
QUES . Distinguish between ‘care economy’ and ‘monetized economy’. How can care economy be brought into monetized economy through women empowerment? UPSC 2023 GS MAINS PAPER 3, 250 words, 15 marks
HINTS:
Care Economy refers to the often overlooked sphere encompassing unpaid and informal caregiving work traditionally done by women within households, whether it pertains to childcare, elderly care, or household management.
Monetized Economy embodies the structured, formal economy where economic activities are quantified in monetary terms, transactions are tangible, and services and goods are exchanged for money.
Must read: “Empowering women is the key to control population growth.”
What is the difference between Care economy and Monetized economy?
Care economy
֍ The care economy refers to unpaid and caregiving work, often performed by women within households.
֍ It involves child care, elder care, education, healthcare, domestic services, etc.
֍ It ensures well-being of the society, family structures, community cohesion and supports monetised economy.
֍ It is embedded in the welfare of society and communities, with a focus on enhancing the quality of life and fostering social connections.
֍ It is often unpaid or underpaid.
֍ It is informal in nature.
֍ It is not included in GDP. Value is often not measured in monetary terms; focuses on social and emotional well-being.
Must read: Positive and negative effects of globalization on women in India
Monetized economy
֍ The monetized economy primarily revolves around buying and selling goods and services with money as the medium of exchange. It is driven by profit and market forces.
֍ It includes agriculture, manufacturing, banking, IT/ITeS etc.
֍ It ensures production of marketable goods and services. It drives economic growth, income generation, infrastructure development, and technological advancement.
֍ It is frequently driven by the pursuit of profit, competition, and the goal of economic expansion.
֍ It is paid and has market determined wages.
֍ It is formal in nature.
֍ It is included in GDP. Value is directly measured in terms of currency; and monetary compensation.
How can care economy be brought into monetized economy through women empowerment?
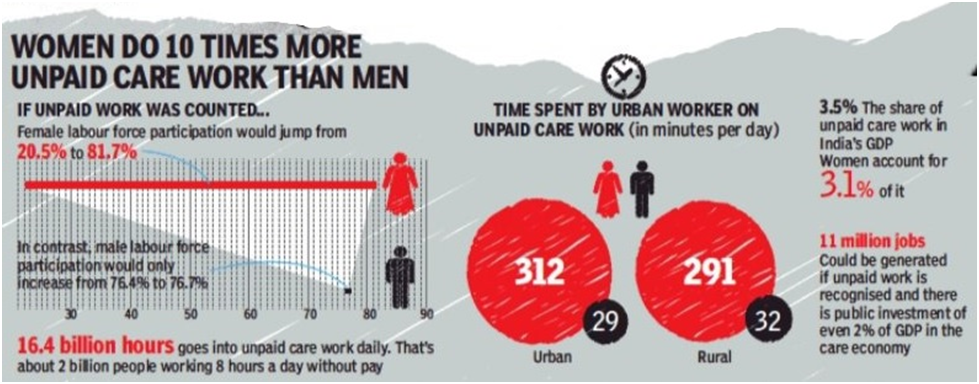
According to the Time Use Survey (TUS) of the National Sample Survey Office (NSSO), Indian women in the working age category of 15 to 60 years spend 7.2 hours on unpaid domestic work compared to 2.8 hours spent by men, indicating they have “time poverty”. Even wage-earning women spend twice the amount of time on unpaid domestic work in comparison to wage-earning men in fulfilling basic needs of the household such as cleaning, preparing meals and caregiving.
Empowering women is essential to integrate the care economy into the monetized economy. It can be done by:
֍ Implement policies that acknowledge and value unpaid care work. The value of care work needs to be recognized and acknowledged. This will enable women who are engaged in care work to be compensated fairly for their services.
֍ Encourage businesses to offer flexible work arrangements that accommodate women’s caregiving responsibilities. For example, Work from home (WFH) culture or part-time opportunities can enable women to balance work and caregiving.
֍ Providing opportunities to participate in the formal labor force through skill development, training, education, and policies that enable work-family balance. For example, programs that train women as healthcare workers, educators, or caregivers can lead to formal employment.
֍ Encourage the formation of self-help groups among women. These groups can engage in economic activities collectively, such as micro-enterprises or agricultural cooperatives. For example, Kudumbashree Programme in Kerala.
֍ Enhance maternity and childcare benefits to support working mothers. Expanding maternity leave provisions and affordable childcare facilities can enable women to return to the workforce.
֍ Encouraging and supporting women to start and grow businesses, especially in sectors related to care services. For example, the government offers “Nari Shakti” grants to empower women entrepreneurs across diverse sectors.
֍ Establishing affordable and high-quality childcare services allows women to participate in the labor force without compromising their care responsibilities. Investing in a combination of childcare infrastructure and parental leave policies will have a higher maternal employment to population ratios.
֍ Reducing gender-based income inequalities. India’s average female daily wage was 59 % of the male wage in 1993-94 and improved to 72 %in 2018-19.
֍ 5R framework– The ILO proposes a 5R framework for decent care work centred around achieving gender equality. It urges on
Recognition : measure and recognize the value of unpaid work.
Reduction : of unpaid care work.
Redistribution : of unpaid care work.
Rewarding : care workers and decent work.
Representation : in social dialogue and collective bargaining.
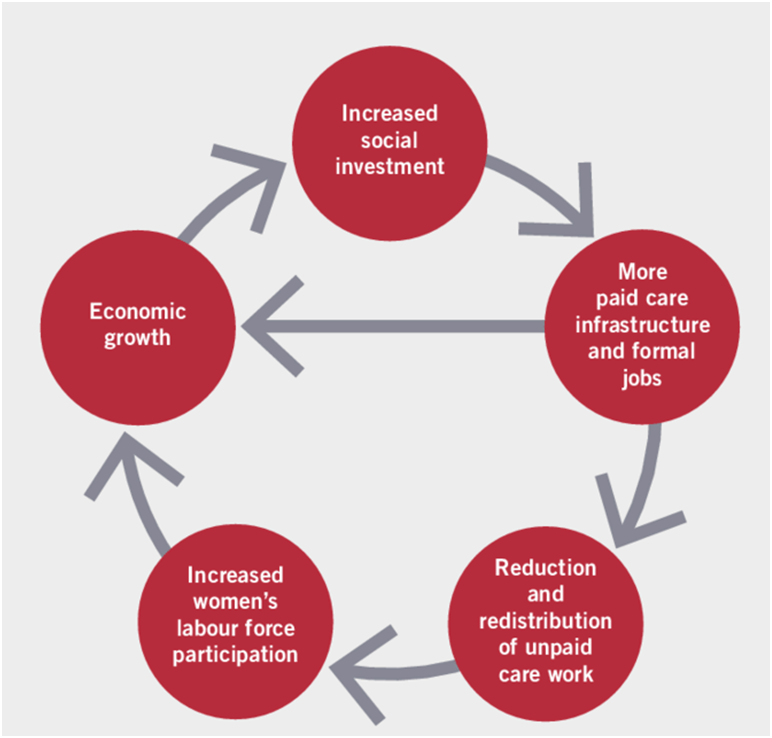
The care economy, while foundational to societal well-being, remains undervalued. Recognizing its significance and empowering women can bridge the gap between care and monetized economies, fostering holistic economic growth.
