QUES . Describe the distribution of black soils in India and their specific use for agriculture.
HINTS:
Black soil or Black Cotton Soil, also known as Regur are mineral soils that are volcanic/ trap lava derivatives. They are found mostly in the Deccan Plateau of India. It is ideal for growing cotton crops that is why it is also called cotton soil.
Origin of black soil or formation of black soil:
They are formed due to the weathering and denudation of indigenous rocks (basalt) or cooling and solidification of lava after volcanic eruption.
Climatic conditions ( for weathering) and parent materials( basalt Igneous rock) are the two important factors for the formation of black soil.
Black soil is a result of weathering of igneous basaltic rocks; it is a sediment of extrusive rock.
Black soil is generally found in the Deccan traps. Deccan trap was formed 66 million years ago.
The thickness or depth of Black soil is around 2000 meters
Distribution of black soil in India:
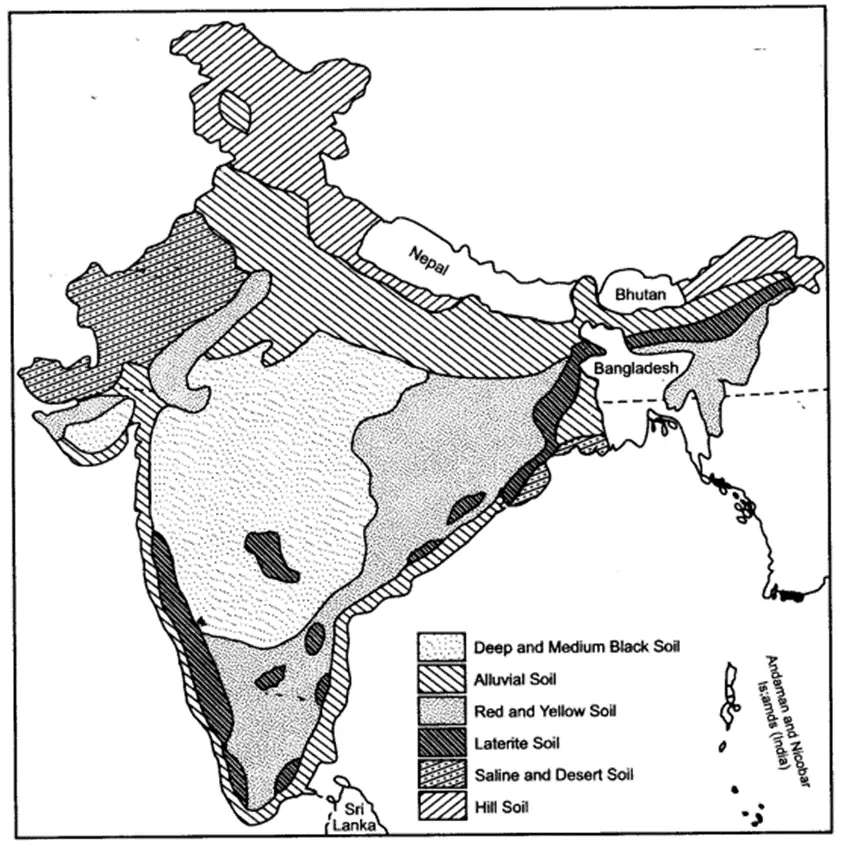
Most of the Deccan trap is covered by black soil. Black soil in India is found in:
Maharashtra’s plateau
Saurashtra region of Gujarat
Part of Madhya Pradesh and Chhattisgarh
Upper parts of Godavari and Krishna valley
Parts of Andhra Pradesh
Northern part of Karnataka and Tamil Nadu
The southeastern part of Rajasthan
Characteristics of black soil:
Major characteristics of Black soil are:
The black colour of these soils has been attributed by some scientists to the presence of a small proportion of titaniferous magnetite or even to iron and black constituents of the parent rock. The black colour of this soil may even be derived from crystalline schists and basic gneisses such as in Tamil Nadu and parts of Andhra Pradesh. Various tints of the black colour such as deep black, medium black, shallow black or even a mixture of red and black may be found in this group of soils.
Black soil is made up of finer clay materials that is why it gets sticky when wet and develop cracks when dry.
As black soil is made up of finer clay materials, it has a high moisture holding capacity.
Black soil is rich in soil nutrients such as: calcium carbonate, magnesium, potash, lime, etc.
Black soil is poor in phosphorous, nitrogen, and humus content.
Black soil develops deep cracks when it dries which helps proper aeration of the soil. It is also called self-ploughed soil.
Black soil gets sticky when wet that is why ploughing is done before monsoon or immediately after the first monsoon shower, otherwise very difficult to plough.
Black soil is very fertile and suitable for diverse variety of crops.
Black soils are generally two types:
(a) Light black soil is found in the higher reaches of the Deccan Trap. which is less fertile.
(b) Deep black soils are found in the lower reaches of the Deccan Trap, and in the upper reaches of the Godavari and Krishna valleys. it is more fertile.
Use of black soil for agriculture
Because of their high fertility and retentivity of moisture, the black soils are widely used for producing several important crops. Some of the major crops grown on the black soils are cotton, wheat, jowar, linseed, Virginia tobacco, castor, sunflower and millets. Rice and sugarcane are equally important where irrigation facilities are available. Large varieties of vegetables and fruits are also successfully grown on the black soils.
