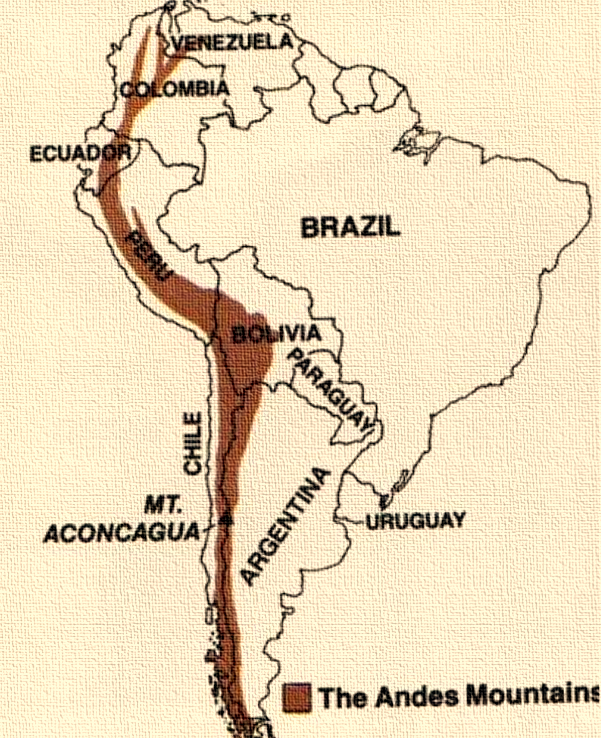
Andes Mountains are the longest continental mountain range in the world.
Andes form a continuous highland along the western edge of South America.
The Andes are the highest mountain range outside of Asia.
The Altiplano Plateau of Andes is the world’s second highest after the Tibetan Plateau.
The range’s highest peak, Argentina’s Aconcagua, rises to an elevation of about 6,961 m above sea level.
The Andes are also part of the American Cordillera, a chain of mountain ranges (cordillera) that consists of an almost continuous sequence of mountain ranges that form the western “backbone” of the Americas and Antarctica.
Extent of Andes Mountains
The Andes range is 8,900 km long and 200 to 700 km wide and has an average height of about 4,000 m.
The Andes extend from south to north through seven South American countries: Argentina, Chile, Bolivia, Peru, Ecuador, Colombia, and Venezuela.
Divisions of Andes
The Andes can be divided into three sections:
The Southern Andes in Argentina and Chile
The Central Andes in Bolivia and Peru
The Northern Andes in Colombia, Ecuador, and Venezuela.
On the basis of climate Andes ranges are grouped into three major divisions : the Tropical Andes, the Dry Andes, and the Wet Andes.
Origin of Andes
The main cause of the rise of the Andes is the contraction of the western rim of the South American Plate due to the subduction of the Nazca Plate and the Antarctic Plate.
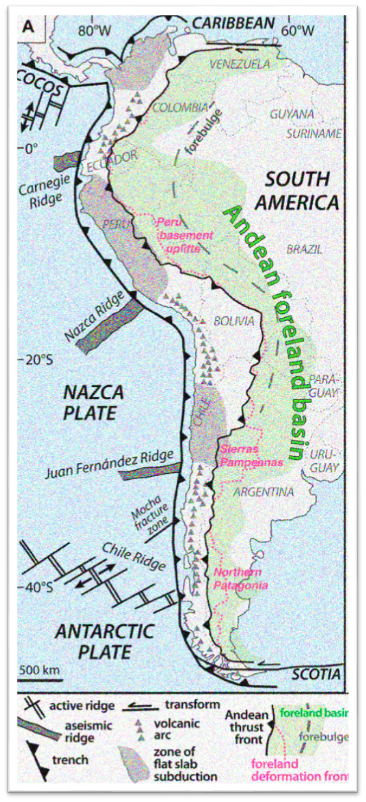
Cause of Seismic activity in Andes
Tectonic forces above the subduction zone along the entire west coast of South America where the Nazca Plate and a part of the Antarctic Plate are sliding beneath the South American Plate, continue to produce an ongoing orogenic event resulting in minor to major earthquakes and volcanic eruptions to this day.
Cause of Volcanism in Andes
The Andes range has many active volcanoes distributed in four volcanic zones separated by areas of inactivity. The Andean volcanism is a result of the subduction of the Nazca Plate and Antarctic Plate underneath the South American Plate.
The world’s highest volcanoes are in the Andes, including Ojos del Salado on the Chile–Argentina border, which rises to 6,893 m.
Ore deposits in Andes
The Andes Mountains host large ore and salt deposits, and some of their eastern fold and thrust belts act as traps for commercially exploitable amounts of hydrocarbons.
In the forelands of the Atacama Desert, some of the largest porphyry copper mineralizations occur, making Chile and Peru the first- and second-largest exporters of copper in the world.
The dry climate in the central western Andes has also led to the creation of extensive saltpeter deposits that were extensively mined until the invention of synthetic nitrates.
Yet another result of the dry climate are the salars of Atacama and Uyuni, the former being the largest source of lithium.
PRACTICE QUESTIONS
QUES . Consider the following countries: UPSC 2025
I. Bolivia
II. Brazil
III. Colombia
IV. Ecuador
V. Paraguay
VI. Venezuela
Andes mountains pass through how many of the above countries?
(a) Only two
(b) Only three
(c) Only four
(d) Only five
Answer (c)
