the atmosphere near the altitude of the tropopause.
What is the speed of jet streams?
On average, jet streams move at about 180 km per hour. But dramatic temperature differences between the warm and cool air masses can cause jet streams to move at much higher speeds — 400 km per hour or faster. Higher speeds usually occur in polar jet streams in the winter time.
What are the four primary jet streams?
Earth has four primary jet streams: two polar jet streams, near the north and south poles, and two subtropical jet streams closer to the equator.
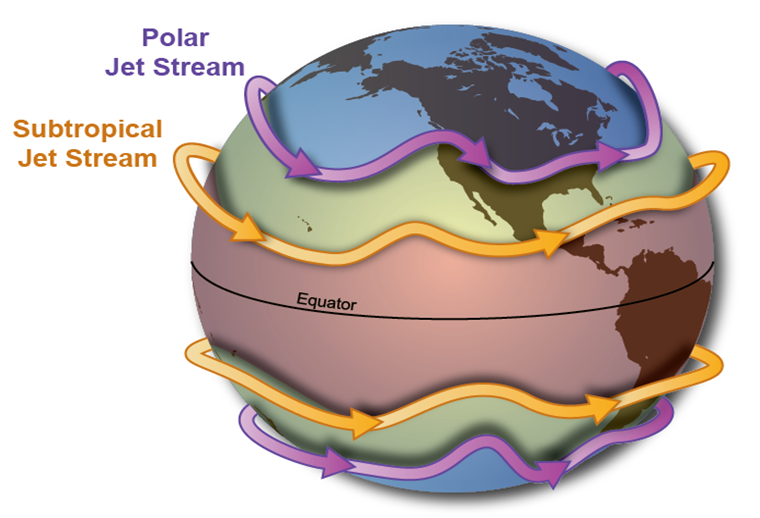
Which jet stream is the strongest?
The strongest jet streams are the polar jets around the polar vortices, at 9–12 km above sea level.
Do other jet streams exist?
Yes, other jet streams also exist. During the Northern Hemisphere summer, easterly jets can form in tropical regions, typically where dry air encounters more humid air at high altitudes.
Low-level jets also are typical of various regions such as the central United States. There are also jet streams in the thermosphere.
What is the position of Polar jet?
The northern hemisphere polar jet flows over the middle to northern latitudes of North America, Europe, and Asia and their intervening oceans, while the southern hemisphere polar jet mostly circles Antarctica, both all year round.
Where do the jet streams form?
The jet streams form near breaks in the tropopause, at the transitions between the polar, Ferrel and Hadley circulation cells, and whose circulation, with the Coriolis force acting on those masses, drives the jet streams.
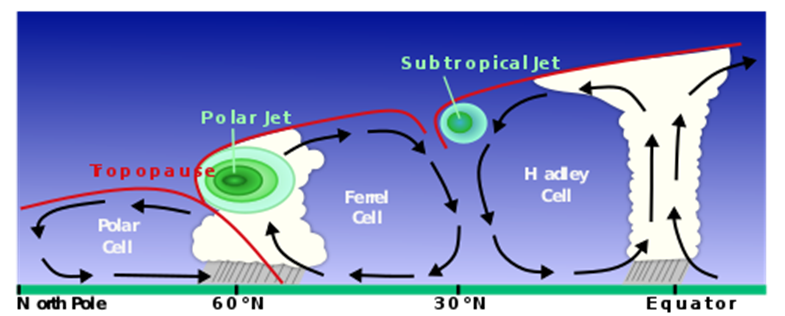
What Causes Jet Streams?
Jet streams are the product of two factors:
(1) The atmospheric heating by solar radiation that produces the large-scale polar, Ferrel, and Hadley circulation cells and
(2) The action of the Coriolis force acting on those moving masses.
Jet streams form when warm air masses meet cold air masses in the atmosphere.
The Sun doesn’t heat the whole Earth evenly. That’s why areas near the equator are hot and areas near the poles are cold.
So when Earth’s warmer air masses meet cooler air masses, the warmer air rises up higher in the atmosphere while cooler air sinks down to replace the warm air. This movement creates jet stream.
The jet stream exists largely because of a difference in heat, which in the northern hemisphere means cold air on the northern side of the jet stream and warm air to the south.
What are Rossby waves?
The path of the jet typically has a meandering shape, and these meanders themselves propagate eastward, at lower speeds than that of the actual wind within the flow.
Each large meander, or wave, within the jet stream is known as a Rossby wave (planetary wave). Rossby waves are caused by changes in the Coriolis effect with latitude
What is the impact of jet stream on weather?
The jet stream flows high overhead and causes changes in the wind and pressure at that level. This affects lower atmosphere nearer the surface, such as areas of high and low pressure, and therefore helps shape the weather we see.
Sometimes, like in a fast-moving river, the jet stream’s movement is very straight and smooth. However, its movement can buckle and loop, like a river’s meander. This will slow things up, making areas of low pressure move less predictably.
What is the impact of jet stream on storms and low pressure systems?
The jet stream can change the strength of an area of low pressure. It acts a bit like a vacuum cleaner, sucking air out of the top and causing it to become more intense, lowering the pressure system. The lower the pressure within a system, generally the stronger the wind, and more stormy the result.
On the other hand, a slower, more buckled jet stream can cause areas of higher pressure to take charge, which typically brings less stormy weather, light winds and dry skies.
Jet streams typically move storms and other weather systems from west to east.
What is the impact of seasons on jet streams?
The seasons also affect the position of the jet stream. In winter, there is more of a temperature difference between the equator and poles, so the jet stream is stronger. The reverse is true in summer, where there tends to be a smaller temperature difference.
How heat dome is linked with jet streams?
Refer https://fotisedu.com/what-is-a-heat-dome/
External link: https://www.noaa.gov/jetstream/global/jet-stream
PRACTICE QUESTIONS
QUES . Consider the following statements: UPSC 2020
1 . Jet streams occur in the Northern Hemisphere only.
2 . Only some cyclones develop an eye.
3 . The temperature inside the eye of a cyclone is nearly 10°C lesser than that of the surroundings.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 2 only
(d) 1 and 3 only
Ans (c) EXPLANATION: Statement 1 is not correct: Jet streams occur in both the Northern and Southern Hemispheres. Statement 2 is correct: The eye is an area of calm weather in the center of strong tropical cyclones. The cyclone’s lowest barometric pressure occurs in the eye. It is usually circular and ranges between 30 and 65 km in diameter. In case of a cyclone it is the place where all the winds coming inside in a spiral motion converge. In an anticyclone it is the part from where all winds move out from. Statement 3 is not correct: The eye is the region of lowest surface pressure and warmest temperatures aloft . The eye temperature may be 10°C warmer or more at an altitude of 12 km than the surrounding environment, but only 0-2°C warmer at the surface in the tropical cyclone.
