The atmosphere is composed of gases, water vapour and dust particles.
The composition of the atmosphere is not static. It changes according to the time and place.
The proportion of gases changes in the higher layers of the atmosphere in such a way that oxygen will be
almost in negligible quantity at the height of 120 km.
Similarly, carbon dioxide and water vapour are found only up to 90 km from the surface of the earth.
Gases
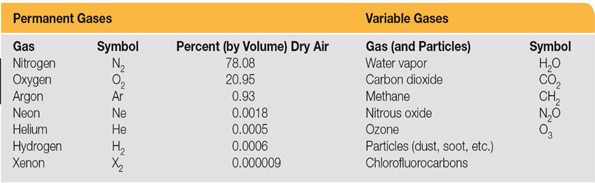
Nitrogen and Oxygen are the two main gases of the atmosphere. 99 percent part of it is made up of these two gases.
Other gases like argon, carbon dioxide, hydrogen, neon, helium etc. form the remaining part of atmosphere.
Gases and their amount (in percentage)
Nitrogen 78.1
Oxygen 20.9
Argon 0.9
Carbon Dioxide 0.03
Hydrogen 0.01
Neon 0.0018
Helium 0.0005
Ozone 0.00006
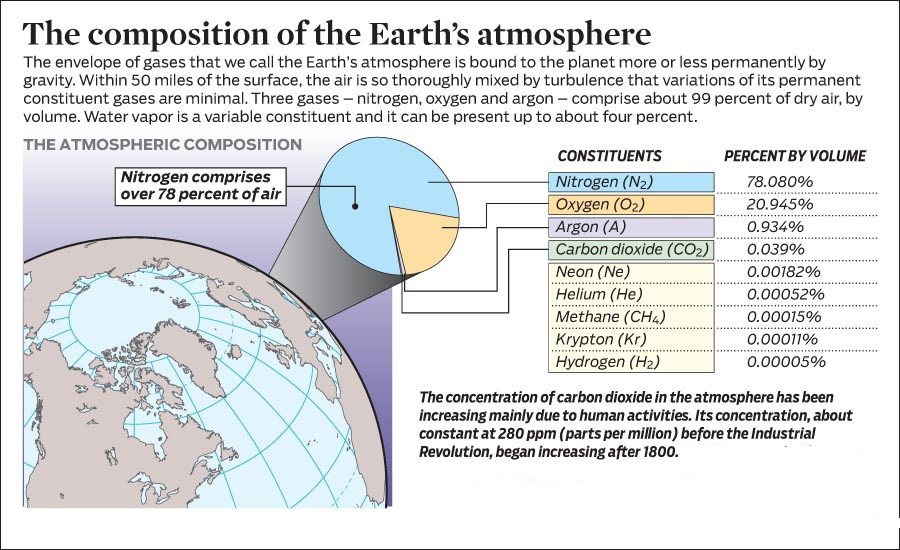
Carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is meteorologically a very important gas as it is transparent to the incoming solar radiation but opaque to the outgoing terrestrial radiation.
It absorbs a part of terrestrial radiation and reflects back some part of it towards the earth’s surface.
It is largely responsible for the green house effect.
The volume of other gases is constant but the volume of carbon dioxide has been rising in the past few decades mainly because of the burning of fossil fuels.
This has also increased the temperature of the air.
Ozone
Ozone is another important component of the atmosphere found between 10 and 50 km above the earth’s surface and acts as a filter and absorbs the ultra-violet rays radiating from the sun and
prevents them from reaching the surface of the earth.
Water Vapour
Water vapour is also a variable gas in the atmosphere, which decreases with altitude.
In the warm and wet tropics, it may account for four per cent of the air by volume, while in the dry and cold areas of desert and polar regions, it may be less than one per cent of the air.
Water vapour also decreases from the equator towards the poles.
It also absorbs parts of the insolation from the sun and preserves the earth’s radiated heat.
It thus, acts like a blanket allowing the earth neither to become too cold nor too hot.
Water vapour also contributes to the stability and instability in the air.
Dust Particles
Atmosphere has a sufficient capacity to keep small solid particles, which may originate from different sources and include sea salts, fine soil, smoke-soot, ash, pollen, dust and disintegrated particles of meteors.
Dust particles are generally concentrated in the lower layers of the atmosphere; yet, convectional air currents may transport them to great heights.
The higher concentration of dust particles is found in subtropical and temperate regions due to dry winds in comparison to equatorial and polar regions.
Dust and salt particles act as hygroscopic nuclei around which water vapour condenses to produce clouds.
Diffusion of light in the atmosphere takes place due to dust particles.
Must read: STRUCTURE OF THE ATMOSPHERE
External link: https://www.noaa.gov/jetstream/atmosphere
PRACTICE QUESTIONS
QUES . With reference to “water vapour”, which of the following statements is/are correct? UPSC 2024
1 . It is a gas, the amount of which decreases with altitude.
2 . Its percentage is maximum at the poles.
Select the answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans (a) Water vapour is a variable gas in the atmosphere, which decreases with altitude. Water vapour decreases from the equator towards the poles.
QUES . Consider the following statements: CDS 2010
1 . Clear sky appears blue due to poor scattering of blue wavelength of visible light.
2 . Red part of light shows more scattering than blue light in the atmosphere.
3 . In the absence of atmosphere, there would be no scattering of light and sky will look black.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct ?
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
(c) Violet and blue lights get scattered more than lights of all other colours by the atmosphere. The sunlight reaching the earth’s atmosphere is scattered in all the directions by gases and particles in air. In the visible spectrum of colours, blue light is scattered the most as its wavelength is the least. Due to this, the sky appears blue.
QUES . As the sunlight passes through the atmosphere, the rays are scattered by tiny particles of dust, pollen, soot and other minute particulate matters present there. However, when we look up, the sky appears blue during mid-day, because CDS 2010
(a) blue light is scattered most
(b) blue light is absorbed most
(c) blue light is reflected most
(d) ultra violet and yellow component of sunlight combine
(a)
QUES . The Sun is observed to be reddish when it is near the horizon, i.e., in the morning and the evening. This is because NDA 2015
(a) red light is least scattered by atmosphere
(b) red light is most scattered by atmosphere
(c) it is the colour of the Sun in the morning and evening
(d) Earth’s atmosphere emits red light
(a) The scattering of light is more when the Sun is near the horizon. As the shorter wavelengths are scattered, only red light is left. As it has the largest wavelength of the seven colours, it is least scattered. Thus the sun appears red during sunrise and sunset.
QUES . A beautiful rainbow on the sky is due to the: NDA 2013
(a) dispersion of sunlight from a wate droplet only.
(b) reflection of sunlight from a wate droplet only.
(c) reflectioin and refraction of sunlight from a water droplet only.
(d) refraction, dispersion and reflection of sunlight from a water droplet.
(d) A rainbow is a natural spectrum appearing in the sky usually after a rain shower. It occurs due to dispersion of sunlight by tiny water droplets, present in the atmosphere. A rainbow is always formed in a direction opposite to that of the Sun to facilitate easy dispersion on sunlight. The water droplets act like small prisms. They refract and disperse the incident sunlight, then reflect it inside the droplet, and finally refract it again when it comes out of the raindrop. Due to the dispersion of light and internal reflection in the droplet, different colors of the rainbow are visible.
QUES . Diffusion of light in the atmosphere takes place due to: UPSC 2003
(a) Carbon dioxide
(b) Dust particles
(c) Helium
(d) Water vapours
(b)
