The weight of a column of air contained in a unit area from the mean sea level to the top of the atmosphere is called the atmospheric pressure.
The atmospheric pressure is expressed in units of mb and Pascals. The widely used unit is kilo Pascal written as kPa.
At sea level the average atmospheric pressure is 1,013.2 mb or 1,013.2 kPa.
Due to gravity the air at the surface is denser and hence has higher pressure.
Air pressure is measured with the help of a mercury barometer or the aneroid barometer.
The pressure decreases with height.
At any elevation pressure varies from place to place and its variation is the primary cause of air motion, i.e. wind which moves from high pressure areas to low pressure areas.
Vertical Variation of Pressure
In the lower atmosphere the pressure decreases rapidly with height.
The decrease amounts to about 1 mb for each 10 m increase in elevation. It does not always decrease at the same rate.
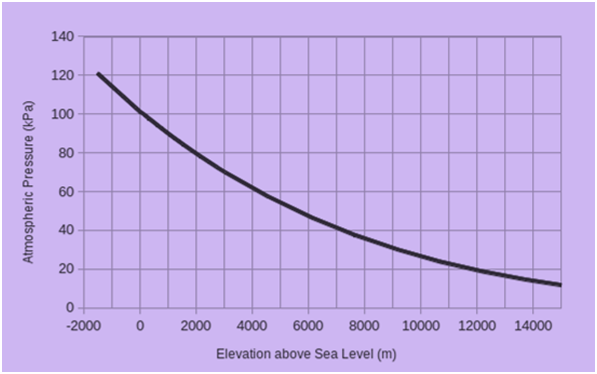
The vertical pressure gradient force is much larger than that of the horizontal pressure gradient. But, it is generally balanced by a nearly equal but opposite gravitational force. Hence, we do not experience strong upward winds.
Horizontal Distribution of Pressure
Small differences in pressure are highly significant in terms of the wind direction and velocity.
Horizontal distribution of pressure is studied by drawing isobars at constant levels.
Isobars are lines connecting places having equal pressure. In order to eliminate the effect of altitude on pressure, it is measured at any station after being reduced to sea level for purposes of comparison.
The sea level pressure distribution is shown by weather maps.
Lowpressure system is enclosed by one or more isobars with the lowest pressure in the centre.
High-pressure system is also enclosed by one or more isobars with the highest pressure in the centre.
World Distribution of Sea Level Pressure
Near the equator the sea level pressure is low and the area is known as equatorial low.
Along 300 N and 300 S are found the high-pressure areas known as the subtropical highs.
Further pole wards along 60o N and 60o S, the low-pressure belts are termed as the sub polar lows.
Near the poles the pressure is high and it is known as the polar high.
These pressure belts are not permanent in nature. They oscillate with the apparent movement of the sun.
In the northern hemisphere in winter they move southwards and in the summer northwards.
