QUES . Give a reasoned account of the difference between the sugar industry of North and Peninsular India.
HINTS:
India is the world’s top producer, user, and second-largest exporter of sugar.
Sugar industry is an important agro-based industry that impacts the rural livelihood of about 50 million sugarcane farmers and around 5 lakh workers directly employed in sugar mills. The sugar industry is the second largest agro-based industry in India after cotton.
Localisation of Sugar Industry

Sugar industry in India is based on sugarcane which is a heavy, low value, weight losing and perishable raw material.
Maharashtra is the largest producer of sugar in India, contributing almost 37 per cent of the total national output.
Sugarcane cannot be stored for long as the loss of sucrose content is inevitable.
Besides, it cannot be transported over long distances because any increase in transportation cost would raise the cost of production and the sugarcane may dry up on the way. The introduction of tractor- trolleys, trucks and even railway wagon have increased the distance covered by sugarcane to 70-75 kms. Beyond which the transportation cost would increase exorbitantly. Therefore, the sugar industry is established in areas of sugarcane cultivation.
Difference between the Sugar Industry of Northern and Peninsular India
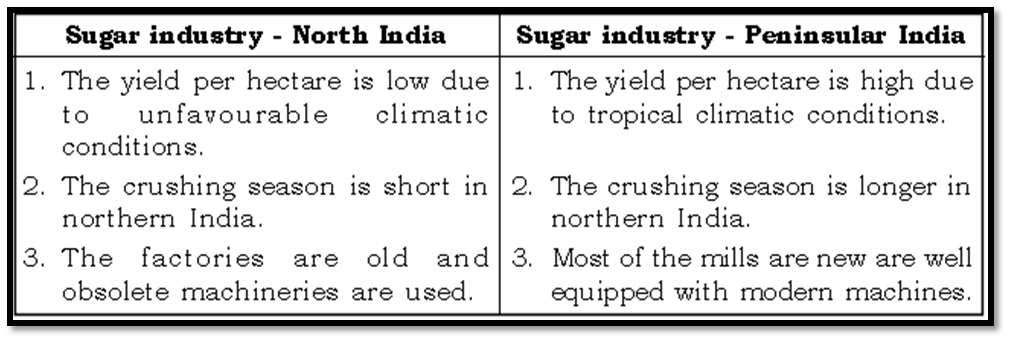
As a result of better conditions prevailing in the peninsular India, the sugar industry is shifting from north India to the peninsular India.
Peninsular India has tropical climate which gives higher yield per unit area as compared to north India.
The sucrose content is also higher in tropical variety of sugarcane in the south.
The crushing season is also much longer in the south than in the north. For example, crushing season is of nearly four months only in the north from November to February, whereas it is of nearly 7-8 months in the south where it starts in October and continues till May and June.
The co-operative sugar mills are better managed in the south than in the north.
Most of the mills in the south are new which are equipped with modern machinery.
The sugarcane industry in India is facing problems like low yield of sugarcane, short crushing season, fluctuating production trends, high cost of production, etc. The Indian Government has taken various initiatives to address the problems of sugar industry like setting up of Indian Institute of Sugar Technology at Kanpur for improving efficiency in the industry. In the year 1982, the sugar development fund was set up with a view to avail loans for modernization of the industry.
