QUES . Explain the characteristics of ecological succession.
HINTS:
Ecological succession is the process by which an ecosystem undergoes predictable and orderly changes in its composition and structure over time. It occurs in response to environmental disturbances or as part of natural ecological development.
Characteristics of ecological succession:
Directional Change: Ecological succession is a directional process. It involves a sequence of changes in the species composition and abundance within an ecosystem, leading to a more organized and stable community over time.
Primary and Secondary Succession: Ecological succession can be categorized into two main types:
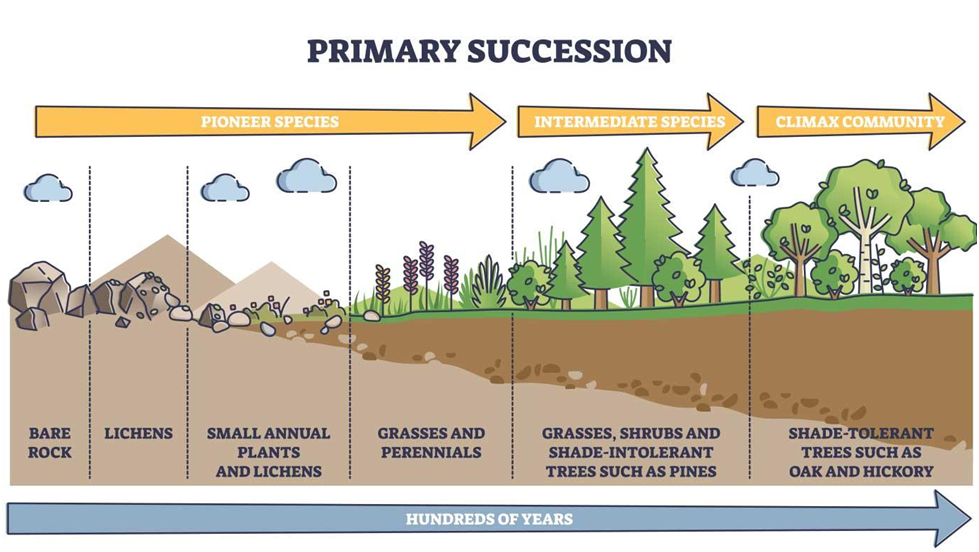
Primary Succession: This occurs in a newly formed or completely barren environment where no soil or life existed before, such as on bare rock or after a volcanic eruption.
Secondary Succession: This occurs in an environment that has experienced a disturbance but still retains its soil and some remnants of its previous biological community. Examples include abandoned agricultural fields or areas recovering from forest fires.
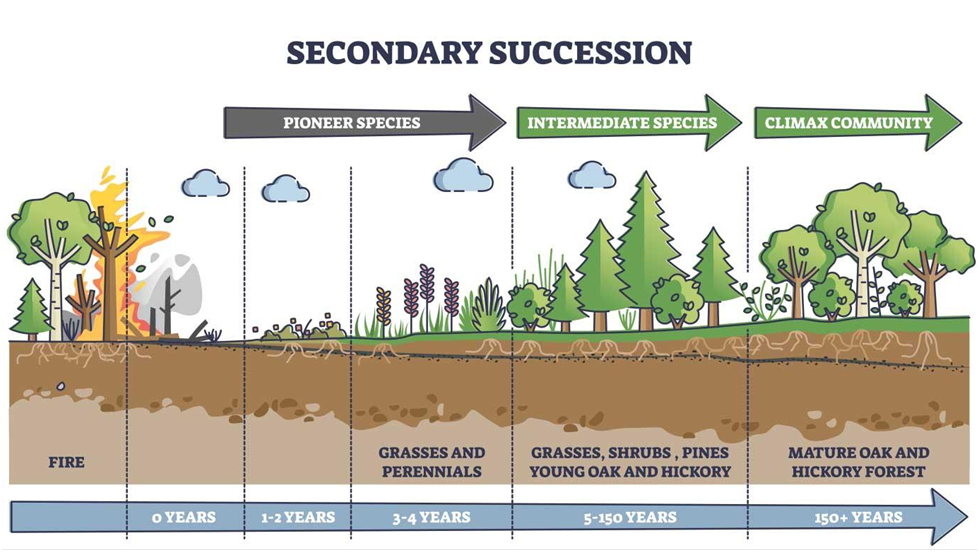
Pioneer Species: In both primary and secondary succession, the process begins with pioneer species. These are the first colonizers of the disturbed or barren area. Pioneer species are often adapted to harsh conditions and play a critical role in preparing the environment for later stages of succession.
Facilitation: As pioneer species establish themselves and modify the environment by adding organic matter, improving soil conditions, or providing shade, they make it more suitable for other, often less hardy species. This process is known as facilitation, and it paves the way for the arrival of new species.
Climax Community: Ecological succession typically progresses through a series of stages, with each stage representing a different community of species. The final stage, called the climax community, represents a relatively stable and self-perpetuating community for the given environmental conditions. It is not always the same in every ecosystem and depends on factors such as climate and soil type.
Disturbance and Resetting: Ecological succession can be disrupted or reset by various disturbances, such as fires, storms, or human activities. Disturbances can return an ecosystem to an earlier stage of succession, where pioneer species once again colonize and initiate the process anew.
Species Diversity: Over time, species diversity tends to increase during succession. As the environment becomes more stable and conditions improve, a greater variety of species can establish and coexist within the ecosystem.
Nutrient Cycling: Nutrient cycling becomes more efficient as succession progresses. Decomposers and nutrient-recycling organisms become established, enhancing the availability of essential nutrients for plant growth.
Ecosystem Services: The ecosystem services provided by the ecosystem, such as soil stabilization, water purification, and habitat provision, tend to improve as succession proceeds and the ecosystem matures.
Time Scale: Ecological succession occurs over a range of time scales, from years to centuries or even millennia, depending on the type of ecosystem and the rate of environmental change.
Human Impact: Human activities, such as agriculture, urbanization, and deforestation, can disrupt natural succession processes and alter ecosystems, sometimes irreversibly. Conservation efforts often aim to restore or protect ecosystems from such disturbances.
Understanding the characteristics of ecological succession is crucial for ecosystem management, conservation, and restoration efforts. It allows scientists and land managers to predict how ecosystems will respond to disturbances and provides insights into the complex interactions among species and the environment.
