Aerosols over South Asia
Anthropogenic pollutant particles over South Asia comprise a mixture of light scattering species (including sulfate, nitrate and others) and light absorbing black carbon (or soot), the latter emitted primarily by traditional technologies like burning biomass fuels.
Must read: Unpredictability of the South-West Monsoon system in India
How do aerosols weaken Indian monsoon?
The monsoon is mainly driven by the thermal contrast between Indian subcontinent and the adjoining ocean. As the land warms up, the air above the land surface is heated and rises up and is less dense than cool air over the ocean.
Must read: Monsoon climate : feeding more than 50 percent of the world population
This contrast in temperature and densities causes the cool moisture bearing wind form the western India Ocean to move into the land mass and bring monsoon rain to the subcontinent.
However, the scenario gets changed due to presence of aerosols. Anthropogenic aerosols, including sulphates, nitrates and dust accumulate over the Indo-Gangetic plains.
These aerosols reduce incoming solar radiation over northern India and northern Indian Ocean, and lead to cooling of both land and sea, thus resulting in a lowered thermal contrast. Hence, monsoon winds and circulation are weakened as both land sea are cooled due to aerosol accumulation.
Mechanisms of aerosol induced suppression
Reduced aerosol loading makes the atmosphere unstable causing reduced divergence of moisture and normal convection leading to uplift of moisture and subsequently normal precipitation. While in case of increased aerosol loading the divergence of moisture is enhanced accompanied with stable atmospheric conditions. Conflation of these effects suppresses the precipitation.
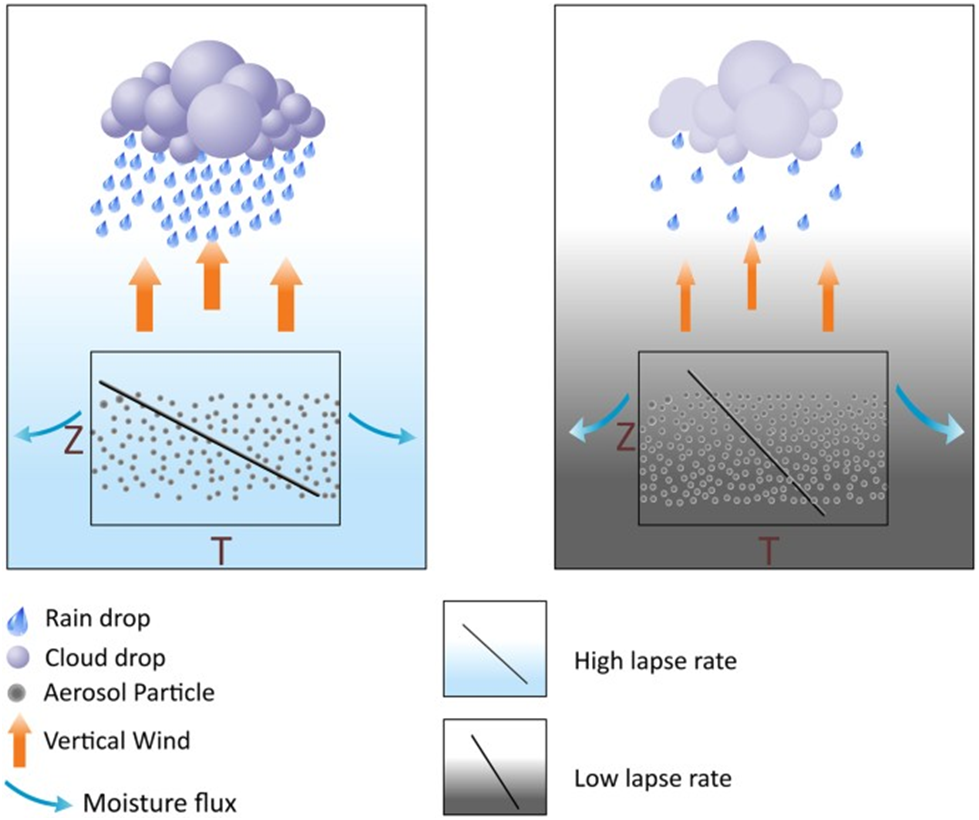
What are the causal influences of aerosols on precipitation suppression?
Short-term rainfall suppression is linked to radiative effects of coincident aerosols, acting through repeated atmospheric stabilization, reduction in convection and increased moisture divergence, leading to aggravation of monsoon break conditions.
Interestingly, in addition to being manifested in deficient monsoon years, causal influences of aerosols on precipitation suppression also occur in a normal monsoon year, indicating the possibility of a widespread occurrence of this phenomenon.
Must read: Why is the South-West Monsoon called Purvaiya (easterly) in Bhojpur Region?
Prolonged breaks in monsoon during latter half of twentieth century
The causal influence of aerosols on precipitation suppression is relevant to the inter-annual variability of monsoon precipitation and the timing of monsoon break spells. Prolonged and intense breaks in the monsoon were associated with rainfall deficits, which have been linked to reduced food grain production during latter half of the twentieth century.
Thus, aerosol-induced precipitation suppression and aggravation of break spells, could influence future rainfall deficits and agricultural vulnerability in India.
External link: https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/india/study-weakening-of-monsoon-linked-to-air-pollution/articleshow/99829080.cms
