Q 1 . With reference to cloning, consider the following statements:
1 . Asexual reproduction is a type of cloning.
2 . Natural clones, also known as identical twins, occur in humans and other mammals.
3 . There can be only gene cloning and therapeutic cloning , reproductive cloning is not possible.
How many of the statements given above are correct?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) All three
(d) None
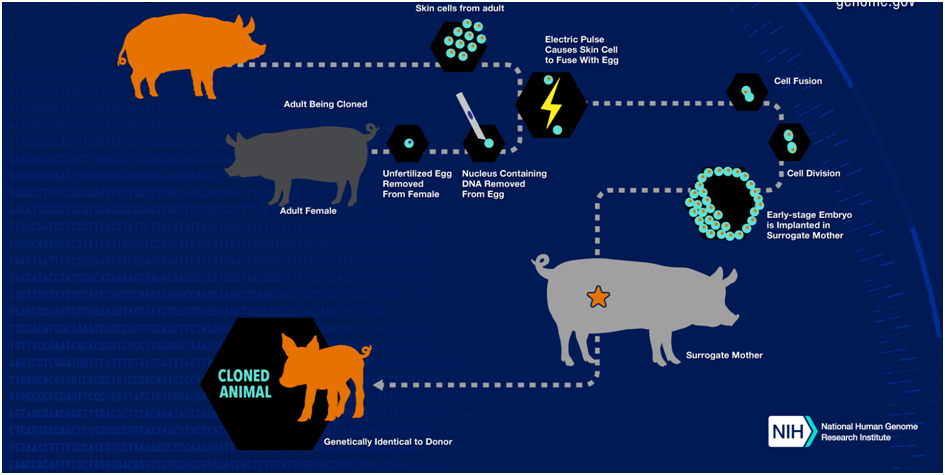
(b) Statement 3 is not correct. Why in news? Recently Ian Wilmut, the British embryologist renowned for leading the team that created Dolly the Sheep, the world’s first cloned mammal from an adult cell, passed away. ■ The term cloning describes a number of different processes that can be used to produce genetically identical copies of a biological entity. The copied material, which has the same genetic makeup as the original, is referred to as a clone. ■ In nature, some plants and single-celled organisms, such as bacteria, produce genetically identical offspring through a process called asexual reproduction. In asexual reproduction, a new individual is generated from a copy of a single cell from the parent organism. ■ Natural clones, also known as identical twins, occur in humans and other mammals. These twins are produced when a fertilized egg splits, creating two or more embryos that carry almost identical DNA. Identical twins have nearly the same genetic makeup as each other, but they are genetically different from either parent. ■ There are three different types of artificial cloning: gene cloning, reproductive cloning and therapeutic cloning. ■ Gene cloning produces copies of genes or segments of DNA. Reproductive cloning produces copies of whole animals. Therapeutic cloning produces embryonic stem cells for experiments aimed at creating tissues to replace injured or diseased tissues.
Q 2 . Consider the following statements :
1 . Thiers’ law : bad money drives out good
2 . Gresham’s law : good money drives out bad
Which among the above statements is/are correct?
(a) Only 1
(b) Only 2
(c) Both 1 & 2
(d) None
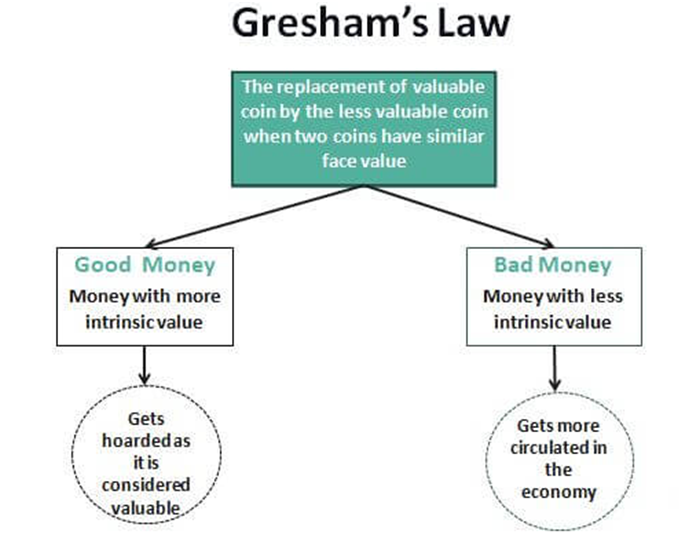
(d) Why in news? Gresham’s law named after English financier Thomas Gresham, came into play most recently during the economic crisis in Sri Lanka last year, during which the Central Bank of Sri Lanka fixed the exchange rate between the Sri Lankan rupee and the U.S. dollar ■ Gresham’s law refers to the dictum that “bad money drives out good.” Gresham’s law comes into play when the exchange rate between two moneys or currencies is fixed by the government at a certain ratio that is different from the market exchange rate. ■ Such price fixing causes the undervalued currency — that is, the currency whose price is fixed at a level below the market rate — to go out of circulation. ■ The overvalued currency, on the other hand, remains in circulation but it does not find enough buyers. ■ It should be noted that the market exchange rate is essentially an equilibrium price at which the supply of a currency is equal to the demand for the currency. Also, the supply of a currency in the market rises as its price rises and falls as its price falls; while, on the other hand, the demand for a currency falls as its price rises and rises as its price falls. ■ So, when the price of a currency is fixed by the government at a level below the market exchange rate, the currency’s supply drops while demand for the currency rises. Thus a price cap can lead to a currency shortage with demand for the currency outpacing supply. ■ EXAMPLE : Imagine you have two coins with the same legal tender face value – say one penny. However, one is made of silver and the other of copper. People will hold onto the silver coins and use just the copper ones for payment. The ‘good’ money (silver) will disappear from circulation, because everybody hoards it, leaving just the ‘bad money’ (copper) in circulation. ■ The phenomenon wherein “good money drives out bad” is called Thiers’ law (named after French politician Adolphe Thiers) and it is seen as a complement to Gresham’s law.
Q 3 . Consider the following statements with respect to “National Strategy for Robotics” (NSR) :
1 . The Ministry of Science and Technology will serve as the nodal agency for robotics, overseeing the “National Strategy for Robotics” through the ‘National Robotics Mission’ (NRM).
2 . According to the World Robotics Report for the year 2022, India ranks 3rd globally in terms of annual industrial installations of robots.
Which among the above statements is/are correct?
(a) Only 1
(b) Only 2
(c) Both 1 & 2
(d) None
(d) ■ Recently, Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) in India has released a draft “National Strategy for Robotics” (NSR) aimed at strengthening the innovation cycle of robotic technology and fostering India’s leadership in robotics by 2030. ■ According to the World Robotics Report for the year 2022, India ranks 10th globally in terms of annual industrial installations of robots. ■ The Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) will serve as the nodal agency for robotics, overseeing the NSR through the ‘National Robotics Mission’ (NRM).
Q 4 . GEOGLAM recently in news is related with:
(a) How to reduce geographical constraints in world trading.
(b) A new world grouping as a successor of NAM.
(c) Global agricultural information for food security.
(d) e Market place for selling of agro commodities.
(c) Why in news? ■ G20 New Delhi Leaders’ Declaration called for strengthening Agricultural Market Information System (AMIS) and Group on Earth Observations Global Agricultural Monitoring (GEOGLAM) to enhance transparency and avoid food price volatility. ■ AMIS, launched in 2011, enhances food market transparency and policy responses for food security. ■ GEOGLAM, with roots in the French G20 Presidency in 2011, offers global agricultural information for market transparency and food security.
Q 5 . With reference to India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEE-EC), consider the following statements:
1 . The Corridor is divided into two Segments – Eastern Corridor connecting India to the Arabian Gulf and Northern Corridor connecting Arabian Gulf to Europe.
2 . India, Saudi Arabia, UAE, France, Germany, Italy, USA and EU are the participants.
3 . The Corridor components include Railway lines, Electricity cable and High-speed data cable.
How many of the statements given above are correct?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) All three
(d) None
(c) Recently on the sidelines of the G20 Summit in New Delhi, an MoU was signed between India, the US, Saudi Arabia, the European Union, the UAE, France, Germany, and Italy to establish the India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEE-EC). ■ Participating Countries : India, Saudi Arabia, UAE, France, Germany, Italy, USA, EU ■ It is part of the Partnership for Rail and Shipping Corridors Global Infrastructure Investment (PGII) and focuses on enhancing global trade and cooperation through critical infrastructure development. ■ Corridor Components include 1 . Railway lines (make trade between India and Europe 40% faster). 2 . Electricity cable and a clean hydrogen pipeline to foster clean energy trade. 3 . High-speed data cable to link innovative digital ecosystems in the world and create business opportunities. ■ Corridor Segments : 1 . Eastern Corridor connecting India to the Arabian Gulf 2 . Northern Corridor connecting Arabian Gulf to Europe ■ The PGII (Partnership for Global Infrastructure Investment) initiative (announced in 2021 during the G7 summit in the UK) is a collaborative effort by G7 countries to fund infrastructure projects in developing nations.
