QUES . Discuss the emergence of linguistic regions and states in India.
HINTS:
India is a country with a diverse linguistic landscape, with over 19,500 languages and dialects spoken across its states and regions. The emergence of linguistic regions and states in India can be traced back to the country’s colonial history, post-independence political movements, and constitutional provisions.
During the British colonial period, the British East India Company introduced English as the official language for administrative purposes. This led to the marginalization of Indian languages and the promotion of English as the language of education and governance. As a result, regional linguistic identities began to emerge in the 19th and 20th centuries as Indians sought to reclaim their linguistic heritage.
The Indian independence movement was also a catalyst for linguistic nationalism. Leaders such as Mahatma Gandhi and Jawaharlal Nehru recognized the importance of linguistic diversity and advocated for the preservation and promotion of regional languages. Post-independence, several linguistic movements emerged, demanding the recognition of their language as the official language of their state.
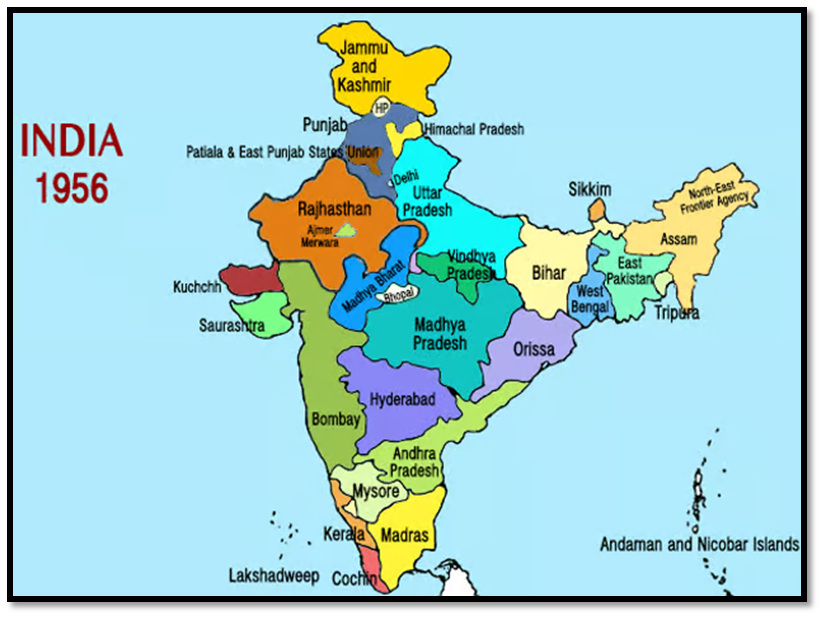
The Constitution of India, adopted in 1950, recognized the importance of linguistic diversity and included provisions for the protection and promotion of regional languages. The creation of linguistic states began in 1953 with the formation of Andhra Pradesh, which was followed by the creation of several other states, such as Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, and Maharashtra. These states were created on the basis of linguistic identity, with each state having its official language.
The emergence of linguistic regions and states has played a crucial role in preserving and promoting linguistic diversity in India. It has also contributed to the development of literature, culture, and education in regional languages. However, linguistic divisions have also led to political tensions and conflicts, particularly in states where there are multiple linguistic groups.
In conclusion, the emergence of linguistic regions and states in India can be traced back to colonial history, post-independence political movements, and constitutional provisions. While it has helped to preserve linguistic diversity and promote regional languages, it has also led to political tensions and conflicts.
