QUES . Discuss the importance of solar energy in the future economic development of India.
HINTS:

Solar power status in India:
With about 300 clear and sunny days in a year, the calculated solar energy incidence on India’s land area is about 5,000 trillion kilowatt-hours (kWh) per year (or 5 EWh/yr). The solar energy available in a single year exceeds the possible energy output of all of the fossil fuel energy reserves in India.
Indian climate is a tropical climate and the tropic of cancer (23.5 degrees North latitude) passes near the middle of India, which is why India has huge potential for solar energy. India’s solar power installed capacity was 123.13 GW as in August 2025.
The International Solar Alliance (ISA), proposed by India as a founder member, is headquartered in India. India has also put forward the concept of “One Sun One World One Grid” and “World Solar Bank” to harness abundant solar power on a global scale.
India is a country with a rapidly growing population, fast-paced urbanization, and increasing demand for energy. However, its traditional energy sources, such as coal and oil, are becoming increasingly scarce and environmentally damaging. This has led to a growing interest in renewable energy, particularly solar energy. Solar energy is key for the future economic development of India.
Importance of solar energy in the future economic development of India
Solar energy is a clean and environmentally friendly source of energy that produces no greenhouse gas emissions. This makes it an ideal energy source for India, as it can help reduce the country’s carbon footprint and mitigate the impacts of climate change.
Solar energy is also cost-effective and provides a reliable source of power, especially in rural areas where access to traditional energy sources is limited. It can help to reduce the country’s dependence on imported oil, which is becoming increasingly expensive and create job opportunities in the renewable energy sector.
Solar energy can provide energy to remote and isolated areas, where access to traditional energy sources is limited. This can help to improve the standard of living in these areas and provide a source of energy for essential services, such as healthcare and education.
Installation of solar energy in rural areas would minimize the dependence of rural houses on firewood, dung cake, kerosene, and diesel. Animal dung will be used as manure for agriculture.
Expansion of Solar energy can improve the quality of millions of the Indian population. It will also generate employment.
Solar cells require very little maintenance, it is not dangerous to use, and they can be set up in remote and inaccessible Hamlet areas.
Degraded lands are generally used for solar parks, in this way it will help in land-use efficiency.
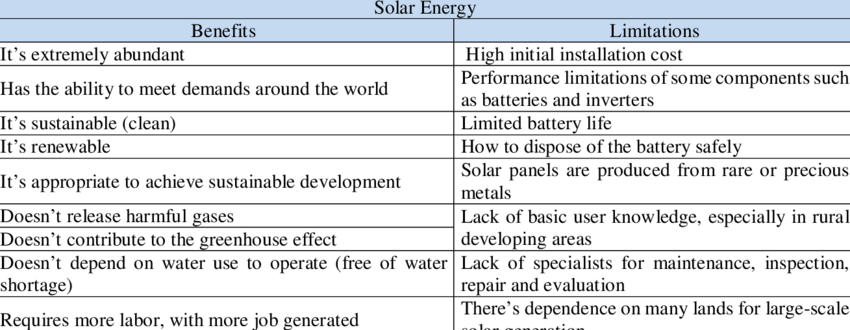
Limitation of Solar Energy
High Cost of Solar Panels: Despite decreases in the cost of solar panels over the past ten years, a complete solar installation still requires significant investment.
Sunlight Dependent: Without sunlight, a system reliant on solar energy cannot produce power. This can pose a problem for consumers in areas with less-than-ideal levels of sun exposure or poor weather.
Space Constraints: Solar panels and the associated wiring take up space. Depending on the number of solar panels needed, finding enough space with adequate exposure can be difficult, especially in less-spacious residential areas.
Solar Energy Storage is Expensive: Since solar batteries store the excess energy generated by your solar panels, they are essential to your solar panel system. However, they can be costly depending on the type and size of the battery.
Environmental Impact of Manufacturing: The production of solar technology has its environmental downsides, as the mining of materials and manufacturing of solar panels creates a considerable amount of greenhouse gas.
Difficulty With Relocation: Uninstalling a solar system and moving it can be difficult, time-consuming and expensive.
Scarcity of Materials: Sunlight may be unlimited, but the materials required to manufacture solar technology are not. The availability of the raw materials required to produce solar products may not be sufficient to meet future demand and the options for mining these materials can have a significant environmental impact. For example, silicon is abundant in nature but special-grade silicon is limited in nature.
Disposal or Recycling Options: Solar technology contains some of the same environmentally-harmful substances in many consumer and industrial electronics, so proper disposal is critical. At present, recycling options for solar panels remain limited.
