QUES . Groundwater contamination in the fast expanding urban landscape of India appears to have become a major public health issue. Discuss.
HINTS:
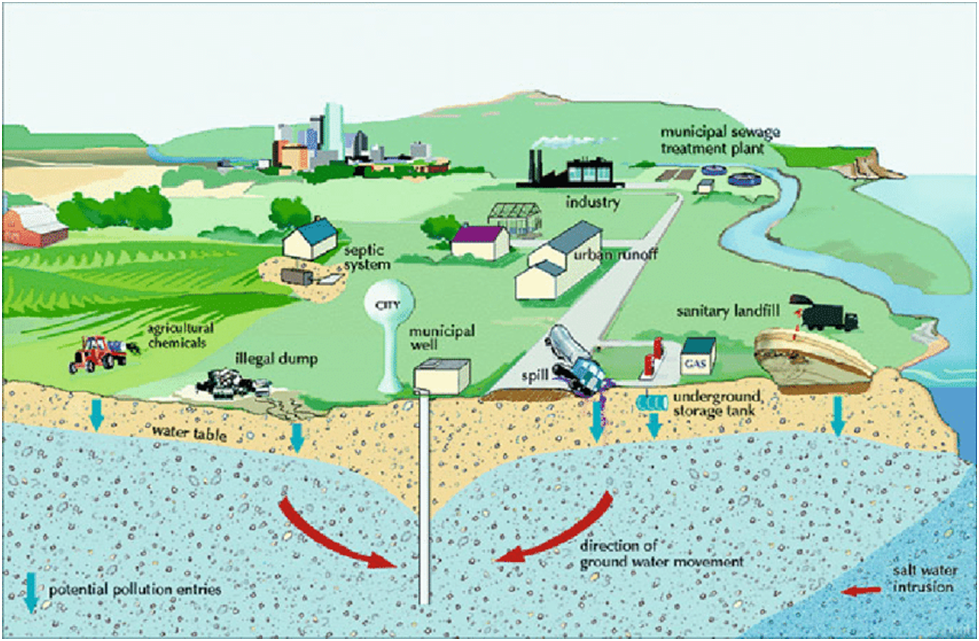
Groundwater contamination has indeed become a significant public health issue in India, especially in the rapidly expanding urban landscape. India is the world’s second-most populous country, and with rapid urbanization, the pressure on natural resources, including groundwater, has increased dramatically. Unfortunately, groundwater contamination is widespread, and the situation is getting worse day by day.
Several factors contribute to groundwater contamination in urban areas in India. One of the most significant factors is the improper disposal of solid and liquid waste, including industrial waste, which seeps into the groundwater and pollutes it. The lack of proper sewage treatment facilities is another major contributor to groundwater pollution. A vast majority of India’s urban areas do not have adequate wastewater treatment facilities, and untreated sewage is dumped into open drains, which eventually find their way into the groundwater.
Additionally, overuse and depletion of groundwater resources also exacerbate the contamination issue. As the population continues to grow, the demand for water increases, and people resort to drilling deeper and deeper wells. This practice, coupled with inadequate regulatory mechanisms, often results in groundwater exploitation and contamination.
The impact of groundwater contamination on public health is alarming. Contaminated groundwater can cause a range of illnesses, from gastrointestinal infections to cancer. It can also lead to long-term health issues such as kidney damage and neurological disorders. The most vulnerable to groundwater contamination are children, pregnant women, and the elderly.
In conclusion, groundwater contamination is a severe public health issue in India’s fast-expanding urban landscape. The problem is complex, and addressing it requires significant efforts from both the government and citizens. Effective measures such as proper disposal of waste, improved sewage treatment facilities, and sustainable groundwater management policies can go a long way in addressing this issue and protecting public health.
