
QUES . How does e-Technology help farmers in production and marketing of agricultural produce? Explain it. UPSC 2023 GS MAINS PAPER III , 150 words, 10 Marks
HINTS:
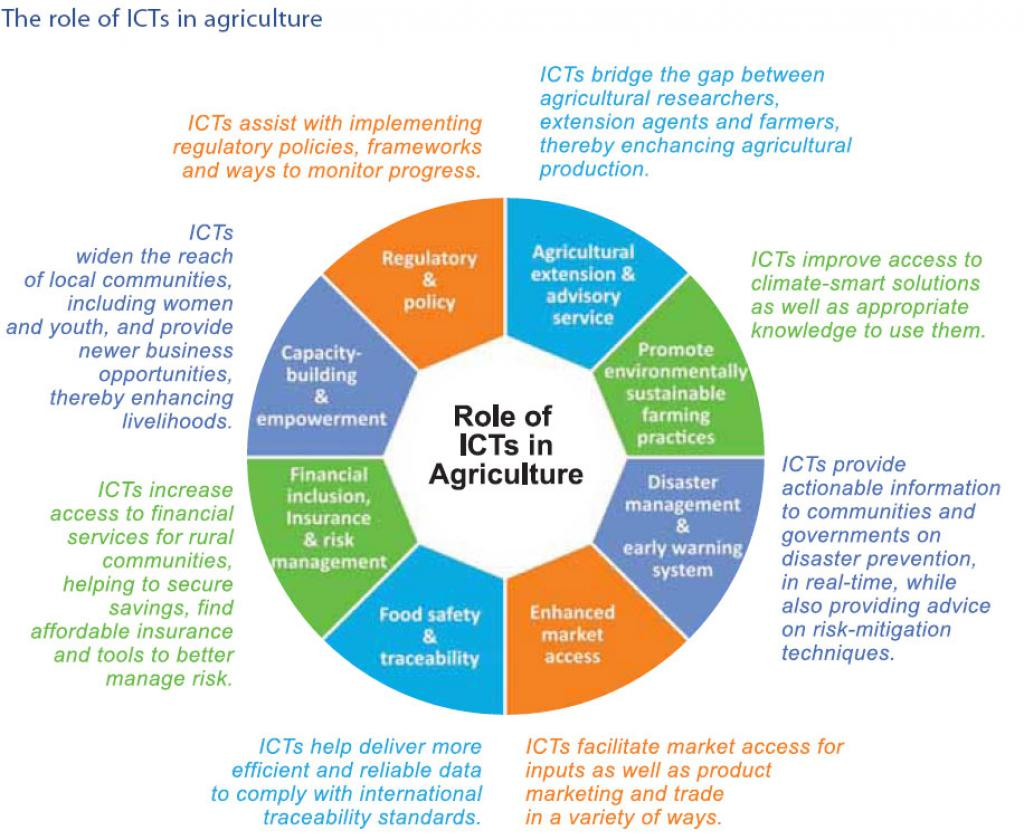
e-technology is transforming Indian agriculture by offering the farmers information, markets, financial services, etc. and thus enhancing productivity, reducing costs, and bolstering food security.
Role of e-Technology in production
Facilitate physical delivery of inputs such as seeds, fertilizers etc. through online platforms. Example :
BharatRohan . Using drones, BharatRohan has been offering services such as plant health status, nutrient management, pest and disease management, soil testing, water management, weather advisory, acreage estimation and market linkage among others to farmer producer organisations.
Environmental Monitoring: Can help reduce pesticide use and minimise soil erosion via real time monitoring.
Increased Mechanization through Custom hiring centres and apps such as Gold Farm. Karnataka based Gold Farm is an Agri-Tech start-up offering a mobile app-based tractor booking platform for farmers in India. They also provide solar water pumps for farmers working in power deficit regions in India.
Agricultural extension services: Providing access to agricultural crop information, new seed varieties etc.
Precision agriculture: According to a report by the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR), precision agriculture can help farmers to increase their yields by up to 20% and reduce their input costs by up to 10%.
Information on what crop to grow, what variety of seed to buy, when to sow, and what best practices to adopt. Example : Kisan Suvidha App. The app is engineered to provide all information at a common place that a farmer or agriculture stakeholder in agriculture sector may require. The app has very simple interface with focus on providing information on six essential areas of farming:-Weather details; Dealers; Market Price; Plant Protection; Agro Advisory and Kisan Call Centre (KCC).
Monitoring of crops: Farmers can deploy drones for continuous and real time monitoring of all types of pest attacks, hailstorms.
Facilitate easier access to Loans through Digital India Land Records Modernization Programme. Example
Karnataka’s Bhoomi Project.
Optimally utilize resources such as water and fertilizers through AI, IoT etc. Example : FASAL (Forecasting Agricultural output using Space,Agro-meteorology and Land based observations). Also farmers can use soil moisture sensors to automatically turn irrigation systems on and off when needed. This can help counter the declining groundwater level.
Enhanced coverage and effectiveness of Government’s schemes. Example : DBT for PM KISAN, Karnataka’s FRUITS (Farmer Registration and Unified beneficiary InformaTion System) Platform.
Role of e-Technology in marketing
E-commerce can provide farmers with direct access to consumers hence fetching higher price. Example : e-NAM.
Through digital platforms and social media, farmers can promote their products directly to consumers, restaurants, and retailers.
Elimination of middlemen through initiatives such as Ninjacart and ITC’s e-choupal.
Global market access: getting to know the trends of international prices, international market regulations and certifications.
Facilitate inverse fork-to-farm strategy to enable farmers to grow crops according to their demand
Ex: AGMARKNET.
e-technology holds the promise to transform Indian agriculture by addressing major farmer challenges in production and marketing. Utilizing digital tools, farmers can increase productivity, cut costs, and tap into new markets, uplifting their lives and ensuring national food security.
