QUES . Define ecosystem and describe briefly its various components
HINTS:
An ecosystem is a complex, interconnected community of living organisms (biotic) and their physical environment (abiotic) within a defined geographical area.
Ecosystems can vary in size, from small microcosms like a pond to vast biomes like a rainforest. They encompass the interactions and relationships between organisms and their surroundings, including the exchange of energy, nutrients, and matter.
Components of an Ecosystem
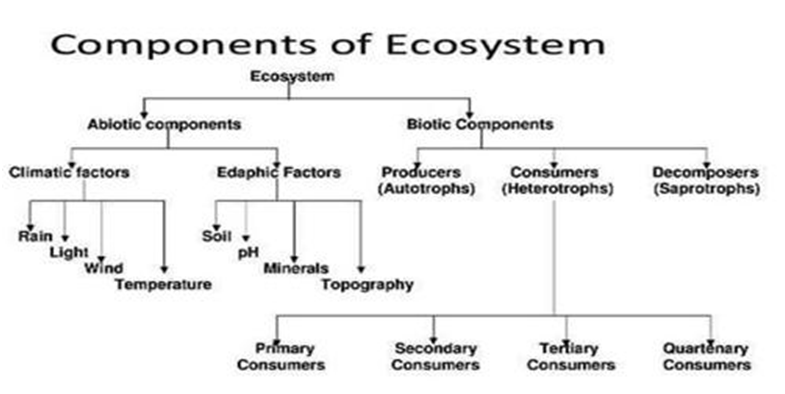
Ecosystems consist of several key components:
1 . Abiotic Components: The Physical Environment
This includes non-living factors such as climate, temperature, precipitation, soil, sunlight, topography, and water availability. These factors shape the physical conditions of the ecosystem.
2 . Biotic Components:
• Producers (Autotrophs): Producers are typically plants, algae, and some bacteria that capture energy from sunlight (photosynthesis) or chemicals (chemosynthesis) to convert it into organic compounds, forming the base of the food chain.
• Consumers (Heterotrophs): Consumers are organisms that rely on other organisms for food. They can be herbivores (eating plants), carnivores (eating other animals), or omnivores (eating both plants and animals).
• Decomposers: Decomposers, like bacteria and fungi, break down dead organic matter (detritus) and recycle nutrients back into the ecosystem. They play a crucial role in nutrient cycling.
Predators and Prey: Interactions between predators and prey help regulate population sizes and maintain ecosystem balance.
Energy Flow: Ecosystems rely on the flow of energy, primarily from the sun, through the trophic levels (producer, consumer, decomposer). Energy is transferred as organisms are eaten, and some energy is lost as heat during each transfer.
Nutrient Cycling: Nutrients like carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus cycle through the ecosystem. Decomposers play a central role in breaking down organic matter and releasing nutrients for plants to use.
However, impacts from human activity on land and in the water can influence ecosystems profoundly. Climate change, ocean acidification, permafrost melting, habitat loss, eutrophication, stormwater runoff, air pollution, contaminants, and invasive species are among many problems facing ecosystems.
