QUES . How was the controversial McMahon Line responsible for the Indo-China War of 1962? UPSC IES/ISS EXAM 2014 General Studies. 200 Words. 5 Marks
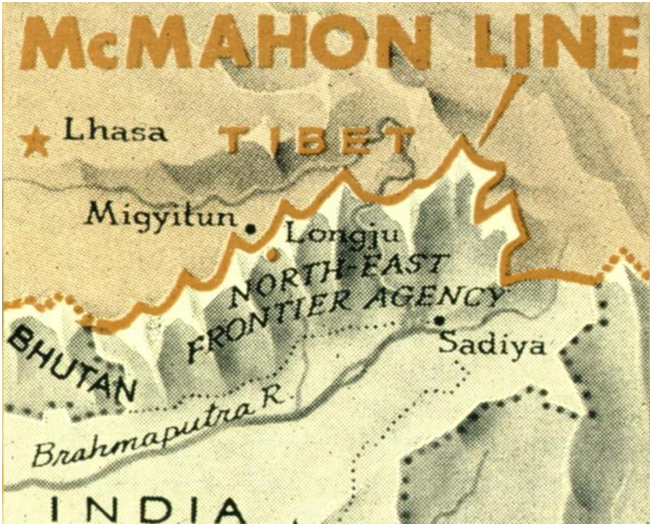
McMahon Line, a frontier between Tibet and Assam in British India, was negotiated between Tibet and Great Britain at the end of the Shimla Conference (October 1913–July 1914). It was named for the chief British negotiator, Sir Henry McMahon.
It runs from the eastern border of Bhutan along the crest of the Himalayas until it reaches the great bend in the Brahmaputra River where that river emerges from its Tibetan course into the Assam Valley.
Delegates of the Chinese republican government also attended the Shimla Conference, but they refused to sign the principal agreement on the status and boundaries of Tibet on the ground that Tibet was not a sovereign state and had not the power to make treaties. The Chinese have maintained this position to the present day and also have claimed that Chinese territory extends southward to the base of the Himalayan foothills.
In response to China’s claim, India argues that China had no claim to the area that is Arunchal Pradesh. It began to raise the claim after it annexed Tibet.
Must read: Peaceful co-existence remains the cornerstone of India’s foreign policy
This frontier controversy with independent India led to the Sino-Indian hostilities of October–November 1962. In that conflict the Chinese forces occupied Indian territory south of the McMahon Line but subsequently withdrew after a cease-fire had been achieved.
China rejects the Simla Convention and the McMahon Line. However China recognizes the line as part of the Line of Actual Control between the two countries, according to a 1959 diplomatic note by Prime Minister Zhou Enlai.
Chinese maps show some 65,000 square kilometer of the territory south of the line as part of the Tibet Autonomous Region, known as South Tibet in China. Chinese forces briefly occupied a part of this area during the Sino-Indian War of 1962 and later withdrew.
Although China has given territorial concessions to countries like Kyrgyzstan and Tajikistan, it is often criticised for claiming territories which were under any form of Chinese domination in the past. It has also renounced any treaty signed by them before the communist revolution (1949).
External link: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/McMahon_Line
