River Gandak
The Gandak River, also known as the Narayani and Gandaki, is one of the major rivers in Nepal and a left-bank tributary of the Ganges in India.
The river is older than the Himalayas. As tectonic activity forces the mountains higher, the river has cut through the uplift. In the Nepal Himalayas, the Gandaki is notable for its deep canyon.
The basin also contains three mountains over 8,000 m, namely Dhaulagiri, Manaslu and Annapurna Massif. Dhaulagiri is the highest point of the Gandaki basin.
Its total catchment area is 46,300 km2, most of it in Nepal.
The Kali Gandaki river source is at the border with Tibet at an elevation of 6,268 metres.
Kali Gandaki is joined by tributaries like Trishuli, East Rapti, etc in Nepal.
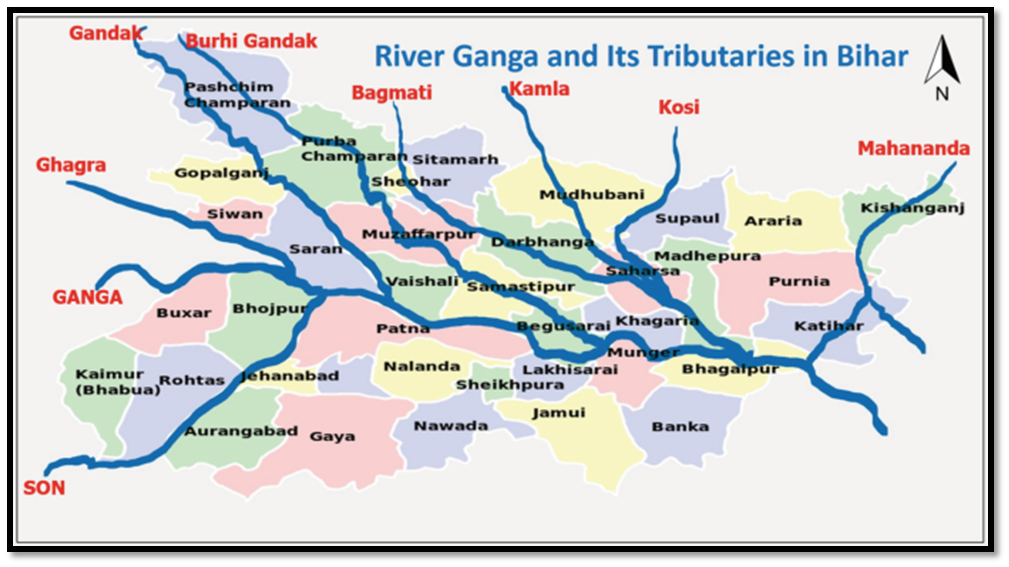
The Gandak enters India at first in Maharajganj District of Uttar Pradesh for around 25 km, it also passes through Kushinagar District before entering Bihar. The Gandak flows southeast 300 km across the Gangetic plain of Bihar state through West Champaran, Gopalganj, Saran , Samastipur and Muzaffarpur districts.
It joins the Ganges near Patna just downstream of Hajipur at Sonpur.
Its drainage area in India is 7,620 km2
River Burhi Gandak
The Burhi Gandak River is a tributary of the Ganges. The Burhi Gandak flows parallel to and east of the Gandak River in an old channel.
The Burhi Gandak originates from Chautarwa Chaur near Bisambharpur in the district of West Champaran in Bihar.
It initially flows through the East Champaran district. After flowing for a distance of about 56 kilometres, the river takes a southerly turn where two rivers – the Dubhara and the Tour – join it. Thereafter, the river flows in a south-easterly direction through the Muzaffarpur district for about 32 kilometres. In this portion, the river spills over its banks and a number of spill channels take off and rejoin it later.
The Burhi Gandak runs a zig-zag course through the districts of Samastipur and Begusarai before covering a short distance in Khagaria district, running by the side of the town of Khagaria, and flows into the Ganges near Gogri and near Bairarpur in Munger . It forms the western boundary of the Khagaria town and a protection embankment built along the eastern side of this river, protects Khagaria town from the floods of Burhi Gandak.
A residual oxbow lake known as Kanwar Lake or Kabar Taal has been formed due to meandering of Burhi Gandak river in Begusarai district of Bihar. It is Asia’s largest freshwater oxbow lake. It is the first Ramsar site in Bihar.
The total length of the river is 320 kilometres.
The drainage area of the river is 10,150 square kilometres.
PRACTICE QUESTIONS
QUES . Consider the following statements: UPSC 2023
1 . Jhelum River passes through Wular Lake.
2 . Krishna River directly feeds Kolleru Lake
3 . Meandering of Gandak River formed Kanwar Lake.
How many of the statements given above are correct?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) All three
(d) None
Ans (a) EXPLANATION: ● Wular Lake is the largest freshwater lake in India and is located in Jammu and Kashmir. It lies at the north end of the Vale of Kashmir, 32 km north-northwest of Srinagar. This lake also has a small island in its center called the ‘Zaina Lank’. This island was constructed by King Zainul-Abi-Din. The lake controls the flow of the Jhelum River, which traverses it. So, statement 1 is correct. ● Kolleru Lake is fed directly by water from the seasonal Budameru and Tammileru streams and is connected to the Krishna and Godavari systems by over 68 inflowing drains and channels. Kolleru Lake is situated between the two major river basins of the Godavari and the Krishna. It functions as a natural flood balancing reservoir between the deltas of the two rivers. It serves as a habitat for migratory birds. Thus, the Krishna River does not directly feed Kolleru Lake. So, statement 2 is not correct. ● Kanwar Lake, also known as Kabar Taal, is the largest freshwater lake in Bihar. Kanwar jheel, as it is locally called, is located 22 km north-west of Begusarai town. It is Asia’s largest freshwater oxbow lake. It is a residual oxbow lake, formed due to meandering of Burhi Gandak river, a tributary of Ganga, in the geological past. It is the first Ramsar site in Bihar. So, statement 3 is not correct.. Therefore, option (a) is the correct answer.
